Podcast
Questions and Answers
What defines the relationships of authority within an organization?
What defines the relationships of authority within an organization?
- Employee skill sets
- Organizational chart (correct)
- Organizational goals
- Task assignments
Which of the following is NOT a type of organizational structure mentioned?
Which of the following is NOT a type of organizational structure mentioned?
- Team-based
- Matrix
- Circular (correct)
- Divisional
What is a primary disadvantage of a hierarchical organizational structure?
What is a primary disadvantage of a hierarchical organizational structure?
- Slows down innovation due to bureaucracy (correct)
- Promotes teamwork between departments
- Defines levels of authority clearly
- Motivates employees through clear career paths
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the nature of an organization?
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the nature of an organization?
In a functional organizational structure, employees are grouped based on what criteria?
In a functional organizational structure, employees are grouped based on what criteria?
What is one advantage of a hierarchical organizational structure?
What is one advantage of a hierarchical organizational structure?
How does an organizational chart benefit employees?
How does an organizational chart benefit employees?
What can be a consequence of employees acting in the interest of their department in a hierarchical structure?
What can be a consequence of employees acting in the interest of their department in a hierarchical structure?
What is a major disadvantage of a functional organizational structure?
What is a major disadvantage of a functional organizational structure?
Which factor typically defines a divisional organizational structure?
Which factor typically defines a divisional organizational structure?
What is a significant advantage of a horizontal or flat organizational structure?
What is a significant advantage of a horizontal or flat organizational structure?
What can be a drawback of maintaining a horizontal organizational structure as a company grows?
What can be a drawback of maintaining a horizontal organizational structure as a company grows?
In a functional organizational structure, which of the following is an advantage?
In a functional organizational structure, which of the following is an advantage?
What is a common feature of divisional organizational structures?
What is a common feature of divisional organizational structures?
What is a potential disadvantage of specialization in functional organizational structures?
What is a potential disadvantage of specialization in functional organizational structures?
What is a primary outcome of having few managers in a horizontal organizational structure?
What is a primary outcome of having few managers in a horizontal organizational structure?
What is one advantage of a divisional organizational structure?
What is one advantage of a divisional organizational structure?
What is a potential disadvantage of a divisional organizational structure?
What is a potential disadvantage of a divisional organizational structure?
Which divisional structure is best suited for a supermarket chain?
Which divisional structure is best suited for a supermarket chain?
What is a key characteristic of a matrix organizational structure?
What is a key characteristic of a matrix organizational structure?
What challenge is commonly associated with matrix organizational structures?
What challenge is commonly associated with matrix organizational structures?
What is a primary feature of team-based organizational structures?
What is a primary feature of team-based organizational structures?
How do team-based organizational structures reinforce problem-solving?
How do team-based organizational structures reinforce problem-solving?
What can frequently change in a matrix organization?
What can frequently change in a matrix organization?
What is one advantage of a team-based organizational structure?
What is one advantage of a team-based organizational structure?
What is a key disadvantage of a network organizational structure?
What is a key disadvantage of a network organizational structure?
Which element of organizational structure involves separating work into different jobs?
Which element of organizational structure involves separating work into different jobs?
How does a team-based organizational structure typically change traditional career models?
How does a team-based organizational structure typically change traditional career models?
What is one disadvantage of the division of labor?
What is one disadvantage of the division of labor?
What advantage does a network organizational structure provide regarding employee collaboration?
What advantage does a network organizational structure provide regarding employee collaboration?
What disadvantage do employees face in a team-based organizational structure?
What disadvantage do employees face in a team-based organizational structure?
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of division of labor?
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of division of labor?
What is the primary focus of process departmentalization?
What is the primary focus of process departmentalization?
Which of the following best describes customer departmentalization?
Which of the following best describes customer departmentalization?
What is one potential drawback of product or service departmentalization?
What is one potential drawback of product or service departmentalization?
What does span of control refer to in an organizational structure?
What does span of control refer to in an organizational structure?
Which of the following is NOT a common grouping in departmentalization?
Which of the following is NOT a common grouping in departmentalization?
What is the fundamental purpose of integration within organizational structures?
What is the fundamental purpose of integration within organizational structures?
Which aspect does NOT characterize business function departmentalization?
Which aspect does NOT characterize business function departmentalization?
In what way does span of control influence an organization?
In what way does span of control influence an organization?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Organization
- A goal-directed entity with deliberate processes and systems.
- A collection of people working together to accomplish something better than working separately.
- Social actors (influences or are influenced by the environment).
Organization Structure
- The system of task, reporting, and authority relationships within which the work of the organization is done.
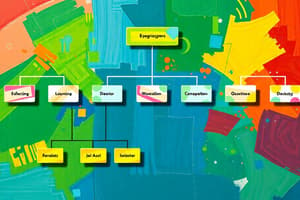
- Defines how the parts of an organization fit together, as seen in the organizational chart.
Organizational Chart
- Shows internal structure of an organization.
- Helps employees identify their function.
- Helps employees understand the organization's goals and aims.
- Outlines how activities, supervision, and coordination work towards achieving organizational goals.
Types of Organizational Structures
- Hierarchical.
- Functional.
- Horizontal.
- Divisional (market-based, product-based, geographical).
- Matrix.
- Team-based.
- Network.
Hierarchical Organizational Structure
- Typical for larger businesses and organizations.
- Different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels.
- Decision-making is formal and flows from top to down.
Advantages
- Defines authority and responsibility.
- Shows reporting lines.
- Motivates employees with career paths and promotional opportunities.
- Creates employee specializations.
- Builds camaraderie within departments.
Disadvantages
- Slows down innovation or changes due to bureaucracy.
- Can cause employees to act in the department's interest rather than the company's interest.
- Low-level employees might feel less ownership and unable to express ideas.
Functional Organizational Structure
- Groups employees into departments based on expertise.
- Common in large companies with specialized functions.
Advantages
- Employee focus on their role.
- Encourages specialization.
- Creates self-determined teams and departments.
- Easily scalable for any company size.
Disadvantages
- Creates silos within the organization.
- Hampers interdepartmental communication.
- Obscures processes and strategies for different markets or products.
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structure
- Few managers with many employees.
- Allows employees to make decisions without manager approval.
- Common in start-ups before they grow large enough to divide departments.
Advantages
- Gives employees more responsibility.
- Fosters open communication.
- Improves coordination and speed of new idea implementation.
Disadvantages
- Confusion about employee reporting lines.
- Can create employees with generalized skills and knowledge.
- Difficult to maintain as a company grows beyond start-up status.
Divisional Organizational Structure
- Segmentation by products, markets, or geographical variations.
- Suitable for larger companies dealing with multiple products and markets.
- Independent divisions operate autonomously under head office supervision.
Advantages
- Helps large companies remain flexible.
- Allows for quicker response to industry changes or customer needs.
- Promotes independence, autonomy, and a customized approach.
Disadvantages
- Can lead to duplicate resources.
- Can mean unclear or insufficient communication between headquarters and divisions.
- Can result in a company competing with itself.
Types of Divisional Structures
- Market-based: Divisions separated by market, industry, or customer type (e.g., supermarket).
- Product-based: Divisions separated by product line (e.g., tech company with separate cloud offerings and software divisions).
- Geographical: Divisions separated by region, territories, or districts for effective localization and logistics (e.g., companies with satellite offices worldwide).
Matrix Organizational Structure
- Combination of two or more organizational structures.
- Sets up reporting relationships as a grid or matrix.
Advantages
- Supervisors can easily select individuals based on project needs.
- Provides a dynamic view of the organization.
- Encourages employees to utilize skills in various capacities outside their original roles.
Disadvantages
- Conflict between department managers and project managers.
- More frequent changes than other organizational chart types.
Team-based Organizational Structure
- Teams working towards a common goal while completing individual tasks.
- Less hierarchical with flexible structures that reinforce problem-solving, decision-making, and teamwork.
Advantages
- Increases productivity, performance, and transparency by breaking down silo mentality.
- Promotes a growth mindset.
- Changes traditional career paths through lateral movement.
- Values experience over seniority.
- Requires minimal management.
- Fits well with agile companies using Scrum or Tiger Teams.
Disadvantages
- Goes against many companies' inclination towards purely hierarchical structures.
- May make promotional paths less clear for employees.
Network Organizational Structure
- Groups specific types of employees based on specialization.
- These specialists form partnerships with others across the organization for projects and common goals.
Advantages
- Visualizes complex relationships between onsite and offsite employees and stakeholders.
- Allows companies to be more flexible and agile.
- Empowers employees to collaborate, take initiative, and make decisions.
- Helps employees and stakeholders understand workflows and processes.
Disadvantages
- Can become overly complex with lots of offsite processes.
- Can make it difficult for employees to determine decision authority.
Elements of Organizational Structure
- Division of labor: Separating organization's work into different jobs for individuals.
- Coordinating Divided Tasks: Integrating various tasks and roles to achieve goals.
- Departmentalization: Combining and allocating divided tasks to work groups.
- Span of Control: Number of people reporting to a manager, defining the size of a work group.
- Administrative hierarchy: Different levels of authority and reporting relationships within an organization.
Division of Labor
- Also known as specialization.
- The extent to which the organization's work is separated into different jobs.
Advantages
- Efficient use of labor.
- Reduced training costs.
- Increased standardization and uniformity of output.
- Increased expertise through task repetition.
Disadvantages
- Routine and repetitive jobs.
- Reduced job satisfaction.
- Decreased worker involvement and commitment.
- Increased worker alienation.
- Possible incompatibility with computerized manufacturing technologies.
Coordinating Divided Tasks
- Integration: The process of coordinating tasks and roles to achieve goal accomplishment.
Departmentalization
- The manner in which divided tasks are combined and allocated to work groups.
- Five common groupings:
- Business function (internal operations).
- Process (internal).
- Product or service (external).
- Customer (external).
- Geography (external).
Business Function Departmentalization
- Based on traditional business functions (e.g., marketing, manufacturing, human resource administration).
- Employees learn from each other.
- Lacks autocratic mechanisms for coordinating workflow.
Process Departmentalization
- Similar to functional structure, but focuses on specific jobs grouped according to activity.
- Encourages specialization and expertise among employees.
- Develops an internal career path.
Product or Service Departmentalization
- Employees working on a particular product or service are in the same department, regardless of function or process.
- Enhances interaction and communication among employees producing the same product or service.
- May reduce coordination problems.
- Employees might become too focused on their product or service and miss technological improvements or innovations.
Customer Departmentalization
- Also called departmentalization by market.
- Less process specialization.
- Offers best coordination of workflow tailored to customer needs.
- Isolates employees based on their expertise.
Span of Control
- Also called span of management.
- The number of people reporting to a manager.
- Determines the size of a work group.
- Small span of control = close supervision.
Mintzberg's five conditions in determining span of control:
- Complexity of work: More complex work requires a smaller span of control.
- Similarity of tasks: Similar tasks permit a larger span of control.
- Proximity of subordinates: Close proximity allows for a larger span of control.
- Frequency of problems: Frequent problems require a smaller span of control.
- managerial experience: More experienced managers can handle a larger span of control.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.