Podcast
Questions and Answers
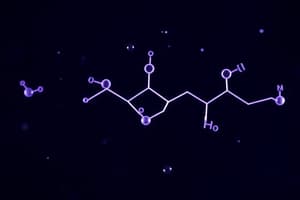
What is the correct formula of the molecule represented in the provided diagram containing OH and NH2 groups?
What is the correct formula of the molecule represented in the provided diagram containing OH and NH2 groups?
- C16H23BrClNO
- C15H25BrClNO2 (correct)
- C15H23BrClNO2
- C16H23ClBrNO2
What is the double bond equivalent (DBE) of the molecule that contains Cl and NH2?
What is the double bond equivalent (DBE) of the molecule that contains Cl and NH2?
- 8
- 5
- 6
- 7 (correct)
Which of the following molecules is NOT aromatic?
Which of the following molecules is NOT aromatic?
- A molecule with a complete octet on all atoms
- A molecule with sp3 hybridized carbons (correct)
- A cyclic molecule with alternating double bonds
- A molecule containing multiple resonance structures
Which statement about chemical analysis techniques is true?
Which statement about chemical analysis techniques is true?
In NMR spectroscopy, what aspect primarily affects the chemical shift of protons?
In NMR spectroscopy, what aspect primarily affects the chemical shift of protons?
Which statement accurately describes the application of high-resolution mass spectrometry?
Which statement accurately describes the application of high-resolution mass spectrometry?
What characteristic of carbon NMR spectroscopy is NOT true?
What characteristic of carbon NMR spectroscopy is NOT true?
What is the key reason that lighter atoms exhibit higher vibrational frequencies in IR spectroscopy?
What is the key reason that lighter atoms exhibit higher vibrational frequencies in IR spectroscopy?
Which molecular orbital of the aldehyde is filled by the electron pair from the alcohol during the formation of a hemiacetal?
Which molecular orbital of the aldehyde is filled by the electron pair from the alcohol during the formation of a hemiacetal?
In the context of decreasing pKaH, which is the correct ranking of I-IV?
In the context of decreasing pKaH, which is the correct ranking of I-IV?
How do structures I and II relate to each other?
How do structures I and II relate to each other?
Which compound is likely to have the lowest activation energy in its cyclization rate-determining step?
Which compound is likely to have the lowest activation energy in its cyclization rate-determining step?
Among the π molecular orbitals of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene, which orbital has the highest energy?
Among the π molecular orbitals of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene, which orbital has the highest energy?
What is the nature of the bond formed between the aldehyde and alcohol during hemiacetal formation?
What is the nature of the bond formed between the aldehyde and alcohol during hemiacetal formation?
Which species acts as a nucleophile in the formation of a hemiacetal from an aldehyde?
Which species acts as a nucleophile in the formation of a hemiacetal from an aldehyde?
What characteristic do the compounds in question 8 share that affects their rate of cyclization?
What characteristic do the compounds in question 8 share that affects their rate of cyclization?
Which orbital has the second lowest energy?
Which orbital has the second lowest energy?
How many nodes does the 'h' orbital have?
How many nodes does the 'h' orbital have?
Which orbital is typically referred to as the LUMO?
Which orbital is typically referred to as the LUMO?
In terms of acidity, which of the following compounds has the lowest pKa?
In terms of acidity, which of the following compounds has the lowest pKa?
Which compound is more acidic between OH and NH2?
Which compound is more acidic between OH and NH2?
In a 13C NMR spectrum, what would indicate a unique signal?
In a 13C NMR spectrum, what would indicate a unique signal?
Which reaction mechanism would produce an aromatic compound?
Which reaction mechanism would produce an aromatic compound?
What is the major product when hydroxyl (-OH) reacts with PCC?
What is the major product when hydroxyl (-OH) reacts with PCC?
What is the pKa range for a typical alkane?
What is the pKa range for a typical alkane?
How does resonance affect the pKa of compounds like acetone and acetylacetone?
How does resonance affect the pKa of compounds like acetone and acetylacetone?
Which compound has the lowest pKa value among those listed?
Which compound has the lowest pKa value among those listed?
Why does fluorene have a significantly lower pKa than 9,10-dihydroanthracene?
Why does fluorene have a significantly lower pKa than 9,10-dihydroanthracene?
What does the degree of unsaturation (DBE) indicate in the molecular formula C10H10O2?
What does the degree of unsaturation (DBE) indicate in the molecular formula C10H10O2?
Which structure corresponds to o-dichlorobenzene?
Which structure corresponds to o-dichlorobenzene?
Which structure is representative of p-dichlorobenzene?
Which structure is representative of p-dichlorobenzene?
What is the significance of formal charge in molecular structures?
What is the significance of formal charge in molecular structures?
Which structure has the correct formal charge for the nitrogen atom?
Which structure has the correct formal charge for the nitrogen atom?
Which 13C NMR spectrum corresponds to acetylsalicylic acid?
Which 13C NMR spectrum corresponds to acetylsalicylic acid?
What is an incorrect interpretation of the 13C NMR spectrum for acetylsalicylic acid?
What is an incorrect interpretation of the 13C NMR spectrum for acetylsalicylic acid?
In NMR spectroscopy, what does a higher ppm value typically indicate?
In NMR spectroscopy, what does a higher ppm value typically indicate?
Which of the following statements about acetylsalicylic acid is true?
Which of the following statements about acetylsalicylic acid is true?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Exam Information
- Exam I for Organic Chemistry 315 will be held on October 7, 2024.
- Students must fill out all required information on the exam sheet neatly and legibly.
- Students must print their first and last name on every page.
- Students must read and sign the pledge prior to submitting the exam.
Multiple Choice Questions
- Question 1: The correct formula for the given molecule is C16H23BrClNO2.
- Question 2: The double bond equivalent (DBE) of the molecule is 7.
- Question 3: The molecule in option E is not aromatic.
- Question 4: The true statement is "Mass-spectrometry is a technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of either positive ions or negative ions."
- Question 5: The structure in option B has the correct formal charge assigned.
- Question 6: The correct 13C NMR spectrum of acetylsalicylic acid is A.
- Question 7: The order of decreasing pKa values of the compounds is pKaH I > II > IV > III.
- Question 8: When an aldehyde reacts with an alcohol to form a hemiacetal, the electron pair from the alcohol fills the π molecular orbital* of the aldehyde.
- Question 9: Structures I and II are resonance structures with different electron cloud distribution.
- Question 10: The compound in option A has the lowest activation energy for cyclization.
Open Ended Questions
- Question 11:
- Orbital g has the highest energy.
- Orbital a has the second lowest energy.
- Orbital h has 3 nodes.
- Orbital g is the LUMO.
- Question 12:
- 1) CH3CH2OH
- 2) NH3
- 3) CH3COOH
- 4) CH3CH2Cl
- 5) CH3CH2OH
- 6) CF3CH2OH
- 7) N(CH3)3
- 8) H2O
- Question 13:
- The resonance structure of molecule (a) shows the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom moving to form a double bond with the adjacent carbon atom, while the double bond between carbon and oxygen becomes a single bond with the negative charge being placed on the oxygen atom.
- The resonance structure of molecule (b) shows the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom moving to form a double bond with the adjacent carbon atom, while the double bond between carbon and oxygen becomes a single bond with the negative charge being placed on the oxygen atom.
- Question 14:
- a) The product is phenol.
- b) The product is benzoic acid.
- c) The product is benzaldehyde.
- Question 15:
- The number of signals in the 13C NMR spectrum of the first molecule is 4.
- The number of signals in the 13C NMR spectrum of the second molecule is 6.
- The number of signals in the 13C NMR spectrum of the third molecule is 5.
- Question 16:
- The mechanism of the transformation involves protonation of the carbonyl oxygen of the ketone, followed by nucleophilic attack of the hydroxyl group on the carbonyl carbon, leading to the formation of a hemiacetal.
- Question 17:
- The lower pKa values of the compounds are due to the stabilization of their conjugate bases by resonance.
- The conjugate base of 9,10-dihydroanthracene is stabilized by resonance delocalization of the negative charge into the aromatic ring.
- The conjugate base of fluorene is stabilized by resonance delocalization of the negative charge into the two aromatic rings.
- The conjugate base of acetone is stabilized by resonance delocalization of the negative charge into the carbonyl group.
- The conjugate base of acetylacetone is stabilized by resonance delocalization of the negative charge into the two carbonyl groups.
- Fluorene has a significantly lower pKa than 9,10-dihydroanthracene because the negative charge in the conjugate base of fluorene can be delocalized into two aromatic rings, while the negative charge in the conjugate base of 9,10-dihydroanthracene can only be delocalized into one aromatic ring, resulting in greater stabilization.
- The lower pKa values of the compounds are due to the stabilization of their conjugate bases by resonance.
- Question 18:
- The molecular structure based on the information provided is 1,2-Dimethoxybenzene.
- The structure is shown in the provided rectangular box.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.