Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a systemic factor that can predispose an individual to oral candidiasis?
Which of the following is NOT a systemic factor that can predispose an individual to oral candidiasis?
- Malignancy
- Dental caries (correct)
- AIDS
- Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Which type of oral candidiasis is characterized by creamy white plaques that can be wiped off, leaving a red, raw, and painful mucosal surface?
Which type of oral candidiasis is characterized by creamy white plaques that can be wiped off, leaving a red, raw, and painful mucosal surface?
- Pseudomembranous Candidiasis (Thrush) (correct)
- Angular Cheilitis
- Erythematous (atrophic) candidiasis
- Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis (Candidal leukoplakia)
Which of the following is a local factor that can increase the risk of oral candidiasis?
Which of the following is a local factor that can increase the risk of oral candidiasis?
- Poor oral hygiene (correct)
- Genetic predisposition
- High intake of sugary foods
- Use of corticosteroids
What is the clinical presentation of Erythematous (atrophic) candidiasis?
What is the clinical presentation of Erythematous (atrophic) candidiasis?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of oral candidiasis?
Which of the following is NOT a common symptom of oral candidiasis?
What is the primary diagnostic tool used for oral candidiasis?
What is the primary diagnostic tool used for oral candidiasis?
What characterizes median rhomboid glossitis?
What characterizes median rhomboid glossitis?
Which of the following is a common clinical presentation associated with denture use?
Which of the following is a common clinical presentation associated with denture use?
How are antifungal drugs classified based on their spectrum of activity?
How are antifungal drugs classified based on their spectrum of activity?
Which drug is classified as a polyene antifungal agent?
Which drug is classified as a polyene antifungal agent?
Which antifungal activity type refers to agents that inhibit the growth of fungi without killing them?
Which antifungal activity type refers to agents that inhibit the growth of fungi without killing them?
Which form of candidiasis is the least commonly observed?
Which form of candidiasis is the least commonly observed?
What is unique about the cell membrane of fungal cells compared to human cells?
What is unique about the cell membrane of fungal cells compared to human cells?
What is the normal state of Candida albicans in humans?
What is the normal state of Candida albicans in humans?
Which antifungal drug is used topically?
Which antifungal drug is used topically?
What is the term for the study of the movement of drugs in the body?
What is the term for the study of the movement of drugs in the body?
What is the name of the fungal infection caused by Candida albicans?
What is the name of the fungal infection caused by Candida albicans?
What is the primary site of action of Amphotericin-B?
What is the primary site of action of Amphotericin-B?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Pathogenesis of Oral Candidiasis
- Transition from commensalism to pathogenicity often triggered by predisposing factors.
- Systemic Factors include:
- AIDS
- Malignancies
- Diabetes mellitus (DM)
- Immunosuppressive medications (e.g., broad-spectrum antibiotics)
- Local Factors include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Use of acrylic dentures
- Decreased salivary flow (xerostomia)
Classification of Oral Candidiasis
-
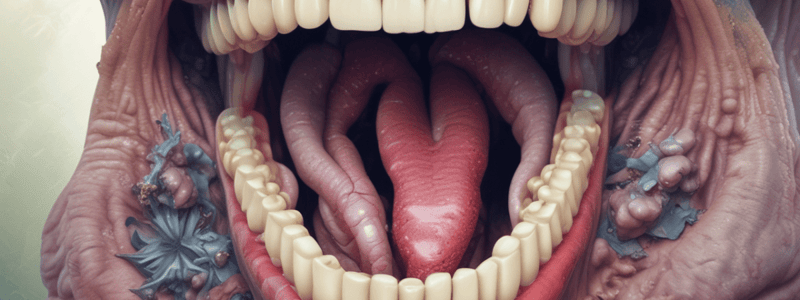
Pseudomembranous Candidiasis (Thrush)
- Most common form
- Characterized by soft, friable, creamy white plaques on mucosa
- Plaques can be wiped off, revealing a red, painful surface
- Symptoms may include burning sensation and dysgeusia
- Affects buccal mucosa, palate, tongue, oropharynx
-
Erythematous (Atrophic) Candidiasis
- Appears as flat, painful, red patches lacking a pseudomembranous coating
- Commonly associated with burning sensation
- Key clinical presentations include:
- Median rhomboid glossitis (depapillation of the tongue)
- Kissing lesions in palates
- Angular cheilitis
- Denture stomatitis (erythema on denture-bearing surface)
-
Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis (Candidal Leukoplakia)
- Presents with white papules or plaques that cannot be scraped off
- Least common form
- Affects corners of the mouth and dorsal surface of the tongue
Diagnosis of Oral Candidiasis
- Based on clinical signs and symptoms (burning sensation, dysgeusia, dysphagia)
- Culture or biopsy may be necessary in some cases
Antifungal Drugs
- Classified based on spectrum and activity:
- Broad-Spectrum: inhibits a variety of fungi, including yeasts and molds
- Narrow-Spectrum: inhibits a limited range of fungi
- Mechanisms of action:
- Fungistatic: inhibits growth of fungi
- Fungicidal: kills fungi
Types of Antifungal Drugs
- Membrane Disruptors:
- Polyenes: Amphotericin B (AMB), Nystatin
- Azoles:
- Topical: Clotrimazole, Miconazole
- Systemic: Ketoconazole, Fluconazole
- Other antifungals include Griseofulvin and Flucytosine
Introduction to Fungi
- Fungi comprise yeasts, molds, and mushrooms, possessing a membrane-bound nucleus.
- Fungal cell structures are similar to human cells but contain ergosterol instead of cholesterol.
Oral Candidiasis Overview
- Caused by Candida albicans, the most common opportunistic fungal infection in humans.
- Normally exists as a non-pathogenic member of human flora in the skin, oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and vagina.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.