Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which retinal condition is NOT typically identified using Macular OCT?
Which retinal condition is NOT typically identified using Macular OCT?
- Macular hole
- Corneal edema (correct)
- Retinal detachment
- Macular pucker
What can cause an erroneous RNFL thickness measurement?
What can cause an erroneous RNFL thickness measurement?
- Vitreous heme
- Optic nerve edema
- Glaucoma
- Tilted discs (correct)
What is the main role of the External Limiting Membrane (ELM) in OCT?
What is the main role of the External Limiting Membrane (ELM) in OCT?
- Facilitates vitreous gel maintenance
- Ensures photoreceptor integrity (correct)
- Separates inner and outer retinal layers
- Regulates blood flow
Which condition is associated with falsely high RNFL thickness leading to inaccurate glaucoma evaluations?
Which condition is associated with falsely high RNFL thickness leading to inaccurate glaucoma evaluations?
Which hyperreflective structure is NOT considered essential for maintaining good visual acuity?
Which hyperreflective structure is NOT considered essential for maintaining good visual acuity?
In which scenario is B-scan ultrasonography particularly useful?
In which scenario is B-scan ultrasonography particularly useful?
What does a decenter scan in OCT lead to?
What does a decenter scan in OCT lead to?
What does a positive Jones II test indicate?
What does a positive Jones II test indicate?
What does the Schirmer I test primarily measure?
What does the Schirmer I test primarily measure?
What is indicated by a negative Jones II test?
What is indicated by a negative Jones II test?
Which statement about Schirmer II test is accurate?
Which statement about Schirmer II test is accurate?
When performing the Schirmer I test, what is crucial to ensure?
When performing the Schirmer I test, what is crucial to ensure?
What phase occurs immediately after the pre-arterial phase in fluorescein angiography?
What phase occurs immediately after the pre-arterial phase in fluorescein angiography?
What clinical feature is indicative of a hypo-fluorescent signal during Autofluorescence Analysis (AFA)?
What clinical feature is indicative of a hypo-fluorescent signal during Autofluorescence Analysis (AFA)?
What condition is indicated by a late phase with areas of hyperfluorescence in fluorescein angiography?
What condition is indicated by a late phase with areas of hyperfluorescence in fluorescein angiography?
Which structure can be affected by differentiating between optic disc edema and optic disc drusens?
Which structure can be affected by differentiating between optic disc edema and optic disc drusens?
What technique is used to assess the depth of a foreign body in the cornea?
What technique is used to assess the depth of a foreign body in the cornea?
In the conical beam examination, what do floating WBCs in the anterior chamber indicate?
In the conical beam examination, what do floating WBCs in the anterior chamber indicate?
What duration after fluorescein injection does the venous mid-stage typically occur?
What duration after fluorescein injection does the venous mid-stage typically occur?
What illumination technique is used to evaluate the vitreous with a slit lamp?
What illumination technique is used to evaluate the vitreous with a slit lamp?
What is the primary purpose of the Venous Early Stage in fluorescein angiography?
What is the primary purpose of the Venous Early Stage in fluorescein angiography?
What type of treatment is recommended after corneal foreign body removal?
What type of treatment is recommended after corneal foreign body removal?
Which of the following treatments is contraindicated until re-epithelization occurs?
Which of the following treatments is contraindicated until re-epithelization occurs?
What is a potential risk of using broad-spectrum contact lenses after foreign body removal?
What is a potential risk of using broad-spectrum contact lenses after foreign body removal?
What is the main purpose of using Homatropine after excessive inflammation due to a foreign body?
What is the main purpose of using Homatropine after excessive inflammation due to a foreign body?
In which situation could subconjunctival hemorrhages occur?
In which situation could subconjunctival hemorrhages occur?
When monitoring a patient after foreign body removal, when should contact lenses be evaluated for edema and striae?
When monitoring a patient after foreign body removal, when should contact lenses be evaluated for edema and striae?
What type of injury may be caused by a high-speed projectile in the bulbar conjunctiva?
What type of injury may be caused by a high-speed projectile in the bulbar conjunctiva?
According to the Imbert-Fick law, what does the pressure inside an ideal sphere depend on?
According to the Imbert-Fick law, what does the pressure inside an ideal sphere depend on?
What condition is most likely to require the use of an amniotic membrane?
What condition is most likely to require the use of an amniotic membrane?
Which recommendation is appropriate for superficial punctate keratitis occurring after irrigation?
Which recommendation is appropriate for superficial punctate keratitis occurring after irrigation?
What is the primary purpose of using specular reflection in corneal evaluation?
What is the primary purpose of using specular reflection in corneal evaluation?
What is the recommended illumination level when conducting a biomicroscope examination?
What is the recommended illumination level when conducting a biomicroscope examination?
At what angle should the microscope be positioned to obtain a sharply focused parallelepiped of the cornea?
At what angle should the microscope be positioned to obtain a sharply focused parallelepiped of the cornea?
What visual effect indicates that the examining practitioner is looking at the ghostlike image of the filament?
What visual effect indicates that the examining practitioner is looking at the ghostlike image of the filament?
Which type of reflection allows the evaluation of corneal layers using a high-contrast approach?
Which type of reflection allows the evaluation of corneal layers using a high-contrast approach?
What should a practitioner observe for when advancing the parallelepiped across the cornea?
What should a practitioner observe for when advancing the parallelepiped across the cornea?
What is the purpose of sclerotic scatter in corneal examinations?
What is the purpose of sclerotic scatter in corneal examinations?
Which imaging technique is optimal for pre- and post-operative corneal assessments?
Which imaging technique is optimal for pre- and post-operative corneal assessments?
What is the appearance noted when the correct focus is achieved on the ghostlike image during examination?
What is the appearance noted when the correct focus is achieved on the ghostlike image during examination?
In the case of Central Corneal Clouding (CCC), how is it typically observed?
In the case of Central Corneal Clouding (CCC), how is it typically observed?
Flashcards
Macular OCT
Macular OCT
A type of optical coherence tomography (OCT) that provides detailed imaging of the macula – the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. It allows clinicians to visualize the retinal layers and identify various macular conditions.
RNFL Thinning
RNFL Thinning
A reduction in the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL), which is a layer of nerve fibers that carry information from the retina to the brain. It can be a sign of glaucoma or other eye conditions.
What are hyperreflective bands?
What are hyperreflective bands?
Four key structures within the retina that reflect light strongly and are essential for good visual acuity. These include the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), interdigitation zone (IZ), ellipsoid zone (EZ), and external limiting membrane (ELM).
ONH OCT
ONH OCT
Signup and view all the flashcards
A-Scan Ultrasound
A-Scan Ultrasound
Signup and view all the flashcards
B-Scan Ultrasound
B-Scan Ultrasound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluorescein Angiography (FA) Stages
Fluorescein Angiography (FA) Stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
FA Pre-arterial Phase
FA Pre-arterial Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
FA Arterial Phase
FA Arterial Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
FA Capillary Phase
FA Capillary Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
FA Venous Phase
FA Venous Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
FA Late Phase
FA Late Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autofluorescence (AF) and its Interpretation
Autofluorescence (AF) and its Interpretation
Signup and view all the flashcards
AF Hypofluorescent Signal
AF Hypofluorescent Signal
Signup and view all the flashcards
AF Hyperfluorescent Signal
AF Hyperfluorescent Signal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jones II Test
Jones II Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Jones II
Positive Jones II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Jones II
Negative Jones II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Schirmer I Test
Schirmer I Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does Schirmer I test for?
What does Schirmer I test for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foreign Body Removal
Foreign Body Removal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cycloplegia
Cycloplegia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Infections
Secondary Infections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial Punctate Keratitis
Superficial Punctate Keratitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subconjunctival Hemes
Subconjunctival Hemes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perforating Injury
Perforating Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Broad-spectrum Antibiotics
Broad-spectrum Antibiotics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pressure Patch
Pressure Patch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homatropine
Homatropine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic Membrane
Amniotic Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retro-illumination
Retro-illumination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parallelepiped
Parallelepiped
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specular Reflection
Specular Reflection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endothelial Cells
Endothelial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Cells
Epithelial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sclerotic Scatter
Sclerotic Scatter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Corneal Clouding (CCC)
Central Corneal Clouding (CCC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
How to evaluate endothelial cells?
How to evaluate endothelial cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How to find ghostlike image?
How to find ghostlike image?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Observation angle for CCC?
Observation angle for CCC?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Macular OCT
- Retinal layers are identified by OCT, including the posterior hyaloid membrane, outer nuclear layer (ONL), outer plexiform layer (OPL), etc
- Common conditions detected with OCT include narrow angles, retinal disease, and corneal pathologies
Tested Eye Identification
- OCT images show different layers of the eye allowing identification and diagnosis
- Structures illustrated include the temporal nerve fiber layer, choroid, blood vessels, etc
Common Conditions Identified with OCT
- OCT aids in diagnosing and managing patients with various eye conditions
- Conditions include narrow angles, retinal disease, corneal pathologies, retinal detachment, vitreus detachment, macular conditions (macular hole, macular pucker, macular edema), and optic nerve abnormalities, etc.
Causes for Falsely High/Low Results
- Bifurcation of the superior vascular trunk can create a split bundle, leading to the appearance of RNFL thinning, but this is actually a physiological process
- Tilted discs may appear to be shifted temporally causing an abnormal presentation
- Myelinated peripapillary RNFL and other non-glaucomatous conditions may produce thick RNFL, reducing the reliability of glaucoma analysis
Hyperreflective Bands
- Four important hyperreflective structures essential for good visual acuity: RPE, interdigitation zone (IZ), ellipsoid zone (EZ), and inner/outer segment (IS/OS)
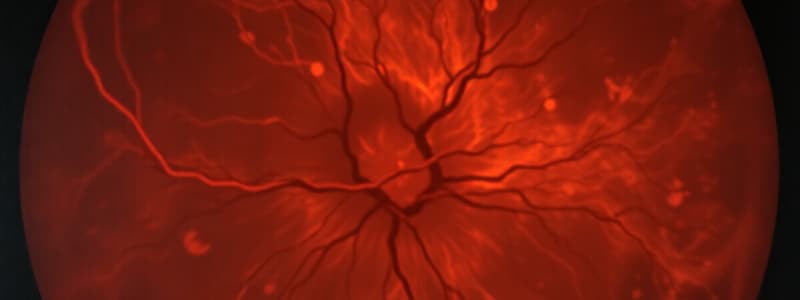
ONH OCT
- Glaucoma is a common condition identified with ONH OCT that can present as asymmetry of the nerve, RNFL thinning, and ON head edema
- Other conditions, like diabetic retinopathy, which may exhibit the signs mentioned above, should be considered as differential diagnoses
A-Scan Structures
- Peak identification on an A-scan indicates different eye structures such as cornea, lens, retina, choroid, and vitreous
- Reflectivity variations in various structures (cornea, lens, retina, etc.) help assess their integrity
- Comparing results to normative data aids in identifying abnormal values
B-Scan Common Conditions Diagnosed
- B-scan provides a two-dimensional view of ocular structures when internal view is obstructed
- Detects conditions like dense cataracts, vitreous hemorrhages, opaque corneas, eyelid pathology, anterior chamber opacities, and miosis
- Aids in diagnosing posterior segment disorders such as ciliary body lesions, ocular tumors, and vitreous pathology and retinal detachments (serous, rhegmatogenous, exudative)
Pre-Arterial Phase
- Choroidal circulation is filled with dye, no dye has reached the retinal arteries
Arterial Phase
- Dye appears in the retinal arteries following the prearterial phase to fill them fully
Capillary Phase
- Arteries and capillaries are complete filled
- Retinal capillaries are visibly around the optic nerve head (ONH) and fovea
Venous Phase
- Venous filling occurs after complete arterial and capillary filling
- Divided into early (arterio-venous) and mid/late stages based on filling status, and dye concentration
Conditions Identified with FAN
- Useful in evaluating retinal and choroidal circulation
- Used to diagnose anomalies in areas such as RPE changes
AFA Molecule
- Lipofuscin is stimulated by a low energy laser
- A barrier filter isolates the RPE lipofuscin response from other signals
- Provides a single monochromatic image with high contrast
- Helps in detecting hypo/hyper lesions
Gonioscopy
- Gonioscopy procedure to evaluate the anterior chamber angle
- Assessing the structures within and around the iris, trabecular meshwork, and scleral spur
Lacrimal Test (Jones)
- Procedure to test lacrimal duct patency in cases of excessive tear production
- Instill fluorescein in the lower conjunctival sac, and examine the tissue for presence of fluorescein post 5 mins
- Positive result indicates the duct is not obstructed, while negative result indicates an obstruction
Schirmer I & II Tests
- Measures lacrimal secretion, to evaluate the integrity of the aqueous production system
- Assesses aqueous production and tear film secretion
- Schirmer 1: applying the strip to lower eyelid, measuring the wetted area
- Schirmer 2: same procedure as Schirmer 1 but done on the conjunctival side and following the Schirmer 1 test (if negative), to test patency
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.