Podcast
Questions and Answers
A higher score on the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) indicates greater disability.
A higher score on the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) indicates greater disability.
- False
- True (correct)
Select the MOST appropriate statement regarding disc findings on Imaging (MRI)
Select the MOST appropriate statement regarding disc findings on Imaging (MRI)
- Not all MRI findings correlate to patient symptoms (correct)
- All of the above are accurate statements
- It is very uncommon to find disc changes on imaging before the age of 60
- All disc herniations found on an MRI cause symptoms
The patient present with a “band” of pain localized to the low back. Pain is aggravated by bending forward, prolonged sitting, and sitting on the toilet. Select the most likely pathology.
The patient present with a “band” of pain localized to the low back. Pain is aggravated by bending forward, prolonged sitting, and sitting on the toilet. Select the most likely pathology.
- Spondylolisthesis
- Disc herniation (correct)
- Sacroiliac joint pain
- Facet joint pain
The patient presents with unilateral, localized low back pain worsened with active range of motion into extension, an extension quadrant, and unilateral-posterior-to-anterior (UPA) at L4/L5. X-rays are negative (no findings) for fracture. Select the MOST likely pathology.
The patient presents with unilateral, localized low back pain worsened with active range of motion into extension, an extension quadrant, and unilateral-posterior-to-anterior (UPA) at L4/L5. X-rays are negative (no findings) for fracture. Select the MOST likely pathology.
Select the clinical feature(s) of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Select the clinical feature(s) of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Select the following that best describes a Grade 2 joint mobilization
Select the following that best describes a Grade 2 joint mobilization
Symptom IRRITABILITY can be defined as
Symptom IRRITABILITY can be defined as
Which of the following is a neurodynamic test to assess neural mechanosensitivity?
Which of the following is a neurodynamic test to assess neural mechanosensitivity?
Select the BEST combination of tests to rule out the SI joint
Select the BEST combination of tests to rule out the SI joint
Which of the following in your patient history would MOST increase the likelihood of spinal malignancy?
Which of the following in your patient history would MOST increase the likelihood of spinal malignancy?
A patient present with low back pain that extends into their right leg down to their foot. You direct the patient to perform 10 repetitions of standing lumbar extension. After the 10 repetitions, the patient reports pain has increased in their low back, but is no longer in their leg. What is the most appropriate next step?
A patient present with low back pain that extends into their right leg down to their foot. You direct the patient to perform 10 repetitions of standing lumbar extension. After the 10 repetitions, the patient reports pain has increased in their low back, but is no longer in their leg. What is the most appropriate next step?
Select the response that BEST describes a neurodynamic SLIDER technique
Select the response that BEST describes a neurodynamic SLIDER technique
A 70-year-old patient presents with numbness in both calves and feet when walking or standing for long periods. Their symptoms are eased by sitting and leaning forward onto a shopping cart. Select the most appropriate treatment strategy for this patient.
A 70-year-old patient presents with numbness in both calves and feet when walking or standing for long periods. Their symptoms are eased by sitting and leaning forward onto a shopping cart. Select the most appropriate treatment strategy for this patient.
The patient reports symptoms in their low back and down their right leg extending into the toes. When the patient performs repeated extension exercises, the pain disappears in their foot, but worsens in their back. During the repeated extension exercises, the patient is experiencing which of the following?
The patient reports symptoms in their low back and down their right leg extending into the toes. When the patient performs repeated extension exercises, the pain disappears in their foot, but worsens in their back. During the repeated extension exercises, the patient is experiencing which of the following?
Select the contraindications for lumbar manipulation. Select all that apply.
Select the contraindications for lumbar manipulation. Select all that apply.
Manipulation is more effective than mobilization for patients with low back pain.
Manipulation is more effective than mobilization for patients with low back pain.
The treatment-based classification aims to subgroup patients into categories that likely benefit from similar treatment approaches
The treatment-based classification aims to subgroup patients into categories that likely benefit from similar treatment approaches
Which of the following was NOT an original treatment-based classification option for low back pain?
Which of the following was NOT an original treatment-based classification option for low back pain?
Which of the following are ICF classifications for low back pain?
Which of the following are ICF classifications for low back pain?
The patient presents with a lateral shift and an extension directional preference. What is the most appropriate course of action to treat this patient based on the McKenzie approach?
The patient presents with a lateral shift and an extension directional preference. What is the most appropriate course of action to treat this patient based on the McKenzie approach?
The patient received a L4/L5 facet joint injection for long-standing localized low back pain. Their pain has reduced significantly following the injection. Which of the following is an appropriate rehabilitation goal for this patient?
The patient received a L4/L5 facet joint injection for long-standing localized low back pain. Their pain has reduced significantly following the injection. Which of the following is an appropriate rehabilitation goal for this patient?
The sacroiliac joints have a joint orientation and a robust ligamentous support system that makes them inherently stable and allows them to transfer load between the lower extremities and trunk.
The sacroiliac joints have a joint orientation and a robust ligamentous support system that makes them inherently stable and allows them to transfer load between the lower extremities and trunk.
The patient’s right leg is shorter than their left in supine and longer than their left in long sitting. Based solely on this information, what would be an appropriate initial treatment?
The patient’s right leg is shorter than their left in supine and longer than their left in long sitting. Based solely on this information, what would be an appropriate initial treatment?
In the functional optimization stage, patients should be encouraged to perform exercises that mimic their activities of daily living prior to discharge.
In the functional optimization stage, patients should be encouraged to perform exercises that mimic their activities of daily living prior to discharge.
Which of the following procedures may be indicated for a patient with lumbar spinal stenosis who has not responded to management with a physical therapist
Which of the following procedures may be indicated for a patient with lumbar spinal stenosis who has not responded to management with a physical therapist
The patient is able to consistently contract and relax their abdominal muscles without an increase in pain. However, they demonstrate difficulty flexing at the hips while squatting due to impaired movement control. They demonstrate full passive hip flexion range of motion. Which of the following would be an appropriate exercise to improve their ability to flex their hips squatting?
The patient is able to consistently contract and relax their abdominal muscles without an increase in pain. However, they demonstrate difficulty flexing at the hips while squatting due to impaired movement control. They demonstrate full passive hip flexion range of motion. Which of the following would be an appropriate exercise to improve their ability to flex their hips squatting?
Isolated muscle activation may not be as important as the patient’s ability to contract and relax the trunk muscles.
Isolated muscle activation may not be as important as the patient’s ability to contract and relax the trunk muscles.
The patient presents with a recent recurrence of generalized low back pain. They demonstrate positive findings on the Active Straight Leg Raise Test, Prone Instability Test, Hypermobility of L1-L5 segments with Central Posterior-to-Anterior accessory examination, and aberrant motion with return from active range of motion flexion. The patient scores a total of 4 on the Fear Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire (FABQ). What is the most appropriate ICF classification based on this information?
The patient presents with a recent recurrence of generalized low back pain. They demonstrate positive findings on the Active Straight Leg Raise Test, Prone Instability Test, Hypermobility of L1-L5 segments with Central Posterior-to-Anterior accessory examination, and aberrant motion with return from active range of motion flexion. The patient scores a total of 4 on the Fear Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire (FABQ). What is the most appropriate ICF classification based on this information?
What is the most appropriate treatment strategy for a patient with chronic non-specific low back pain with related cognitive or affective tendencies?
What is the most appropriate treatment strategy for a patient with chronic non-specific low back pain with related cognitive or affective tendencies?
Muscle relaxants provide a small effect on pain in patients with acute low back pain and DO NOT increase the risk of adverse events.
Muscle relaxants provide a small effect on pain in patients with acute low back pain and DO NOT increase the risk of adverse events.
Ischiopubic ramus, pubic bone, perineal body, ischial tuberosity are pelvic floor landmarks found on bodies of both sexes
Ischiopubic ramus, pubic bone, perineal body, ischial tuberosity are pelvic floor landmarks found on bodies of both sexes
Choose the statement that most accurately describes optimal toileting position for to promote a bowel movement
Choose the statement that most accurately describes optimal toileting position for to promote a bowel movement
Select the MOST accurate statement. Etiological factors of an overactive pelvic floor discussed in class include...
Select the MOST accurate statement. Etiological factors of an overactive pelvic floor discussed in class include...
Which diagnosis present with the following symptoms: a sensation of fullness and heaviness in the vaginal canal that worsens as the day goes on?
Which diagnosis present with the following symptoms: a sensation of fullness and heaviness in the vaginal canal that worsens as the day goes on?
Dyspareunia is defined as painful sexual intercourse
Dyspareunia is defined as painful sexual intercourse
Diastasis recti symptoms include a feeling of instability and/or bulge along the Linea Alba that improves with increased intraabdominal pressure, but worsens with activities such as coughing, lifting, crunching, sit ups, and quadruped positions
Diastasis recti symptoms include a feeling of instability and/or bulge along the Linea Alba that improves with increased intraabdominal pressure, but worsens with activities such as coughing, lifting, crunching, sit ups, and quadruped positions
Risk factors of perineal tears during vaginal births include all of the following, EXCEPT:
Risk factors of perineal tears during vaginal births include all of the following, EXCEPT:
A 3rd degree perineal tear is defined as tearing of the skin, perineal muscles, and entire anal sphincter
A 3rd degree perineal tear is defined as tearing of the skin, perineal muscles, and entire anal sphincter
At what gestation week is it recommended to begin perineal massage to reduce risk of perineal tearing during vaginal birth?
At what gestation week is it recommended to begin perineal massage to reduce risk of perineal tearing during vaginal birth?
Match the clinical presentation with the correct diagnosis. One of the diagnoses can be used twice.
Match the clinical presentation with the correct diagnosis. One of the diagnoses can be used twice.
A 15 year old female dancer reports bilateral lower back pain worsening over the past 6 months. Her spinal range of motion is full but reproduces symptoms during lumbar extension. Reflexes, dermatomes, and myotomes are intact. Palpation reveals a step-off deformity at L3/L4. Given this information, which pathology is MOST likely?
A 15 year old female dancer reports bilateral lower back pain worsening over the past 6 months. Her spinal range of motion is full but reproduces symptoms during lumbar extension. Reflexes, dermatomes, and myotomes are intact. Palpation reveals a step-off deformity at L3/L4. Given this information, which pathology is MOST likely?
A 65 year old male presents with a recent exacerbation of his chronic low back and right buttock pain. He reports a history of lung cancer, type II diabetes, and high cholesterol. He also reports unintentional weight loss of 20 lbs and inability to find a comfortable position to sleep due to pain. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate next step?
A 65 year old male presents with a recent exacerbation of his chronic low back and right buttock pain. He reports a history of lung cancer, type II diabetes, and high cholesterol. He also reports unintentional weight loss of 20 lbs and inability to find a comfortable position to sleep due to pain. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate next step?
A patient experiences pain reproduction in the posterior right thigh that is aggravated when the therapist performs a right straight leg raise test. Which test outcome during the straight leg raise test confirms lower lumbar spine nerve involvement?
A patient experiences pain reproduction in the posterior right thigh that is aggravated when the therapist performs a right straight leg raise test. Which test outcome during the straight leg raise test confirms lower lumbar spine nerve involvement?
A 70 yr old male reports a 6 month history of worsening low back pain and occasional numbness in both feet. Back and leg symptoms are worsened with prolonged standing and walking. Lower back and leg symptoms are eased with sitting and leaning forward. Which additional test information would rule in the MOST likely diagnosis?
A 70 yr old male reports a 6 month history of worsening low back pain and occasional numbness in both feet. Back and leg symptoms are worsened with prolonged standing and walking. Lower back and leg symptoms are eased with sitting and leaning forward. Which additional test information would rule in the MOST likely diagnosis?
A patient with lateral shift and an extension directional preference presents for treatment. What is the MOST appropriate initial intervention in this patient’s care?
A patient with lateral shift and an extension directional preference presents for treatment. What is the MOST appropriate initial intervention in this patient’s care?
A 30-year-old female reports right low back pain localized to the lumbar region for 1 month. She denies any injury that she can remember. She states the pain is usually worse in the morning but eases within an hour after moving around. She notices it more after prolonged periods of sitting at her desk at work. She describes the pain as sharp but not radiating. Pain is exacerbated by a combination of right lumbar side bending and extension. Given the above history and examination findings, what is the MOST likely diagnosis?
A 30-year-old female reports right low back pain localized to the lumbar region for 1 month. She denies any injury that she can remember. She states the pain is usually worse in the morning but eases within an hour after moving around. She notices it more after prolonged periods of sitting at her desk at work. She describes the pain as sharp but not radiating. Pain is exacerbated by a combination of right lumbar side bending and extension. Given the above history and examination findings, what is the MOST likely diagnosis?
A 45-year-old male presents to physical therapy with a 3-day history of right localized low back pain. He scores 12 on the fear avoidance beliefs questionnaire and 30% on the Modified Oswestry Disability Index. Upon physical examination, he presents with limited movement and pain with active range of motion testing in flexion, extension, right rotation, and right lateral flexion. What is the MOST appropriate initial intervention for this patient’s care?
A 45-year-old male presents to physical therapy with a 3-day history of right localized low back pain. He scores 12 on the fear avoidance beliefs questionnaire and 30% on the Modified Oswestry Disability Index. Upon physical examination, he presents with limited movement and pain with active range of motion testing in flexion, extension, right rotation, and right lateral flexion. What is the MOST appropriate initial intervention for this patient’s care?
A 22-year-old female reports a 3-month history of generalized low back pain. Pain began following an increase in aerobic exercise, primarily bicycling. Upon examination, her active range of motion is full in flexion, extension, and lateral flexion bilaterally. She experiences pain when returning to an upright position from forward flexion, necessitating thigh climbing to complete the motion. Her straight leg raise is measured at 95 degrees on each leg, and she present with a positive prone instability test. Passive accessory mobility testing reveals hypermobility at L4 and L5 with CPA assessment. She demonstrates difficulty consistently activating the abdominal muscles in the hook lying position. She denies any pain in the lower extremities. What is the MOST appropriate initial intervention for this patient’s care?
A 22-year-old female reports a 3-month history of generalized low back pain. Pain began following an increase in aerobic exercise, primarily bicycling. Upon examination, her active range of motion is full in flexion, extension, and lateral flexion bilaterally. She experiences pain when returning to an upright position from forward flexion, necessitating thigh climbing to complete the motion. Her straight leg raise is measured at 95 degrees on each leg, and she present with a positive prone instability test. Passive accessory mobility testing reveals hypermobility at L4 and L5 with CPA assessment. She demonstrates difficulty consistently activating the abdominal muscles in the hook lying position. She denies any pain in the lower extremities. What is the MOST appropriate initial intervention for this patient’s care?
A patient presents to physical therapy evaluation with low back pain, diminished inner thigh sensation, difficulty fully emptying his bladder, and diminished lower extremity deep tendon reflexes; 1+ for Patellar and Achilles. What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A patient presents to physical therapy evaluation with low back pain, diminished inner thigh sensation, difficulty fully emptying his bladder, and diminished lower extremity deep tendon reflexes; 1+ for Patellar and Achilles. What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A patient presents with pain in the shaded area on the image. The patient reports falling on her right buttock 6 days ago. Physical examination reveals positive Thigh Thrust and Sacral Thrust Tests. Lumbar active range of motion and passive accessory testing are negative for symptom provocation. During the Marcher’s Test, the patient’s right PSIS does not move posteroinferiorly relative to S2. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate initial intervention?
A patient presents with pain in the shaded area on the image. The patient reports falling on her right buttock 6 days ago. Physical examination reveals positive Thigh Thrust and Sacral Thrust Tests. Lumbar active range of motion and passive accessory testing are negative for symptom provocation. During the Marcher’s Test, the patient’s right PSIS does not move posteroinferiorly relative to S2. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate initial intervention?
A 45-year-old male presents to direct access physical therapy with right lower back pain accompanied by right posterior thigh and right heel numbness that began 2 weeks ago without a mechanism of injury. The patient denies recent bowel/bladder changes and inner thigh numbness. He reports that pain wakens him at night and that it typically takes 5-10 minutes to fall back to sleep. He also reports losing 5 pounds over the last 3 months, which he attributes to his modified eating habits. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate next step?
A 45-year-old male presents to direct access physical therapy with right lower back pain accompanied by right posterior thigh and right heel numbness that began 2 weeks ago without a mechanism of injury. The patient denies recent bowel/bladder changes and inner thigh numbness. He reports that pain wakens him at night and that it typically takes 5-10 minutes to fall back to sleep. He also reports losing 5 pounds over the last 3 months, which he attributes to his modified eating habits. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate next step?
The patient reports a 20-year history of generalized low back pain. The patient scores 50% on the Modified Oswestry Disability Index and 21 on the FABQ-Physical Activity Scale. The patient reports that they “feel like their back is damaged” and that they “will end up in a wheelchair because of their bad back”. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate ICF Diagnosis?
The patient reports a 20-year history of generalized low back pain. The patient scores 50% on the Modified Oswestry Disability Index and 21 on the FABQ-Physical Activity Scale. The patient reports that they “feel like their back is damaged” and that they “will end up in a wheelchair because of their bad back”. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate ICF Diagnosis?
A 30-year-old female presents with a five-year history of generalized lower back pain. She reports increased pain with prolonged sitting and prolonged standing. Upon physical examination, she presents with pain at the end-range of flexion and extension active range of motion. Central Posterior-to-Anterior joint mobility assessment reveals hypermobility at L4 and L5. She presents with Fair (3/5) manual muscle tests for trunk flexors and trunk extensors. Which additional test would assist the physical therapist in confirming the MOST likely diagnosis?
A 30-year-old female presents with a five-year history of generalized lower back pain. She reports increased pain with prolonged sitting and prolonged standing. Upon physical examination, she presents with pain at the end-range of flexion and extension active range of motion. Central Posterior-to-Anterior joint mobility assessment reveals hypermobility at L4 and L5. She presents with Fair (3/5) manual muscle tests for trunk flexors and trunk extensors. Which additional test would assist the physical therapist in confirming the MOST likely diagnosis?
A patient presents with lower back pain and heel pain. Which of the following additional findings is MOST likely to indicate the lower back pain and heel pain are related?
A patient presents with lower back pain and heel pain. Which of the following additional findings is MOST likely to indicate the lower back pain and heel pain are related?
A 38-year-old male presents to physical therapy with right-sided low back pain that began after lifting a heavy object three days ago. He describes the pain as localized to the right lower back, sharp with movement, and worse during trunk side-bending to the left. He denies any radiating pain, numbness, or tingling. Physical examination reveals:
Full lumbar active range of motion, limited by pain at end-range left lumbar lateral flexion. All other motions are pain-free, Pain reproduction with resisted right lateral flexion, no pain reproduction with Central or Unilateral Posterior-to-Anterior accessory examination of L1-S1, Negative straight leg raise test, thigh thrust test, and sacroiliac joint compression test, Tenderness to palpation over the right quadratus lumborum.
Given this information, what is the MOST likely diagnosis?
A 38-year-old male presents to physical therapy with right-sided low back pain that began after lifting a heavy object three days ago. He describes the pain as localized to the right lower back, sharp with movement, and worse during trunk side-bending to the left. He denies any radiating pain, numbness, or tingling. Physical examination reveals:
Full lumbar active range of motion, limited by pain at end-range left lumbar lateral flexion. All other motions are pain-free, Pain reproduction with resisted right lateral flexion, no pain reproduction with Central or Unilateral Posterior-to-Anterior accessory examination of L1-S1, Negative straight leg raise test, thigh thrust test, and sacroiliac joint compression test, Tenderness to palpation over the right quadratus lumborum.
Given this information, what is the MOST likely diagnosis?
A 45-year-old patient with a three-year history of chronic low back pain and movement coordination impairments is being seen in a direct-access physical therapy clinic. The patient has completed two physical therapy visits over the past week following her initial physical therapy evaluation. Her treatment plan has included lower abdominal strengthening and coordination exercises and education regarding functional movements. Today, she reports frustration with her lack of progress, stating that her pain level remains unchanged since starting physical therapy. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate next step in managing this patient’s care?
A 45-year-old patient with a three-year history of chronic low back pain and movement coordination impairments is being seen in a direct-access physical therapy clinic. The patient has completed two physical therapy visits over the past week following her initial physical therapy evaluation. Her treatment plan has included lower abdominal strengthening and coordination exercises and education regarding functional movements. Today, she reports frustration with her lack of progress, stating that her pain level remains unchanged since starting physical therapy. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate next step in managing this patient’s care?
A patient presents with left-sided low back pain radiating into the left buttock. Symptoms are aggravated by prolonged sitting and are reproduced with a straight leg raise test. Examination reveals diminished sensation in the L5 dermatome. Given this information, what is the MOST likely ICF Classification?
A patient presents with left-sided low back pain radiating into the left buttock. Symptoms are aggravated by prolonged sitting and are reproduced with a straight leg raise test. Examination reveals diminished sensation in the L5 dermatome. Given this information, what is the MOST likely ICF Classification?
A 55-year-old male presents with a 10-year history of chronic low back pain. He scores 65% on the Modified Oswestry Disability Index and 25 on the Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire-Physical Activity Scale. The patient states, “I think something is seriously wrong with my back, and I avoid walking for more than a few minutes because it makes the pain worse.” He denies recent imaging or medical workup for his symptoms. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate initial intervention for this patient?
A 55-year-old male presents with a 10-year history of chronic low back pain. He scores 65% on the Modified Oswestry Disability Index and 25 on the Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire-Physical Activity Scale. The patient states, “I think something is seriously wrong with my back, and I avoid walking for more than a few minutes because it makes the pain worse.” He denies recent imaging or medical workup for his symptoms. Given this information, what is the MOST appropriate initial intervention for this patient?
A 42-year-old patient presents 3 weeks following lumbar fusion surgery at levels L3-S1 for degenerative disc disease. The patient reports difficulty transitioning from sit to stand and mild lower back discomfort. Physical examination reveals reduced lumbar active range of motion in lumbar extension and lumbar flexion. The patient demonstrates difficulty activating lower abdominal muscles in a hooklying and seated position. Which intervention is MOST appropriate at this stage of recovery?
A 42-year-old patient presents 3 weeks following lumbar fusion surgery at levels L3-S1 for degenerative disc disease. The patient reports difficulty transitioning from sit to stand and mild lower back discomfort. Physical examination reveals reduced lumbar active range of motion in lumbar extension and lumbar flexion. The patient demonstrates difficulty activating lower abdominal muscles in a hooklying and seated position. Which intervention is MOST appropriate at this stage of recovery?
A 60-year-old female presents with localized left lower back pain that began 6 weeks ago. Her X-ray report notes "moderate lumbar osteophyte formation" and "severe disc space narrowing." She reports occasional discomfort but continues daily activities without difficulty. Physical examination reveals minor limitations in active range of motion with pain reproduced at end range extension. Lower extremity myotomes, dermatomes, and deep tendon reflexes are intact. She presents with pain reproduction and hypomobility with unilateral posterior-to-anterior assessment at the left L4/L5 facet. What is the MOST appropriate initial management approach for this patient?
A 60-year-old female presents with localized left lower back pain that began 6 weeks ago. Her X-ray report notes "moderate lumbar osteophyte formation" and "severe disc space narrowing." She reports occasional discomfort but continues daily activities without difficulty. Physical examination reveals minor limitations in active range of motion with pain reproduced at end range extension. Lower extremity myotomes, dermatomes, and deep tendon reflexes are intact. She presents with pain reproduction and hypomobility with unilateral posterior-to-anterior assessment at the left L4/L5 facet. What is the MOST appropriate initial management approach for this patient?
A 25-year-old female underwent a hip arthroscopy for right anterior groin pain secondary to a hip labral tear she suffered nearly 2 years ago. The patient is now 12 weeks post-op with no report of pain during all activities of daily living, presents with a normal and symmetrical gait pattern, and has completed 6 weeks of "late stage" rehab consisting of squats, lunges, and other lower body strengthening activities. Which of the following criteria needs to be met prior to the patient initiating some type of running into her rehab?
A 25-year-old female underwent a hip arthroscopy for right anterior groin pain secondary to a hip labral tear she suffered nearly 2 years ago. The patient is now 12 weeks post-op with no report of pain during all activities of daily living, presents with a normal and symmetrical gait pattern, and has completed 6 weeks of "late stage" rehab consisting of squats, lunges, and other lower body strengthening activities. Which of the following criteria needs to be met prior to the patient initiating some type of running into her rehab?
A 78-year-old male presents to the clinic 3 days postoperative a cemented right total hip arthroplasty (THA). The physical therapist notes in the operating report that the surgeon utilized a posterolateral incision. Which of the following is the most appropriate acute precaution to reinforce with this patient?
A 78-year-old male presents to the clinic 3 days postoperative a cemented right total hip arthroplasty (THA). The physical therapist notes in the operating report that the surgeon utilized a posterolateral incision. Which of the following is the most appropriate acute precaution to reinforce with this patient?
Which manual therapy technique is used primarily for pain relief?
Which manual therapy technique is used primarily for pain relief?
The CPG for Hip OA specifically identifies these muscles for strengthening
The CPG for Hip OA specifically identifies these muscles for strengthening
The following precautions should be taken when rehabbing someone who is status post total hip replacement, anterior approach:
The following precautions should be taken when rehabbing someone who is status post total hip replacement, anterior approach:
For a patient post op total hip replacement, in which phase should you focus on normalizing gait with the least restrictive assistive device
For a patient post op total hip replacement, in which phase should you focus on normalizing gait with the least restrictive assistive device
The following is criteria to move to Phase 4 rehabilitation s/p hip arthroscopy
The following is criteria to move to Phase 4 rehabilitation s/p hip arthroscopy
The following is a precaution for progressing to Phase 2 s/p hip arthroscopy
The following is a precaution for progressing to Phase 2 s/p hip arthroscopy
Tonely, 2010 suggest that phase 3 of piriformis syndrome rehabilitation should include functional training. Which of the following exercises would be performed in Phase 3?
Tonely, 2010 suggest that phase 3 of piriformis syndrome rehabilitation should include functional training. Which of the following exercises would be performed in Phase 3?
The following would classify as a motor control exercise for femoroacetabular Impingement as per the Mansell et al, 2016 articular:
The following would classify as a motor control exercise for femoroacetabular Impingement as per the Mansell et al, 2016 articular:
A 16-year-old patient presents to therapy with complaint of right-sided knee pain after having sustained a fall to the ground. She is unable to ambulate more than 8 steps. What is the most appropriate next step?
A 16-year-old patient presents to therapy with complaint of right-sided knee pain after having sustained a fall to the ground. She is unable to ambulate more than 8 steps. What is the most appropriate next step?
A patient presents with the following symptoms:
Reddish streaks on bilateral shins
Fever
Swelling of bilateral lower extremities
The most likely diagnosis requiring referral is:
A patient presents with the following symptoms:
Reddish streaks on bilateral shins
Fever
Swelling of bilateral lower extremities
The most likely diagnosis requiring referral is:
A positive Lachman’s test is most like confirmation of which of the following diagnoses?
A positive Lachman’s test is most like confirmation of which of the following diagnoses?
According to the clinical practice guideline, which of the following self-report measures is most appropriate for knee ligament sprains?
According to the clinical practice guideline, which of the following self-report measures is most appropriate for knee ligament sprains?
According to the clinical practice guideline for patellofemoral pain, when a patient performs a squat which of the following clinical findings is most likely associated with patellofemoral pain?
According to the clinical practice guideline for patellofemoral pain, when a patient performs a squat which of the following clinical findings is most likely associated with patellofemoral pain?
A patient is a 55-year-old female with a history of knee osteoarthritis. The patient presents to therapy with complaints of pain over the medial proximal tibia and observable swelling. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A patient is a 55-year-old female with a history of knee osteoarthritis. The patient presents to therapy with complaints of pain over the medial proximal tibia and observable swelling. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A patient reports to therapy with complaints of anterior knee pain aggravated by kneeling but is able to achieve pain-free jumping. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A patient reports to therapy with complaints of anterior knee pain aggravated by kneeling but is able to achieve pain-free jumping. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
According to the clinical practice guideline, what is the best intervention of early rehabilitation after knee meniscus surgery?
According to the clinical practice guideline, what is the best intervention of early rehabilitation after knee meniscus surgery?
When assessing a patient with knee pain, which of the following types of pain most likely an inflammatory disease?
When assessing a patient with knee pain, which of the following types of pain most likely an inflammatory disease?
According to the Wells Criteria, which score indicates a high probability of a deep vein thrombosis?
According to the Wells Criteria, which score indicates a high probability of a deep vein thrombosis?
The knee joint deformity can be viewed in a lateral view postural assessment:
The knee joint deformity can be viewed in a lateral view postural assessment:
The clinical practice guideline for patellofemoral pain indicates which of the following tests were appropriate for the overuse/overload classification?
The clinical practice guideline for patellofemoral pain indicates which of the following tests were appropriate for the overuse/overload classification?
The following pictures depicts which knee deformity?
The following pictures depicts which knee deformity?
The phenomenon that occurs when the knee bows out during weightbearing is known as:
The phenomenon that occurs when the knee bows out during weightbearing is known as:
In this test, a positive test occurs when the patient straightens the knee out to gain patellar stability or attempts to avoid lateral glide:
In this test, a positive test occurs when the patient straightens the knee out to gain patellar stability or attempts to avoid lateral glide:
For the Brush/Bulge Test, a grade 2+ is scored when:
For the Brush/Bulge Test, a grade 2+ is scored when:
This test is performed with the patient in prone with the knee in 90 degrees of flexion and an axial load applied while the knee is internally and externally rotated:
This test is performed with the patient in prone with the knee in 90 degrees of flexion and an axial load applied while the knee is internally and externally rotated:
Which score would classify as a fall risk in older adults on the Functional Gait Assessment outcome measure:
Which score would classify as a fall risk in older adults on the Functional Gait Assessment outcome measure:
In examination of a patient referred to physical therapy for knee pain you determine a positive Lachman’s test, what is your next step?
In examination of a patient referred to physical therapy for knee pain you determine a positive Lachman’s test, what is your next step?
This knee stability hop test is untimed:
This knee stability hop test is untimed:
This manual therapy technique is used to help to improve knee flexion mobility
This manual therapy technique is used to help to improve knee flexion mobility
A patient has been attending physical therapy for knee osteoarthritis. They are now ready to increase endurance for activity to return to ADLs like independent grocery shopping. The exercise dose recommended is:
A patient has been attending physical therapy for knee osteoarthritis. They are now ready to increase endurance for activity to return to ADLs like independent grocery shopping. The exercise dose recommended is:
When screening for ACL surgery, one item that an individual must meet to be classified as a coper is:
When screening for ACL surgery, one item that an individual must meet to be classified as a coper is:
In postoperative care following Knee Meniscectomy, what is arguably the MOST important for the patient to achieve in the rehabilitation process:
In postoperative care following Knee Meniscectomy, what is arguably the MOST important for the patient to achieve in the rehabilitation process:
In the clinical practice guideline, which of the following is recommended exercise for most patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis?
In the clinical practice guideline, which of the following is recommended exercise for most patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis?
A patient presents with acute patellar tendinopathy. Select the best initial intervention
A patient presents with acute patellar tendinopathy. Select the best initial intervention
Clinicians CAN recommend the use of knee sleeves or braces for patients suffering from Osgood Schlatter’s
Clinicians CAN recommend the use of knee sleeves or braces for patients suffering from Osgood Schlatter’s
The clinical practice guideline for patellofemoral pain syndrome suggests that orthoses can be used for individuals with greater than normal supination to reduce pain
The clinical practice guideline for patellofemoral pain syndrome suggests that orthoses can be used for individuals with greater than normal supination to reduce pain
Rehabilitation for a partially torn acute ACL SHOULD show promise for improvement of instability within 3 months
Rehabilitation for a partially torn acute ACL SHOULD show promise for improvement of instability within 3 months
For patients who fall into the patellofemoral pain with mobility impairments classification, which of the following interventions would be MOST helpful?
For patients who fall into the patellofemoral pain with mobility impairments classification, which of the following interventions would be MOST helpful?
The patient presents to the clinic following an Achilles tendon rupture and repair. Please select the most appropriate patient-reported outcome measure for this patient.
The patient presents to the clinic following an Achilles tendon rupture and repair. Please select the most appropriate patient-reported outcome measure for this patient.
The patient presents to the clinic following an ankle sprain in which the mechanism of injury forced the ankle into combined plantarflexion and inversion. Which ligament was most likely injured?
The patient presents to the clinic following an ankle sprain in which the mechanism of injury forced the ankle into combined plantarflexion and inversion. Which ligament was most likely injured?
Which of the following movements is avoided initially following an acute “high” ankle sprain?
Which of the following movements is avoided initially following an acute “high” ankle sprain?
The patient has a history of a tibial stress fracture 2 years ago and reports a new onset of localized distal anterior shin pain following a week of increased running mileage. She also reports that her first menstrual cycle occurred at age 15, her BMI is 18kg/m2, and she was a gymnast when she was younger. What pathology do you suspect based on this information?
The patient has a history of a tibial stress fracture 2 years ago and reports a new onset of localized distal anterior shin pain following a week of increased running mileage. She also reports that her first menstrual cycle occurred at age 15, her BMI is 18kg/m2, and she was a gymnast when she was younger. What pathology do you suspect based on this information?
The patient reports plantar forefoot pain and numbness between their 3rd and 4th toes and. They report no other symptoms. Which of the options is the most likely diagnosis?
The patient reports plantar forefoot pain and numbness between their 3rd and 4th toes and. They report no other symptoms. Which of the options is the most likely diagnosis?
Based on the Clinical Practice Guidelines, what is the best management option for a patient with chronic Achilles mid-portion tendinopathy?
Based on the Clinical Practice Guidelines, what is the best management option for a patient with chronic Achilles mid-portion tendinopathy?
The patient presents with acute, painful plantar fasciopathy. What is the best initial management strategy for this patient?
The patient presents with acute, painful plantar fasciopathy. What is the best initial management strategy for this patient?
You suspect the patient demonstrates signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. Which test would help confirm this diagnosis?
You suspect the patient demonstrates signs and symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. Which test would help confirm this diagnosis?
The patient is seen in your clinic direct access following an acute inversion (lateral) ankle sprain. Based on the Ottawa Ankle Rules, which of the following findings would indicate the need for imaging?
The patient is seen in your clinic direct access following an acute inversion (lateral) ankle sprain. Based on the Ottawa Ankle Rules, which of the following findings would indicate the need for imaging?
The patient experienced a lateral ankle sprain 2 years ago. They continue to report feelings of instability and giving way in their ankle in addition to repeated ankle sprains. The patient wants to continue playing basketball. What is the most appropriate education regarding ankle support (bracing)?
The patient experienced a lateral ankle sprain 2 years ago. They continue to report feelings of instability and giving way in their ankle in addition to repeated ankle sprains. The patient wants to continue playing basketball. What is the most appropriate education regarding ankle support (bracing)?
With the patient in prone, you assess the forefoot relationship to the hindfoot in subtalar neutral. The first MTP is elevated in comparison to the other MTP joints. What does this represent?
With the patient in prone, you assess the forefoot relationship to the hindfoot in subtalar neutral. The first MTP is elevated in comparison to the other MTP joints. What does this represent?
The foot posture index (FPI-6) score is +8. What does this score indicate?
The foot posture index (FPI-6) score is +8. What does this score indicate?
Which of the following joint mobility findings would match with a finding of limited ankle dorsiflexion?
Which of the following joint mobility findings would match with a finding of limited ankle dorsiflexion?
You are trying to bias one of the peripheral nerves near the ankle. The position of the ankle/foot is in ankle dorsiflexion, subtalar inversion, and toe flexion. What nerve is being biased in this position?
You are trying to bias one of the peripheral nerves near the ankle. The position of the ankle/foot is in ankle dorsiflexion, subtalar inversion, and toe flexion. What nerve is being biased in this position?
At the pre-swing phase of gait the foot should be in a rigid, supinated position to serve as a rigid lever for push-off.
At the pre-swing phase of gait the foot should be in a rigid, supinated position to serve as a rigid lever for push-off.
Select the test that would help you rule in plantar fasciopathy as a diagnosis.
Select the test that would help you rule in plantar fasciopathy as a diagnosis.
A positive Thompson Test would indicate which of the following?
A positive Thompson Test would indicate which of the following?
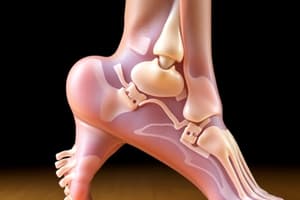
A patient injures their ankle with a mechanism of injury consistent with the image below (tacklers lands on lateral ankle with foot planted). What special tests would BEST confirm the most likely diagnosis based on the mechanism of injury?
A patient injures their ankle with a mechanism of injury consistent with the image below (tacklers lands on lateral ankle with foot planted). What special tests would BEST confirm the most likely diagnosis based on the mechanism of injury?
A patient presents with numbness on the plantar aspect of their foot. Which of the following combinations correctly lists the nerve injured and special test used to help confirm a diagnosis of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome?
A patient presents with numbness on the plantar aspect of their foot. Which of the following combinations correctly lists the nerve injured and special test used to help confirm a diagnosis of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome?
Palpation of which bony landmark is used to confirm a diagnosis of plantar fasciopathy?
Palpation of which bony landmark is used to confirm a diagnosis of plantar fasciopathy?
A patient with compensated forefoot varus would benefit from a post under which part of their foot to improve foot posture?
A patient with compensated forefoot varus would benefit from a post under which part of their foot to improve foot posture?
A patient is performing a balance training program. They can perform single limb stance with their eyes open without any issues. What is the BEST next progression from this exercise?
A patient is performing a balance training program. They can perform single limb stance with their eyes open without any issues. What is the BEST next progression from this exercise?
A patient presents with acute, insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Select the best initial intervention.
A patient presents with acute, insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Select the best initial intervention.
What physical examination metric is important to determine long-term functional biomechanics following Achilles tendon rupture and repair?
What physical examination metric is important to determine long-term functional biomechanics following Achilles tendon rupture and repair?
Clinicians SHOULD use either prefabricated or custom fabricated orthoses as an isolated treatment for short-term pain relief in individuals with plantar fasciopathy
Clinicians SHOULD use either prefabricated or custom fabricated orthoses as an isolated treatment for short-term pain relief in individuals with plantar fasciopathy
Which exercise would best strengthen the plantar foot intrinsic muscles?
Which exercise would best strengthen the plantar foot intrinsic muscles?
A patient presents with limited dorsiflexion range of motion. What is the most appropriate manual therapy intervention to improve this impairment?
A patient presents with limited dorsiflexion range of motion. What is the most appropriate manual therapy intervention to improve this impairment?
The patient demonstrates overstriding at initial contact during running and is being treated for patellofemoral pain. Which cue is likely to have the most beneficial effect to decrease patellofemoral loads and subsequent pain?
The patient demonstrates overstriding at initial contact during running and is being treated for patellofemoral pain. Which cue is likely to have the most beneficial effect to decrease patellofemoral loads and subsequent pain?
For patients following Achilles tendon rupture and repair, avoid stretching the Achilles tendon past 0 degrees dorsiflexion for 12 weeks post-operatively
For patients following Achilles tendon rupture and repair, avoid stretching the Achilles tendon past 0 degrees dorsiflexion for 12 weeks post-operatively
Flashcards
Capital of France (example flashcard)
Capital of France (example flashcard)
Paris