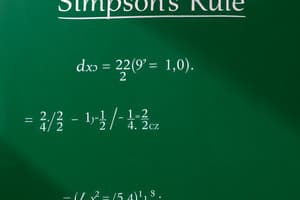Podcast
Questions and Answers
The frontal lobe is the largest lobe of the brain, occupying about one-third of the cerebral hemisphere.
The frontal lobe is the largest lobe of the brain, occupying about one-third of the cerebral hemisphere.
True (A)
The frontal lobe is located in the posterior aspect of the cranial cavity.
The frontal lobe is located in the posterior aspect of the cranial cavity.
False (B)
The frontal lobe accounts for 41% of the total neocortical volume.
The frontal lobe accounts for 41% of the total neocortical volume.
True (A)
What groove separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe posteriorly?
What groove separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe posteriorly?
What sulcus separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe inferolaterally?
What sulcus separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe inferolaterally?
What are the four principal gyri of the frontal lobe?
What are the four principal gyri of the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobe lies largely in the anterior cranial fossa of the skull.
The frontal lobe lies largely in the anterior cranial fossa of the skull.
The frontal lobe occupies one-half of the cerebral hemisphere.
The frontal lobe occupies one-half of the cerebral hemisphere.
Posterior and inferior to the frontal lobe is the _____ lobe.
Posterior and inferior to the frontal lobe is the _____ lobe.
The _____ demarcates the posterior border of the frontal lobe.
The _____ demarcates the posterior border of the frontal lobe.
Flashcards
Frontal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
Largest lobe of the brain, occupying about one-third of the cerebral hemisphere.
Central Sulcus
Central Sulcus
Separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe posteriorly.
Lateral Sulcus
Lateral Sulcus
Separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe inferolaterally.
Frontal Pole
Frontal Pole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Location Relative to Frontal Lobe
Location Relative to Frontal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Sulcus Border
Central Sulcus Border
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sylvian Fissure Border
Sylvian Fissure Border
Signup and view all the flashcards
Four Principal Gyri of Frontal Lobe
Four Principal Gyri of Frontal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Numerical differentiation and integration covered
- Newton-Cotes Integration Formulas are introduced, including the trapezoidal rule and Simpson's rules
Numerical Differentiation
-
Finds the rate of change $f'(x)$ of a function $f(x)$
-
The formula for the numerical differentiation is:
- $f'(x) = \lim_{\Delta x \to 0} \frac{f(x + \Delta x) - f(x)}{\Delta x}$
-
Derivatives are approximated using a small $\Delta x$
-
The formula for the forward difference approximation:
- $f'(x) \approx \frac{f(x + \Delta x) - f(x)}{\Delta x}$
-
The formula for the backward difference approximation:
- $f'(x) \approx \frac{f(x) - f(x - \Delta x)}{\Delta x}$
-
The formula for the central difference approximation:
- $f'(x) \approx \frac{f(x + \Delta x) - f(x - \Delta x)}{2 \Delta x}$
Example of derivative of $f(x) = e^x$ at $x = 2$ where $\Delta x = 0.1$:
- The true solution is $f'(x) = e^x$, so $f'(2) = e^2 = 7.389056099$
- Forward difference approximation:
- $= \frac{e^{2.1} - e^2}{0.1} = 7.707426066$
- Absolute error $ = |7.707426066 - 7.389056099| = 0.318369967$
- Relative error $ = |\frac{0.318369967}{7.389056099}| = 0.0430869$
- Backward difference approximation:
- $\frac{e^{2} - e^{1.9}}{0.1} = 7.081880265$
- Absolute error $ = |7.081880265 - 7.389056099| = 0.307175834$
- Relative error $ = |\frac{0.307175834}{7.389056099}| = 0.0415713$
- Central difference approximation
- $\frac{e^{2.1} - e^{1.9}}{0.2} = 7.394653166$
- Absolute error $ = |7.394653166 - 7.389056099| = 0.005597067$
- Relative error $ = |\frac{0.005597067}{7.389056099}| = 0.0007575$
- $f''(x)$ second derivative approximation:
- $f''(x) \approx \frac{f'(x + \Delta x) - f'(x - \Delta x)}{2 \Delta x}$
- Using central difference approximation for $f'(x + \Delta x)$ and $f'(x - \Delta x)$:
- $f''(x) \approx \frac{f(x + 2\Delta x) - 2f(x) + f(x - 2\Delta x)}{(2 \Delta x)^2}$
Numerical Integration
- Finds the area under the curve of $f(x)$
- Numerical integration approximates a definite integral using numerical methods, dividing the interval $[a, b]$ into subintervals to approximate the area in each
Newton-Cotes Integration Formulas
- Approximates the integrand $f(x)$ with a polynomial
- Approximates the integral of $f(x)$ with the integral of the polynomial
- The most common are the trapezoidal rule and Simpson's rule
Trapezoidal Rule
- Approximates the integral of $f(x)$ by dividing the area under the curve into trapezoids
- The area of each trapezoid is:
- $A_i = \frac{f(x_i) + f(x_{i+1})}{2} \Delta x$
- The integral is approximated by the sum of the areas of the trapezoids using:
- $\int_a^b f(x) dx \approx \frac{\Delta x}{2} [f(x_1) + 2f(x_2) + 2f(x_3) +... + 2f(x_{n-1}) + f(x_n)]$
Example using the trapezoidal rule of $f(x) = x^2$ from $a = 0$ to $b = 2$ using $n = 4$ subintervals
- The width of each subinterval is $\Delta x = \frac{b - a}{n} = \frac{2 - 0}{4} = 0.5$
- The $x$ values are $x_1 = 0, x_2 = 0.5, x_3 = 1, x_4 = 1.5, x_5 = 2$
- $\int_0^2 x^2 dx \approx \frac{0.5}{2} [0^2 + 2(0.5)^2 + 2(1)^2 + 2(1.5)^2 + 2^2] = 2.75$
- The true solution is $\int_0^2 x^2 dx = \frac{x^3}{3} |_0^2 = \frac{8}{3} = 2.666666667$
Simpson's Rules
- Approximates the integrand $f(x)$ with quadratic polynomials
- Simpson's 1/3 rule approximates the integral of $f(x)$ by dividing the area under the curve into parabolas, using the formula:
- $\int_a^b f(x) dx \approx \frac{\Delta x}{3} [f(x_1) + 4f(x_2) + 2f(x_3) + 4f(x_4) +... + 2f(x_{n-1}) + 4f(x_n) + f(x_{n+1})]$
- $n$ must be even for Simpson's 1/3 rule
- Simpson's 3/8 rule approximates the integral of $f(x)$ by dividing the area under the curve into cubic polynomials, using the formula:
- $\int_a^b f(x) dx \approx \frac{3\Delta x}{8} [f(x_1) + 3f(x_2) + 3f(x_3) + 2f(x_4) + 3f(x_5) + 3f(x_6) + 2f(x_7) +... + f(x_n)]$
- $n$ must be a multiple of 3 for Simpson's 3/8 rule
Example of Simpson's 1/3 rule with $f(x) = x^2$ from $a = 0$ to $b = 2$ using $n = 4$ subintervals
- The width of each subinterval is $\Delta x = \frac{b - a}{n} = \frac{2 - 0}{4} = 0.5$
- The $x$ values are $x_1 = 0, x_2 = 0.5, x_3 = 1, x_4 = 1.5, x_5 = 2$
- $\int_0^2 x^2 dx \approx \frac{0.5}{3} [0^2 + 4(0.5)^2 + 2(1)^2 + 4(1.5)^2 + 2^2] = 2.666666667$
- The true solution is $\int_0^2 x^2 dx = \frac{x^3}{3} |_0^2 = \frac{8}{3} = 2.666666667$
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.