Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system?
What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system?
- To initiate a 'fight or flight' response only
- To control voluntary movements
- To transmit sensory information to the brain
- To regulate involuntary body functions and maintain internal homeostasis (correct)
What is the primary neurotransmitter involved in the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the primary neurotransmitter involved in the sympathetic nervous system?
- Dopamine
- Acetylcholine
- Serotonin
- Norepinephrine (correct)
What is the term for an abnormal sensation of imbalance or movement, or a feeling of falling?
What is the term for an abnormal sensation of imbalance or movement, or a feeling of falling?
- Disorientation
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness (correct)
- Vertigo
What is the term for an illusion of movement, usually a spinning sensation?
What is the term for an illusion of movement, usually a spinning sensation?
What is the primary purpose of the nursing process in caring for patients with neurologic disorders?
What is the primary purpose of the nursing process in caring for patients with neurologic disorders?
What is the term for a posture characterized by adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, and plantar flexion of feet?
What is the term for a posture characterized by adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, and plantar flexion of feet?
What is the primary objective of the health history in neurologic assessment?
What is the primary objective of the health history in neurologic assessment?
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
What is a potential complication for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a goal of nursing care for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a goal of nursing care for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to maintain tissue integrity in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to maintain tissue integrity in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
Why is it important to maintain the patient's dignity and privacy in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
Why is it important to maintain the patient's dignity and privacy in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent aspiration in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent aspiration in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a method to assess fluid status in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a method to assess fluid status in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent corneal irritation in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent corneal irritation in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of immobility in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of immobility in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What should be done to a patient with elevated temperature?
What should be done to a patient with elevated temperature?
Why is it important to monitor bowel movements in a comatose patient?
Why is it important to monitor bowel movements in a comatose patient?
What is the purpose of bladder training program?
What is the purpose of bladder training program?
What is the primary goal of sensory stimulation and communication in a comatose patient?
What is the primary goal of sensory stimulation and communication in a comatose patient?
What happens when there is fluid accumulation or a lesion in the cranial cavity?
What happens when there is fluid accumulation or a lesion in the cranial cavity?
What is the typical respiratory pattern alteration seen in patients with increased ICP?
What is the typical respiratory pattern alteration seen in patients with increased ICP?
What is the role of the family in the care of a comatose patient?
What is the role of the family in the care of a comatose patient?
What is the primary goal of restricting fluids in patients with increased ICP?
What is the primary goal of restricting fluids in patients with increased ICP?
Why is it important to maintain a normal day-night pattern of activity in a comatose patient?
Why is it important to maintain a normal day-night pattern of activity in a comatose patient?
What is the purpose of using a hypothermia blanket in a comatose patient with elevated temperature?
What is the purpose of using a hypothermia blanket in a comatose patient with elevated temperature?
What is the purpose of pupil checks in patients with increased ICP?
What is the purpose of pupil checks in patients with increased ICP?
Which medication is NOT typically used to manage increased ICP?
Which medication is NOT typically used to manage increased ICP?
What is the primary method of invasive monitoring of ICP?
What is the primary method of invasive monitoring of ICP?
What is the typical systolic blood pressure change seen in patients with increased ICP?
What is the typical systolic blood pressure change seen in patients with increased ICP?
What is a potential complication of increased intracranial pressure?
What is a potential complication of increased intracranial pressure?
Which of the following is a major goal of caring for a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
Which of the following is a major goal of caring for a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the recommended range for systolic arterial pressure in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the recommended range for systolic arterial pressure in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
Why is it important to avoid hip flexion in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
Why is it important to avoid hip flexion in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the purpose of using a cervical collar in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the purpose of using a cervical collar in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What should be monitored carefully in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What should be monitored carefully in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
Why is it important to maintain a calm, quiet atmosphere in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
Why is it important to maintain a calm, quiet atmosphere in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What should be avoided in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What should be avoided in a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the primary characteristic of decerebrate posturing?
What is the primary characteristic of decerebrate posturing?
Which diagnostic test is used to visualize the spinal subarachnoid space?
Which diagnostic test is used to visualize the spinal subarachnoid space?
What is the term for a state of unconsciousness, unarousability, and unresponsiveness?
What is the term for a state of unconsciousness, unarousability, and unresponsiveness?
What is the term for a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition to coma?
What is the term for a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition to coma?
What is a potential cause of altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential cause of altered level of consciousness?
What is a common assessment finding in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a common assessment finding in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is the primary purpose of diagnostic tests in neurologic dysfunction?
What is the primary purpose of diagnostic tests in neurologic dysfunction?
What is the term for a posture characterized by flexion of the arms and legs, and plantar flexion of the feet?
What is the term for a posture characterized by flexion of the arms and legs, and plantar flexion of the feet?
What is a primary goal of nursing care for a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a primary goal of nursing care for a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent corneal irritation?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent corneal irritation?
Why is it essential to maintain the patient's dignity and privacy?
Why is it essential to maintain the patient's dignity and privacy?
What is a method to assess fluid status in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a method to assess fluid status in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing goal in the care of patients with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing goal in the care of patients with altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential consequence of immobility in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential consequence of immobility in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to maintain patient safety?
What is a nursing intervention to maintain patient safety?
What is a potential indicator of altered level of consciousness in a patient?
What is a potential indicator of altered level of consciousness in a patient?
What is a primary concern for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a primary concern for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of immobility in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of immobility in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a primary goal of nursing care for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a primary goal of nursing care for a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential indicator of hypermetabolism in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential indicator of hypermetabolism in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of altered nutrition in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential complication of altered nutrition in a patient with an altered level of consciousness?
What is the primary role of the autonomic nervous system in regulating involuntary body functions?
What is the primary role of the autonomic nervous system in regulating involuntary body functions?
What is the primary function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the primary function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is indicated by a decorticate posture in a patient?
What is indicated by a decorticate posture in a patient?
What is the primary goal of the nursing process in caring for patients with neurologic disorders?
What is the primary goal of the nursing process in caring for patients with neurologic disorders?
What is a potential complication of increased intracranial pressure in patients?
What is a potential complication of increased intracranial pressure in patients?
What is the primary purpose of neurologic assessment in patients?
What is the primary purpose of neurologic assessment in patients?
What is the primary goal of care for patients with altered levels of consciousness?
What is the primary goal of care for patients with altered levels of consciousness?
What is the primary role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulating involuntary body functions?
What is the primary role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulating involuntary body functions?
What is the primary purpose of invasive ICP monitoring in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the primary purpose of invasive ICP monitoring in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the term for the respiratory pattern alteration characterized by increasing depth and then decreasing depth of respirations, followed by a period of apnea?
What is the term for the respiratory pattern alteration characterized by increasing depth and then decreasing depth of respirations, followed by a period of apnea?
What is the primary goal of restricting fluids in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the primary goal of restricting fluids in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the term for a triad of symptoms that includes bradycardia, hypertension, and bradypnea?
What is the term for a triad of symptoms that includes bradycardia, hypertension, and bradypnea?
What is the primary purpose of using osmotic diuretics such as mannitol in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the primary purpose of using osmotic diuretics such as mannitol in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the term for the posture characterized by adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, and plantar flexion of feet?
What is the term for the posture characterized by adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, and plantar flexion of feet?
What is a sign of a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a sign of a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing diagnosis for a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing diagnosis for a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a possible behavioral change in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a possible behavioral change in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a possible motor response in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a possible motor response in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a possible complication of immobility in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a possible complication of immobility in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent skin breakdown in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a nursing intervention to prevent skin breakdown in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is the primary characteristic of decerebrate posturing?
What is the primary characteristic of decerebrate posturing?
What is the term for a state of unconsciousness, unarousability, and unresponsiveness?
What is the term for a state of unconsciousness, unarousability, and unresponsiveness?
What is the primary purpose of diagnostic tests in neurologic dysfunction?
What is the primary purpose of diagnostic tests in neurologic dysfunction?
What is the term for a posture characterized by flexion of the arms and legs, and plantar flexion of the feet?
What is the term for a posture characterized by flexion of the arms and legs, and plantar flexion of the feet?
What is a potential cause of altered level of consciousness?
What is a potential cause of altered level of consciousness?
What is the term for a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition to coma?
What is the term for a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition to coma?
What is the primary function of the nervous system?
What is the primary function of the nervous system?
What is a common assessment finding in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is a common assessment finding in a patient with altered level of consciousness?
What is the term for a state of unconsciousness, unarousability, and unresponsiveness?
What is the term for a state of unconsciousness, unarousability, and unresponsiveness?
Which diagnostic test is used to visualize the spinal subarachnoid space?
Which diagnostic test is used to visualize the spinal subarachnoid space?
What is the primary objective of the health history in neurologic assessment?
What is the primary objective of the health history in neurologic assessment?
What is the term for a posture characterized by adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, and plantar flexion of feet?
What is the term for a posture characterized by adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, and plantar flexion of feet?
What is the primary goal of caring for a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the primary goal of caring for a patient with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the purpose of pupil checks in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the purpose of pupil checks in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the primary method of invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure?
What is the primary method of invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure?
What is the typical respiratory pattern alteration seen in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the typical respiratory pattern alteration seen in patients with increased intracranial pressure?
What is the normal range of Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is the normal range of Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is the formula to calculate Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP)?
What is the formula to calculate Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP)?
What is the result of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is the result of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is a common cause of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is a common cause of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is Cushing's Triad characterized by?
What is Cushing's Triad characterized by?
What is a manifestation of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is a manifestation of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is the purpose of invasive monitoring of ICP?
What is the purpose of invasive monitoring of ICP?
What is a complication of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is a complication of increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)?
What is a common manifestation of increased ICP?
What is a common manifestation of increased ICP?
What is the Monro-Kellie hypothesis?
What is the Monro-Kellie hypothesis?
What is a management strategy for increased ICP?
What is a management strategy for increased ICP?
What is autoregulation in the context of cerebral blood flow?
What is autoregulation in the context of cerebral blood flow?
What is a nursing intervention to assess neurologic status?
What is a nursing intervention to assess neurologic status?
What is the purpose of osmotic diuretics in managing increased ICP?
What is the purpose of osmotic diuretics in managing increased ICP?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Complications of Altered Level of Consciousness (LOC)
- Respiratory distress or failure
- Pneumonia
- Aspiration
- Pressure ulcers
- Sepsis
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Contractures
- Disturbed gastrointestinal function
Nursing Care for Patients with Altered LOC
Goals
- Maintenance of clear airway
- Protection from injury
- Attainment of fluid volume balance
- Maintenance of skin integrity
- Absence of corneal irritation
- Effective thermoregulation
- Accurate perception of environmental stimuli
- Maintenance of intact family or support system
- Absence of complications
Interventions
- Maintaining a clear airway
- Frequent monitoring of respiratory status
- Auscultation of lung sounds
- Ensuring patent airway
- Positioning to promote accumulation of secretions
- Suctioning, oral hygiene, and CPT
- Administering oxygen via nasal cannula or non-rebreathing mask
- Maintaining tissue integrity
- Assessing skin frequently
- Frequent turning (every 2 hours)
- Careful positioning in correct body alignment
- Passive ROM
- Use of splints, foam boots, trochanter rolls, and specialty beds
- Cleaning eyes with cotton balls moistened with saline
- Using artificial tears as prescribed
- Maintaining fluid status
- Assessing fluid status by examining tissue turgor and mucosa
- Laboratory test data
- I&O
- Promoting bowel and bladder function
- Assessing for urinary retention and incontinence
- May require indwelling or intermittent catheterization
- Bladder training program
- Assessing for abdominal distention, potential constipation, and bowel incontinence
- Monitoring bowel movements
- Promoting elimination with stool softeners, glycerin suppositories, or enemas as indicated
- Sensory stimulation and communication
- Talking to and touching the patient
- Encouraging family to talk to and touch the patient
- Maintaining normal day–night pattern of activity
- Orienting the patient frequently
- Speaking to the patient, using proper name, introducing self, and explaining all care
Neurologic Dysfunction
Objectives
- Reviewing the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system
- Identifying diagnostic tests used to determine neurologic disorders
- Describing the multiple needs of patients with altered LOC, increased intracranial pressure, and seizures
- Using the nursing process as a framework for care of patients with neurologic disorders
The Nervous System
- Consists of two divisions:
- Central Nervous System (CNS):
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System:
- Cranial Nerve
- Spinal Nerve
- Autonomic and Somatic Systems
- Central Nervous System (CNS):
- Functions to control all motor, sensory, autonomic, cognitive, and behavioral activities
Autonomic Nervous System
- Regulates involuntary body functions
- Maintains and restores internal homeostasis
- Divided into:
- Sympathetic Nervous System:
- "Fight or Flight" responses
- Main neurotransmitter is Norepinephrine
- Parasympathetic Nervous System:
- Controls mostly visceral functions
- Regulated by centers in the spinal cord, brainstem, and hypothalamus
- Sympathetic Nervous System:
Neurologic Assessment
- Health history:
- Pain and seizures
- Dizziness and vertigo
- Visual disturbances
- Weakness
- Abnormal sensations
- Decorticate posture
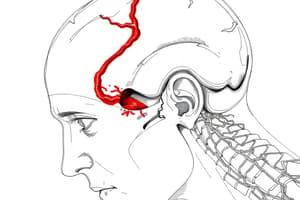
Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
- Compensatory mechanisms:
- Monro-Kellie Hypothesis:
- Limited space in the skull
- Increase in any one component (brain tissue, blood, CSF) causes a change in the volume of the others
- Autoregulation:
- Brain's ability to change the diameter of blood vessels to maintain cerebral blood flow
- CO2 plays a role
- Monro-Kellie Hypothesis:
- Manifestations:
- Late:
- Respiratory and vasomotor changes
- VS: increase in systolic blood pressure, widening of pulse pressure, and slowing of the heart rate
- Temperature increase
- Cushing's Triad: bradycardia, hypertension, bradypnea
- Projectile vomiting
- Further deterioration of LOC
- Hemiplegia, decortication, decerebration, or flaccidity
- Respiratory pattern alterations
- Loss of brainstem reflexes
- Late:
Management of Increased ICP
- Depends on the cause
- Patient requires invasive monitoring of ICP
- Interventions:
- Craniotomy
- Surgical drainage of hematoma or CSF drainage
- Restricting fluids
- Controlling fever
- Maintaining systemic blood pressure
- Oxygenation
- Medications:
- Osmotic diuretics (Mannitol and Dexamethasone)
- GI ulcer prophylactics (Tagamet)
- Anticonvulsants
ICP Monitoring
-
Normal ICP: below 15 mm Hg mean pressure
-
Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP): closely linked to ICP
-
CPP = MAP (mean arterial pressure) - ICP
-
Normal CCP/CPP: 70 to 100
-
CCP/CPP less than 50 results in permanent neurologic damage### Altered Level of Consciousness (LOC)
-
Altered LOC is a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition to coma
-
Coma: unconsciousness, unarousable, unresponsiveness
-
Unconscious state in which the patient is unaware of self or the environment and unresponsive to verbal or painful stimuli
-
Causes of altered LOC: neurologic, toxicologic, or metabolic
-
Patient with altered LOC depends on the nurse for maintenance of all basic human needs
Nursing Process: Assessment
- Assess verbal response and orientation
- Alertness and motor responses
- Respiratory status
- Eye signs and reflexes
- Postures and Glasgow Coma Scale
Nursing Diagnosis
- Ineffective airway clearance
- Risk of injury
- Deficient fluid volume
- Impaired oral mucosa
- Risk for impaired skin integrity and impaired tissue integrity (cornea)
- Ineffective thermoregulation
- Impaired urinary elimination and bowel incontinence
- Disturbed sensory perception
- Interrupted family processes
- Altered Tissue Perfusion
- Risk of Infection
- Altered Nutrition: less than body requirements
Neurologic Assessment
- Decerebrate Posture: extension and internal rotation of the arms, plantar flexion of the feet
- Decorticate Posturing: adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, plantar and feet flexion
Diagnostic Tests of Neurologic Dysfunction
- Computed Tomography Scanning (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Cerebral Angiography
- Myelography (X-ray of spinal subarachnoid space)
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- Lumbar Puncture (LP)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis (CSF)
- Nerve conduction studies
- Neurologic physical examination
Neurologic Dysfunction
- Etiology: Head and Neck Trauma, Meningitis, Encephalitis, Drug Overdose, Toxic Exposure, Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Insulin Shock, Liver Failure, Renal Failure (Uremia), Cardiac Arrest, Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
- Assessment and Diagnostic Findings: Unresponsive to voice and pain, Dilated or pinpoint pupils, Fixed pupils, Involuntary movements, Flaccidity or rigidity of muscles
Management of Patients with Neurologic Dysfunction
- Increase Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
- Objectives: Review the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system, Identify the diagnostic tests used to determine neurologic disorders, Describe the multiple needs of the patients with altered level of consciousness, increased ICP, and seizures in terms of their clinical manifestation, complications, and medical and nursing management
Neurological Dysfunction
- The nervous system consists of two divisions: Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System
- The function of the nervous system is to control all Motor, Sensory, Autonomic, Cognitive, and Behavioral Activities
Autonomic Nervous System
- Regulates involuntary body functions
- Its function is to regulate activities of internal organs and to maintain and restore internal homeostasis
- Sympathetic Nervous System: "Fight or Flight" responses, Main neurotransmitter is Norepinephrine
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Controls mostly visceral functions, Regulated by centers in the spinal cord, brainstem, and hypothalamus
Neurologic Assessment: Health History
- Pain and Seizures
- Dizziness and Vertigo
- Visual disturbances
- Weakness
- Abnormal sensations
- Decorticate Posture: adduction and flexion of upper extremities, internal rotation of legs, plantar and feet flexion
Manifestations of Increased ICP: Late
- Respiratory and Vasomotor changes
- VS: Increase in systolic blood pressure, widening of pulse pressure, and slowing of the heart rate; pulse may fluctuate rapidly from tachycardia to bradycardia; temperature increase
- Cushing's Triad: Bradycardia, Hypertension, Bradypnea
- Projectile vomiting
- Further deterioration of LOC; stupor to coma
- Hemiplegia, decortication, decerebration, or flaccidity
- Respiratory pattern alterations including Cheyne-Stokes breathing and arrest
- Loss of brainstem reflexes: pupil, gag, corneal, and swallowing
Management of Increased ICP
- Depends on cause
- Patient requires invasive monitoring of ICP
- ICP Monitoring: Craniotomy, Surgical drainage of hematoma, or CSF drainage (ventricular; continuous or intermittent) or Lumbar (intrathecal)
- Restricting Fluids
- Controlling Fever
- Maintaining Systemic BP
- Oxygenation
- Medications: Osmotic Diuretics, GI ulcer prophylactics, Anticonvulsants
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.