Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the functional significance of fibers crossing the midline in the habenular commissure?
What is the functional significance of fibers crossing the midline in the habenular commissure?
- Enabling independent control of each limb, unaffected by the other side.
- Connecting olfactory, visceral, and somatic afferent pathways from both sides of the brain. (correct)
- Integrating somatosensory information exclusively from the face.
- Facilitating direct motor control from one hemisphere to the other.
Lesions in which area of the diencephalon would most likely result in the disruption of circadian rhythms?
Lesions in which area of the diencephalon would most likely result in the disruption of circadian rhythms?
- Pineal gland (correct)
- Subthalamus
- Mammillary bodies
- Habenular nuclei
Why would damage to the thalamus result in significant loss of cerebral function?
Why would damage to the thalamus result in significant loss of cerebral function?
- It serves as a key relay station for sensory information (excluding olfaction) to the cerebral cortex. (correct)
- It serves both hemispheres equally; damaging it removes redundancy.
- It directly controls motor output to the peripheral nervous system.
- It integrates cortical processing with other brain areas.
How does the pineal gland influence the function of the anterior pituitary gland?
How does the pineal gland influence the function of the anterior pituitary gland?
What functional deficits would most likely be observed in a patient with a lesion restricted to the subthalamic nucleus?
What functional deficits would most likely be observed in a patient with a lesion restricted to the subthalamic nucleus?
Based on their anatomical location, which of the following structures is most vulnerable to compression by a tumor in the sella turcica?
Based on their anatomical location, which of the following structures is most vulnerable to compression by a tumor in the sella turcica?
What is the primary functional consequence of damage to the internal capsule?
What is the primary functional consequence of damage to the internal capsule?
What is the most direct functional consequence of severing the corpus callosum?
What is the most direct functional consequence of severing the corpus callosum?
Which cellular change would most likely cause Alzheimer plaques?
Which cellular change would most likely cause Alzheimer plaques?
Following a traumatic brain injury, a patient exhibits a complete loss of sensation on the left side of their body. Imaging reveals damage primarily to a specific structure within the diencephalon. What structure is most likely damaged?
Following a traumatic brain injury, a patient exhibits a complete loss of sensation on the left side of their body. Imaging reveals damage primarily to a specific structure within the diencephalon. What structure is most likely damaged?
A patient presents with violent, involuntary movements confined to the right arm and leg. What specific area of the brain is most likely affected?
A patient presents with violent, involuntary movements confined to the right arm and leg. What specific area of the brain is most likely affected?
A 50-year-old patient reports progressive memory loss and disorientation, along with personality changes. A PET scan reveals diminished cortical metabolism. Which neurotransmitter is suspected to be the cause?
A 50-year-old patient reports progressive memory loss and disorientation, along with personality changes. A PET scan reveals diminished cortical metabolism. Which neurotransmitter is suspected to be the cause?
In a patient undergoing treatment for hydrocephalus, a shunt is placed to bypass a blockage in the interventricular foramen. Where will this shunt directly drain excess cerebrospinal fluid?
In a patient undergoing treatment for hydrocephalus, a shunt is placed to bypass a blockage in the interventricular foramen. Where will this shunt directly drain excess cerebrospinal fluid?
After a stroke, a patient is unable to recognize objects placed in their left hand while their vision is occluded, yet can identify the same objects with their right hand. Where is the stroke most likely located?
After a stroke, a patient is unable to recognize objects placed in their left hand while their vision is occluded, yet can identify the same objects with their right hand. Where is the stroke most likely located?
A researcher is studying the effects of a novel drug on the habenular nuclei in rats. If the drug successfully targets its intended area, which of the following structures would be expected to show altered activity?
A researcher is studying the effects of a novel drug on the habenular nuclei in rats. If the drug successfully targets its intended area, which of the following structures would be expected to show altered activity?
A neurosurgeon is planning a surgical approach to remove a tumor located near the pineal gland. What is the most important consideration in order to avoid damaging structures critical for the pupillary light reflex?
A neurosurgeon is planning a surgical approach to remove a tumor located near the pineal gland. What is the most important consideration in order to avoid damaging structures critical for the pupillary light reflex?
During a neurological exam, a physician observes that the patient has difficulty with fine motor movements and displays signs of spasticity. Which pathway from the internal capsule has most likely been affected?
During a neurological exam, a physician observes that the patient has difficulty with fine motor movements and displays signs of spasticity. Which pathway from the internal capsule has most likely been affected?
What clinical observations would most strongly suggest a lesion affecting the uncinate fasciculus in the brain?
What clinical observations would most strongly suggest a lesion affecting the uncinate fasciculus in the brain?
A patient undergoing neurosurgical intervention suddenly develops a fever, becomes hypertensive, and exhibits abnormal posturing. Where is the lesion likely affecting?
A patient undergoing neurosurgical intervention suddenly develops a fever, becomes hypertensive, and exhibits abnormal posturing. Where is the lesion likely affecting?
A patient with an interruption to the medial longitudinal stria exhibits dysfunction in which area?
A patient with an interruption to the medial longitudinal stria exhibits dysfunction in which area?
Damage to the splenium of the corpus callosum creates issues with which kind of tasks?
Damage to the splenium of the corpus callosum creates issues with which kind of tasks?
What key structure must a neurosurgeon be concerned with damaging when performing a surgery near the foramen of Monro?
What key structure must a neurosurgeon be concerned with damaging when performing a surgery near the foramen of Monro?
You have a patient with damage to the splenium of the corpus callosum. What side of the brain is the information unable to reach if you hold an item in the patient's left hand?
You have a patient with damage to the splenium of the corpus callosum. What side of the brain is the information unable to reach if you hold an item in the patient's left hand?
Given that the mammillary bodies possess a central core of gray matter, what kind of cells do you also expect to see in the surrounding areas?
Given that the mammillary bodies possess a central core of gray matter, what kind of cells do you also expect to see in the surrounding areas?
If you were to inject a dye into the lateral ventricle, what is the next site you would expect to find the dye if all structures are functioning correctly?
If you were to inject a dye into the lateral ventricle, what is the next site you would expect to find the dye if all structures are functioning correctly?
Given the components of the epithalamus, what do you expect to see elevated with limited light exposure?
Given the components of the epithalamus, what do you expect to see elevated with limited light exposure?
What is the purpose of the precentral gyrus, and where can you expect to find sensory input?
What is the purpose of the precentral gyrus, and where can you expect to find sensory input?
What is the key property of the central sulcus, and what gyri does it connect?
What is the key property of the central sulcus, and what gyri does it connect?
Given the key role of the thalamus, what area is it in direct communication with?
Given the key role of the thalamus, what area is it in direct communication with?
What clinical observations would arise with a lesion to the pulvinar?
What clinical observations would arise with a lesion to the pulvinar?
What is the function of the lentiform nucleus, and what properties does it have?
What is the function of the lentiform nucleus, and what properties does it have?
What is true of the Tela Choroidea, and where is it located?
What is true of the Tela Choroidea, and where is it located?
If it was observed that a patient has olfactory disruptions, what nuclei is damaged?
If it was observed that a patient has olfactory disruptions, what nuclei is damaged?
Where could you expect the red nucleus to be found?
Where could you expect the red nucleus to be found?
What are the major components of the corpus striatum? What can be said about it?
What are the major components of the corpus striatum? What can be said about it?
In Alzheimer's patients, which areas show effects of neuron death?
In Alzheimer's patients, which areas show effects of neuron death?
Which area of the brain if destroyed shows no sign or symptom?
Which area of the brain if destroyed shows no sign or symptom?
Which aspect of the diencephalon's structure facilitates the crossing of nerve fibers for functional integration?
Which aspect of the diencephalon's structure facilitates the crossing of nerve fibers for functional integration?
How does the hypothalamic sulcus contribute to the functional organization of the diencephalon?
How does the hypothalamic sulcus contribute to the functional organization of the diencephalon?
What is the functional consequence of the pineal gland releasing melatonin into the third ventricle?
What is the functional consequence of the pineal gland releasing melatonin into the third ventricle?
What is the significance of the internal capsule's close relationship to the lentiform nucleus in terms of potential clinical outcomes?
What is the significance of the internal capsule's close relationship to the lentiform nucleus in terms of potential clinical outcomes?
How would severing the stria medullaris thalami impact the function of the habenular nucleus?
How would severing the stria medullaris thalami impact the function of the habenular nucleus?
How does the unique structural characteristic of the pineal gland influence its endocrine function?
How does the unique structural characteristic of the pineal gland influence its endocrine function?
What is the functional relevance of the connections between the subthalamic nucleus and the corpus striatum?
What is the functional relevance of the connections between the subthalamic nucleus and the corpus striatum?
Why is the thalamus considered a critical structure for overall cerebral function, and what broad deficits arise from its damage?
Why is the thalamus considered a critical structure for overall cerebral function, and what broad deficits arise from its damage?
How does the position of the optic chiasma relative to the hypophysis inform treatment considerations for pituitary tumors?
How does the position of the optic chiasma relative to the hypophysis inform treatment considerations for pituitary tumors?
What is the probable outcome of a lesion affecting the habenular commissure?
What is the probable outcome of a lesion affecting the habenular commissure?
If an obstruction occurs at the interventricular foramen, what consequences would accurately describe downstream effects?
If an obstruction occurs at the interventricular foramen, what consequences would accurately describe downstream effects?
If a patient has damage to the medial longitudinal stria, what would be the most likely result?
If a patient has damage to the medial longitudinal stria, what would be the most likely result?
How do the commissure fibers facilitate communication between cortical regions?
How do the commissure fibers facilitate communication between cortical regions?
Which symptom is LEAST likely to indicate issues with the hypothalamus?
Which symptom is LEAST likely to indicate issues with the hypothalamus?
How does the corona radiata contribute functionally to cerebral activity?
How does the corona radiata contribute functionally to cerebral activity?
What role does the tela choroidea play in maintaining CSF balance?
What role does the tela choroidea play in maintaining CSF balance?
How does the relative surface area of gyri and sulci impact cerebral cortex function?
How does the relative surface area of gyri and sulci impact cerebral cortex function?
While performing a surgery, what structure's location is most sensitive to damage when performing surgery near foramen Monoro leading to acute hydrocephalus?
While performing a surgery, what structure's location is most sensitive to damage when performing surgery near foramen Monoro leading to acute hydrocephalus?
In the context of cerebral anatomy, what implication does the organization of white matter have for recovery after stroke?
In the context of cerebral anatomy, what implication does the organization of white matter have for recovery after stroke?
The optic chiasm intersects which area?
The optic chiasm intersects which area?
Damage to the splenium has implications for information traveling between which two lobes?
Damage to the splenium has implications for information traveling between which two lobes?
Compared to an adult patient with the same pineal tumor, what unique symptom might be noticed more readily in a child?
Compared to an adult patient with the same pineal tumor, what unique symptom might be noticed more readily in a child?
A patient presents with the clinical signs of Kluver-Bucy Syndrome along with olfactory hallucinations. What area is most likely to be impacted?
A patient presents with the clinical signs of Kluver-Bucy Syndrome along with olfactory hallucinations. What area is most likely to be impacted?
Which condition may arise from disruption to the anterior/posterior commisures?
Which condition may arise from disruption to the anterior/posterior commisures?
A tumor on the thalamus can affect which area?
A tumor on the thalamus can affect which area?
The Lentiform nucleus is related through ____ to the ______?
The Lentiform nucleus is related through ____ to the ______?
What is a typical symptom that might arise from a damaged caudate nucleus?
What is a typical symptom that might arise from a damaged caudate nucleus?
The frontal lobe is subdivided into superior, middle, and inferior by two ____?
The frontal lobe is subdivided into superior, middle, and inferior by two ____?
The most inferior aspect of the diencephalon's inferior surface is the?
The most inferior aspect of the diencephalon's inferior surface is the?
What feature is related to a patient's thalamus?
What feature is related to a patient's thalamus?
What function would be impacted with issues at tectum of the midbrain?
What function would be impacted with issues at tectum of the midbrain?
How does the blood drain into the tela choroidea and into the ventricles?
How does the blood drain into the tela choroidea and into the ventricles?
If a patient presented with a severe head trauma, what structure would a doctor check given its association to the pineal stalk?
If a patient presented with a severe head trauma, what structure would a doctor check given its association to the pineal stalk?
How can the pituitary compress the optic chiasma, and what symptom is a key indicator?
How can the pituitary compress the optic chiasma, and what symptom is a key indicator?
What provides support and insulation for fibers?
What provides support and insulation for fibers?
A tumor affecting the epithalamus would directly impact which of the following?
A tumor affecting the epithalamus would directly impact which of the following?
What challenge would a neurologist face when diagnosing a lesion strictly confined to the claustrum?
What challenge would a neurologist face when diagnosing a lesion strictly confined to the claustrum?
Disruption to the blood supply of the tela choroidea would most significantly affect the:
Disruption to the blood supply of the tela choroidea would most significantly affect the:
What unique functional role does the anterior commissure play in facilitating interhemispheric communication?
What unique functional role does the anterior commissure play in facilitating interhemispheric communication?
A lesion affecting the subthalamic nucleus is most likely to produce:
A lesion affecting the subthalamic nucleus is most likely to produce:
What anatomical concept explains why a small hemorrhage in the internal capsule can produce widespread contralateral effects?
What anatomical concept explains why a small hemorrhage in the internal capsule can produce widespread contralateral effects?
What best describes the anatomical organization of the cerebral cortex?
What best describes the anatomical organization of the cerebral cortex?
In what manner does the pineal gland mediate its inhibitory effects on the pituitary gland?
In what manner does the pineal gland mediate its inhibitory effects on the pituitary gland?
If a patient was undergoing neurological decline, what findings during a brain scan would be most suggestive of Alzheimer's pathology?
If a patient was undergoing neurological decline, what findings during a brain scan would be most suggestive of Alzheimer's pathology?
What is the functional significance of the interthalamic connection?
What is the functional significance of the interthalamic connection?
How might damage to the mammillary bodies impact behavior?
How might damage to the mammillary bodies impact behavior?
A lesion confined to the fornix would most directly disrupt:
A lesion confined to the fornix would most directly disrupt:
Given the anatomical relationship of structures on the inferior surface of the diencephalon, what is a potential risk of an expanding pituitary tumor?
Given the anatomical relationship of structures on the inferior surface of the diencephalon, what is a potential risk of an expanding pituitary tumor?
What distinguishes the calcarine sulcus from other major sulci of the cerebral cortex regarding its function?
What distinguishes the calcarine sulcus from other major sulci of the cerebral cortex regarding its function?
In an individual affected by hydrocephalus due to a blockage near the interventricular foramen, what indirect affect could stem from this event?
In an individual affected by hydrocephalus due to a blockage near the interventricular foramen, what indirect affect could stem from this event?
Surgical intervention targeting the pineal gland carries increased risk to what neurological function?
Surgical intervention targeting the pineal gland carries increased risk to what neurological function?
What is the primary anatomical distinction between the long and short association fibers in the cerebrum?
What is the primary anatomical distinction between the long and short association fibers in the cerebrum?
When examining a horizontal section of the brain, what key anatomical feature helps distinguish the lentiform nucleus from the caudate nucleus?
When examining a horizontal section of the brain, what key anatomical feature helps distinguish the lentiform nucleus from the caudate nucleus?
Why is the lateral sulcus a critical landmark for regional localization in the cerebrum?
Why is the lateral sulcus a critical landmark for regional localization in the cerebrum?
What is the primary mechanism by which lesions in the thalamus result in significant loss of cerebral function?
What is the primary mechanism by which lesions in the thalamus result in significant loss of cerebral function?
What role do the habenular nuclei and commissure play in the broader context of diencephalic function?
What role do the habenular nuclei and commissure play in the broader context of diencephalic function?
What distinguishes the functional organization of motor areas in the gyrus anterior to the central sulcus?
What distinguishes the functional organization of motor areas in the gyrus anterior to the central sulcus?
What constitutes the anatomical basis for the clinical sign of headache aggravation with changing head position in patients with a colloid cyst of the third ventricle?
What constitutes the anatomical basis for the clinical sign of headache aggravation with changing head position in patients with a colloid cyst of the third ventricle?
What is the relationship between melatonin production within the pineal gland and sleep disorders?
What is the relationship between melatonin production within the pineal gland and sleep disorders?
Following a stroke, which describes the significance of white matter organization for potential recovery?
Following a stroke, which describes the significance of white matter organization for potential recovery?
What impact does substantial damage to the hippocampus have on areas within the cerebral cortex?
What impact does substantial damage to the hippocampus have on areas within the cerebral cortex?
What critical function is uniquely served by the cerebral commissures, and what is the major structure?
What critical function is uniquely served by the cerebral commissures, and what is the major structure?
In what way does the hypothalamus influence the function of peripheral endocrine glands?
In what way does the hypothalamus influence the function of peripheral endocrine glands?
The telencephalon forms the central core of the cerebrum, while the diencephalon forms the cerebral hemispheres.
The telencephalon forms the central core of the cerebrum, while the diencephalon forms the cerebral hemispheres.
The diencephalon is symmetrically divided by the tentorium cerebelli.
The diencephalon is symmetrically divided by the tentorium cerebelli.
The hypothalamus integrates autonomic and endocrine functions, playing a key role in maintaining homeostasis.
The hypothalamus integrates autonomic and endocrine functions, playing a key role in maintaining homeostasis.
Damage solely to the thalamus does not typically result in significant loss of cerebral function.
Damage solely to the thalamus does not typically result in significant loss of cerebral function.
The inferior surface of the diencephalon is entirely concealed within the intact brain.
The inferior surface of the diencephalon is entirely concealed within the intact brain.
The interthalamic connection always exists as a large, solid structure connecting the two halves of the thalamus.
The interthalamic connection always exists as a large, solid structure connecting the two halves of the thalamus.
Unlike other sensory pathways, the olfactory pathway directly involves the thalamus as a key relay station.
Unlike other sensory pathways, the olfactory pathway directly involves the thalamus as a key relay station.
The corpora quadrigemina are part of the diencephalon.
The corpora quadrigemina are part of the diencephalon.
The internal capsule is a nucleus.
The internal capsule is a nucleus.
The interventricular foramina facilitate communication between the third ventricle and the cerebral aqueduct.
The interventricular foramina facilitate communication between the third ventricle and the cerebral aqueduct.
The hypothalamus is located dorsal to the thalamus.
The hypothalamus is located dorsal to the thalamus.
The anterior commissure connects the cerebral hemispheres and is larger than the corpus callosum.
The anterior commissure connects the cerebral hemispheres and is larger than the corpus callosum.
The precentral gyrus, responsible for somatic sensation, is located posterior to the central sulcus.
The precentral gyrus, responsible for somatic sensation, is located posterior to the central sulcus.
The Pineal gland possesses a functional blood-brain barrier.
The Pineal gland possesses a functional blood-brain barrier.
The calcarine sulcus is primarily located on the lateral surface of the hemisphere.
The calcarine sulcus is primarily located on the lateral surface of the hemisphere.
Association fibers connect the cortex to the brain stem.
Association fibers connect the cortex to the brain stem.
Concretions of calcified material called brain sand progressively accumulate within the pineal gland with age.
Concretions of calcified material called brain sand progressively accumulate within the pineal gland with age.
The hypothalamus controls the functions of the somatic nervous system.
The hypothalamus controls the functions of the somatic nervous system.
The optic chiasm is strictly related to vision and serves no part in hormonal regulation.
The optic chiasm is strictly related to vision and serves no part in hormonal regulation.
The fornix is mainly composed of sensory nerve fibers.
The fornix is mainly composed of sensory nerve fibers.
Match the following diencephalon structures with their relative position:
Match the following diencephalon structures with their relative position:
Match each cerebral lobe with its primary function/location:
Match each cerebral lobe with its primary function/location:
Match each component of the basal nuclei with its description:
Match each component of the basal nuclei with its description:
Match each part of the corpus callosum with its description:
Match each part of the corpus callosum with its description:
Match the ventricle walls with their boundaries:
Match the ventricle walls with their boundaries:
Match the structures with the features located on the inferior surface of the diencephalon:
Match the structures with the features located on the inferior surface of the diencephalon:
Match the sulci with the areas they separate:
Match the sulci with the areas they separate:
Match the commissure fibers to their correct definition:
Match the commissure fibers to their correct definition:
Match the following internal capsule structures with their anatomical relationships:
Match the following internal capsule structures with their anatomical relationships:
Match the conditions with the affected areas:
Match the conditions with the affected areas:
Flashcards
Cerebrum
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain, located in the anterior and middle cranial fossae.
Diencephalon
Diencephalon
Central core of the cerebrum, includes the third ventricle.
Telencephalon
Telencephalon
Forms the cerebral hemispheres.
Gross Features of the Diencephalon
Gross Features of the Diencephalon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Ventricle
Third Ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Four Parts of Diencephalon
Four Parts of Diencephalon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thalamus
Thalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subthalamic Nucleus
Subthalamic Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Habenular Nucleus
Habenular Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Habenular Nucleus function
Habenular Nucleus function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pineal Gland's Role
Pineal Gland's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preoptic Area
Preoptic Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Chiasma
Optic Chiasma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tuber Cinereum
Tuber Cinereum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammillary Bodies
Mammillary Bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Ventricle
Third Ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lamina Terminalis
Lamina Terminalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior wall of third ventricle
Posterior wall of third ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral wall of third ventricle
Lateral wall of third ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior wall of third ventricle
Inferior wall of third ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Longitudinal Cerebral Fissure
Longitudinal Cerebral Fissure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Callosum
Corpus Callosum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Falx Cerebri
Falx Cerebri
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Lobes
Cerebral Lobes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precentral Gyrus
Precentral Gyrus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Sulcus
Lateral Sulcus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parieto-occipital Sulcus
Parieto-occipital Sulcus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcarine Sulcus
Calcarine Sulcus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frontal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Callosum (medial)
Corpus Callosum (medial)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cingulate Gyrus
Cingulate Gyrus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paracentral Lobule
Paracentral Lobule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precuneus
Precuneus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cuneus
Cuneus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collateral Sulcus
Collateral Sulcus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Colloid Cyst Headache
Colloid Cyst Headache
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Hemisphere Components
Cerebral Hemisphere Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior Surface of Hypothalamus
Inferior Surface of Hypothalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fornix
Fornix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stria Medullaris Thalami
Stria Medullaris Thalami
Signup and view all the flashcards
Habenular Commissure
Habenular Commissure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Commissure
Posterior Commissure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Sand
Brain Sand
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pineal Gland Secretions
Pineal Gland Secretions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uncinate Fasciculus
Uncinate Fasciculus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cingulum
Cingulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Capsule
Internal Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Commissure Fibers
Commissure Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Association fibers
Association fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Projection Fibers
Projection Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Forceps Minor
Forceps Minor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Forceps Major
Forceps Major
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stria Terminalis
Stria Terminalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Surface of Diencephalon
Lateral Surface of Diencephalon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveus
Alveus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caudate Nucleus
Caudate Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Capsule Hemorrhage
Internal Capsule Hemorrhage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lentiform Nucleus
Lentiform Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Claustrum Location
Claustrum Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amygdaloid Nucleus
Amygdaloid Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genu Location
Genu Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rostrum Description
Rostrum Description
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Hemispheres Internal Structure
Cerebral Hemispheres Internal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Ventricles Definition
Lateral Ventricles Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Striatum
Corpus Striatum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Capsule Function
Internal Capsule Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corona Radiata
Corona Radiata
Signup and view all the flashcards
Commissure Fibers Function
Commissure Fibers Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus
Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Hemispheres
Cerebral Hemispheres
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithalamus
Epithalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fornix Composition
Fornix Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subthalamus location hint
Subthalamus location hint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Capsule positioning
Internal Capsule positioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cerebrum Objectives
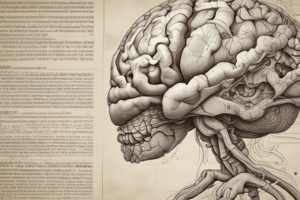
- Introduction targets complexities of the forebrain, defining the diencephalon, accurately locating the thalamus and hypothalamus through brain section study, understanding ascending/descending tract positions, and highlighting pathologic site—internal capsule. The internal capsule is a frequent target of pathologic lesions.
Colloid Cyst Case
- A 23-year-old man shows intermittent headaches, dizziness, left leg weakness/numbness, aggravated by head movement.
- CT scan detects a small, white, opaque ball at the anterior of the third ventricle.
- Resulting diagnosis: colloid cyst of the third ventricle.
- Headache aggravation stems from cyst mobility within the choroid plexus; head repositioning blocks the foramen of Monro, raising intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus.
- Left leg weakness/numbness arises from tumor pressure on the right thalamus and tracts in the right internal capsule.
- Successfully treated via surgical excision of tumor.
General Info
- Cerebral hemispheres originate from the telencephalon and compose the largest brain portion.
- Each hemisphere includes a gray matter cortex, internal gray matter masses (basal nuclei), plus a lateral ventricle.
- Knowledge of anatomical structure is necessary for comprehending complexities tied to functional localization.
Divisions
- The cerebrum is the brain's largest part, located in the anterior and middle cranial fossae, filling the vault concavity.
- Divisible into the diencephalon (central core) and telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres).
Diencephalon makeup and boundaries
- Features the third ventricle and its bounding structures.
- It spans between the cerebral aqueduct posteriorly and interventricular foramina anteriorly.
- Structure arrangement is symmetrical, midline, split into right and left halves.
- Subdivisions are for convenience, nerve fibers freely cross boundaries for functional integration. It is continuous with the cerebral aqueduct
Basic features
- Only area seen on the intact brain's surface is the diencephalon's inferior surface.
- It is formed by hypothalamic structures that feature, anterior to posterior: Optic chiasma with optic tracts, the infundibulum with the tuber cinereum, and mammillary bodies.
- The superior surface is hidden by the fornix (fiber bundle from hippocampus arching over the thalamus to join the mammillary body).
Diencephalon Walls
- Consists of an ependyma layer continuous with the third ventricle
- Superiorly covered by a vascular pia mater fold (tela choroidea of the third ventricle).
- Choroid plexuses of the third ventricle project downward from midline to cavity.
- The lateral surface is defined by the internal capsule (white matter) that conveys connective nerve fibers.
- The medial surface is split in half vertically to mirror each other.
- There are a number of components to the medial surface (lateral wall), and a shallow Sulcus called the hypothalamic sulcus lies at the boundary.
- Superior regions of the medial surface features the Thalamus
- Inferiorly features the hypothalamus
- The stria medullaris thalami runs along the superior margin of the medial surface.
- The diencephalon is divided into; thalamus, subthalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus
Thalamus Facts
- The thalamus is a large egg-shaped gray matter mass.
- It makes up most of the Diencephalon.
- The thalamus relays cells to all sensory parts of your body.
- Olfactory is the only region not relayed by the thalamus.
- Relays information to the cerebral cortex while working closely with the cortex to do other key functions.
- It is a sensory cell station.
- Activities involve integration and relay to cortex and many subcortical areas.
- It plays a role in somatic (body) and visceral (organ) functions.
Internal anatomy
- The caudate nucleus, Then thalamus, lastly hippocampus.
- The claustrum is a fine sheet of gray matter that lines the external surface.
- The main nerve that runs through the cerebrum is the white nervous tissue.
- The white matter has 3 categories; connections with the Commisural fibers, Assocication fibres, Projection fibres.
- Commisural Fibres essentially connects all hemisphere regions
- Ex; corpus callosum
- Ex; anterior commisure
- Ex; posterior commisure
- Ex; fornix
- ex; habenular commisure
- Commisural Fibres essentially connects all hemisphere regions
- The corpus callosum is the main major connection of the 2 brain sections.
- Has Rostrum sections
- Has a Genu secton
- Body segments
- And splenium
- Has Rostrum sections
- Rostrum fibres extend anteriorly
- The Genu Curves anteriorily
- the fibers form into the forceps Minor.
- Main body fibers are bundles of radiata. - These bodies go to the cerebral cortex. - Some fibers that make up the interior lateral walls, and lateral vertriciles
- these are called the tapedum
- lateral fibers in splenium arch backward into occipital lobe and are called Forceps Major
- anterior commisure, small nerve with fibers along midline on lamina terminalis
- Some fibers curve back from sides by grooving inferior lentiorm nucleus.
- bundle connect to the Para sympathetic in oculomotor nuclei.
- anterior commisure, small nerve with fibers along midline on lamina terminalis
<new_section>
###White Matter
- White matter has myelinated fibers, and are supported by neuroglia. Three connection types:
- Commissural Fibers
- Association Fibers
- Projection Fibers.
###Commissure Fibers
- Connect corresponding areas of the two hemispheres including, corpus callosum, anterior commissure, posterior commissure, along with the fornix and the habenular commissure.
- Corpus callosum description: largest brain commissure links the cerebral hemispheres, lies at the base, featuring Rostrum, Genu, Body and Splenium.
- Fibers in the Rostrum extend anteriorly.
- Fibers in the Genu curve anteriorly forming Forceps Minor.
- The fibers of the body extend laterally forming the corona radiata, intersecting association and projection fibers en route to the cerebral cortex.
- Fibers create the roof and lateral wall of the ventricles
- tapetum fibers
- The lateral fibers in splenium curve back to to the occipital lobe - Forceps Major
- Anterior commissure is small nerve, features fiber midline on lamina terminalis.
- Fibres curve back from sides by grooving inferior lentiform nucleus, bundle connects to the parasympathetic in oculomotor nuclei.
- Commissure fibers connect symmetrical brain regions through corpus callosum, anterior commissure, posterior commissure, fornix, and habenular commissure.
- The anterior commissure sends fibers towards temporal lobes The Claustrum is a thin grey layer on the outer surface of of the Lentiform Nucleus </new_section>
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.