Podcast
Questions and Answers
What critical process is disrupted in utero that leads to neural tube disorders?
What critical process is disrupted in utero that leads to neural tube disorders?
- The growth of limbs.
- The development of the heart.
- The folding of the flat plate to form the brain and spinal cord. (correct)
- The formation of the skull.
A pregnant woman with a family history of neural tube defects is planning her prenatal care. What would be the most relevant recommendation regarding her diet?
A pregnant woman with a family history of neural tube defects is planning her prenatal care. What would be the most relevant recommendation regarding her diet?
- Ensure adequate intake of folate (vitamin B-9). (correct)
- Limit sodium consumption.
- Eat more protein sources.
- Increase intake of calcium-rich foods.
In anencephaly, which part of the developing fetus is absent?
In anencephaly, which part of the developing fetus is absent?
- Cerebellum
- Brainstem
- Cerebral hemispheres (correct)
- Spinal cord
Why is labor often prolonged in cases of anencephaly?
Why is labor often prolonged in cases of anencephaly?
What clinical finding would suggest anencephaly during a prenatal screening?
What clinical finding would suggest anencephaly during a prenatal screening?
What is the standard treatment approach for anencephaly?
What is the standard treatment approach for anencephaly?
The fetal brain of infants with microcephaly deviates from normal on the growth chart by how many standard deviations?
The fetal brain of infants with microcephaly deviates from normal on the growth chart by how many standard deviations?
Which of the following intrauterine infections is associated with microcephaly?
Which of the following intrauterine infections is associated with microcephaly?
A child is diagnosed with microcephaly shortly after birth. What aspect of the child's development is most likely to be affected?
A child is diagnosed with microcephaly shortly after birth. What aspect of the child's development is most likely to be affected?
What is the primary focus of treatment for a child with microcephaly?
What is the primary focus of treatment for a child with microcephaly?
Which of the following best describes the primary defect in spina bifida?
Which of the following best describes the primary defect in spina bifida?
Spina Bifida is identified as a 'midline closure disorder', which other condition also falls under this classification?
Spina Bifida is identified as a 'midline closure disorder', which other condition also falls under this classification?
What characteristic is most associated with spina bifida occulta?
What characteristic is most associated with spina bifida occulta?
Where does nonclosure or incomplete closure of the posterior portion of the vertebrae typically occur in spina bifida occulta?
Where does nonclosure or incomplete closure of the posterior portion of the vertebrae typically occur in spina bifida occulta?
What physical sign might suggest spina bifida occulta, even in the absence of other symptoms?
What physical sign might suggest spina bifida occulta, even in the absence of other symptoms?
Why might a child with spina bifida occulta require surgery during adolescence?
Why might a child with spina bifida occulta require surgery during adolescence?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of meningocele?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of meningocele?
What action needs to be taken to minimize potential deficits when a patient is diagnosed with meningocele?
What action needs to be taken to minimize potential deficits when a patient is diagnosed with meningocele?
A newborn is diagnosed with myelomeningocele. What is the most critical risk associated with this condition?
A newborn is diagnosed with myelomeningocele. What is the most critical risk associated with this condition?
A higher anomaly in myelomeningocele typically correlates with what?
A higher anomaly in myelomeningocele typically correlates with what?
A newborn has myelomeningocele with accompanying leg and food disabilities. Which disability are they likely to have?
A newborn has myelomeningocele with accompanying leg and food disabilities. Which disability are they likely to have?
What is the primary surgical goal in the initial treatment of myelomeningocele?
What is the primary surgical goal in the initial treatment of myelomeningocele?
What outcome is predicted in a child that has myelomeningocele, despite surgical measures?
What outcome is predicted in a child that has myelomeningocele, despite surgical measures?
In cases of encephalocele, what best describes the covering of the sac-like protrusion?
In cases of encephalocele, what best describes the covering of the sac-like protrusion?
In what area of the skull does encephalocele most often occur?
In what area of the skull does encephalocele most often occur?
What is a clinical method used to diagnose encephalocele?
What is a clinical method used to diagnose encephalocele?
What is the primary goal of immediate surgery for encephalocele?
What is the primary goal of immediate surgery for encephalocele?
A woman is taking medication for a bipolar disorder. Which medication can cause NTD when taken during pregnancy?
A woman is taking medication for a bipolar disorder. Which medication can cause NTD when taken during pregnancy?
Folate, the natural form of vitamin B-9, can help aid in what?
Folate, the natural form of vitamin B-9, can help aid in what?
When do experts recommend folate consumption?
When do experts recommend folate consumption?
Women with a history of NTD should take what folate dosage?
Women with a history of NTD should take what folate dosage?
What maternal factors increase the risk of neural tube defects?
What maternal factors increase the risk of neural tube defects?
What diagnostic tests are used to diagnosis NTDs?
What diagnostic tests are used to diagnosis NTDs?
A nurse is assessing a newborn for possible neural tube defects. What assessment should she perform?
A nurse is assessing a newborn for possible neural tube defects. What assessment should she perform?
Many children with 'minor defects'are said to be?
Many children with 'minor defects'are said to be?
Name the 'stridor' sign that is an indicator for certain NTDs.
Name the 'stridor' sign that is an indicator for certain NTDs.
What signs are associated with the 'orthopedic' issues that come with NTDs?
What signs are associated with the 'orthopedic' issues that come with NTDs?
What signs are associated with the 'Urologic' issues that come with NTDs?
What signs are associated with the 'Urologic' issues that come with NTDs?
Shunt complications that results in death mostly concerns what?
Shunt complications that results in death mostly concerns what?
What nursing interventions best 'prevent infection' in newborns?
What nursing interventions best 'prevent infection' in newborns?
What are good measures to aid skin integrity?
What are good measures to aid skin integrity?
What is a serious level sign of sleep apnea?
What is a serious level sign of sleep apnea?
Flashcards
Environmental risk factors
Environmental risk factors
Teratogenic process causing abnormal differentiation of the embryonic neural tube.
Anencephaly Definition
Anencephaly Definition
Absence of the cerebral hemispheres in a newborn.
Anencephaly (LLC)
Anencephaly (LLC)
Severe life-limiting condition characterized by the absence of cerebral hemispheres.
Anencephaly Diagnosis
Anencephaly Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anencephaly management
Anencephaly management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microcephaly Definition
Microcephaly Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microcephaly Etiology
Microcephaly Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microcephaly
Microcephaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microcephaly Treatment
Microcephaly Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina bifida meaning
Spina bifida meaning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Cause
Spina Bifida Cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Cause Details
Spina Bifida Cause Details
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Occulta
Spina Bifida Occulta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Occulta: Etiology
Spina Bifida Occulta: Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Occulta: symptoms
Spina Bifida Occulta: symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Occulta: Etiology
Spina Bifida Occulta: Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Occulta management.
Spina Bifida Occulta management.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meningocele
Meningocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meningocele Sac
Meningocele Sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meningocele Major Risk.
Meningocele Major Risk.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meningocele: Treatment
Meningocele: Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele Description
Myelomeningocele Description
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele Signs
Myelomeningocele Signs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele Signs
Myelomeningocele Signs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele: Treatment
Myelomeningocele: Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele Lesion.
Myelomeningocele Lesion.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Encephalocele Definition
Encephalocele Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Features of Encephalocele.
Features of Encephalocele.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Encephalocele diagnosis.
Encephalocele diagnosis.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Encephalocele: Treatment
Encephalocele: Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Folate Deficiency risk.
Folate Deficiency risk.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Family History Risk Factors
Family History Risk Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
NTD and SB chance.
NTD and SB chance.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Factors (Maternal)
Risk Factors (Maternal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Management Plan
Nursing Management Plan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arnold-Chiari (Chiari II) malformation
Arnold-Chiari (Chiari II) malformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type I-definition
Type I-definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chiari malformation related defects:
Chiari malformation related defects:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chiari malformation related symptoms:
Chiari malformation related symptoms:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Riverside College, Inc. is the home of 21st Century Global Leaders and Professionals
Neural Tube & Disorders
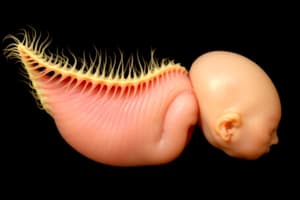
- The neural tube forms during fetal development, beginning as a flat plate that folds to create the brain and spinal cord.
- Malformation can occur during this process.
Etiology of Neural Tube Defects
- The cause is unknown.
- Genetic factors, such as a family history of neural tube defects, can contribute
- Nutritional deficiencies, specifically folate (vitamin B-9) deficiency, can factor in.
- Environmental risk factors (teratogenic processes) lead to failed closure and abnormal differentiation of the embryonic neural tube.
Anencephaly
- Absence of the cerebral hemispheres characterizes this condition.
- Anencephaly is a severe life-limiting condition (LLC).
- It occurs when the upper end of the neural tube fails to close during early intrauterine life.
Manifestation of Anencephaly
- Prolonged labor can occur due to breech presentation or an underdeveloped head.
- Respiratory and cardiac centers located in the medulla may allow the infant to survive for days or weeks, but death is the likely outcome.
Diagnosing Anencephaly
- This can be diagnosed at 12 weeks AOG (weeks of gestation), with death occurring shortly after birth.
- Elevated levels of MAFP (maternal alpha-fetoprotein), detected via amniocentesis or prenatal sonogram, can also reveal anencephaly.
Managing and treating Anencephaly
- Prenatally, parents may be offered the option of pregnancy termination.
- Culturally sensitive and spiritual care should be provided.
- Allowing parents to hold and take photos can help with the grieving process.
- There is no cure; treatment focuses on supportive care to maximize the baby's comfort.
Microcephaly
- Fetal brain grows so slowly that at birth it measures more than 3 standard deviations below normal on growth charts.
Etiology of Microcephaly
- Intrauterine infections like rubella, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, or Zika virus can lead to infantile microcephaly.
- Severe malnutrition or anoxia after birth or during early infancy may also result in microcephaly.
Manifestation and Treatment of Microcephaly
- Individuals with microcephaly typically have cognitive challenges.
- Treatment is supportive, aimed at managing development, behavior, and seizures.
- Potential treatments involve medicines to control seizures and hyperactivity and to improve nerve and muscle function, in addition to speech, physical, and occupational therapy.
Spina Bifida Definition
- Spina bifida originates from the Latin term meaning "split spine/divided spine".
- It is caused by a defect in the neural arch, typically in the lumbosacral region.
- The spine and spinal cord do not properly develop in the womb, creating a gap in the spine and leading to defects in the spinal cord and bones of the spine (vertebrae).
Spina Bifida Development
- The condition occurs due to the lack of fusion of the posterior laminae of the vertebrae, preventing the closure of the embryo's surface during early intrauterine life.
- They can be compared to cleft palate or cleft lip, which are also midline closure disorders.
- A lesion is typically visible on the back after birth.
Spina Bifida Occulta
- Occulta means "hidden" and includes a layer of skin covering the opening of the spinal vertebrae.
- Spina Bifida Occulta is the mildest and most common form of spina bifida.
- Prenatal tests often fail to detect spina bifida occulta.
Spina Bifida Occulta Etiology
- Occurs when the posterior laminae of the vertebrae do not fuse, resulting to a gap between the small bones (vertebrae) and the backbone (spine).
- The cause is the non-closure or incomplete closure of the posterior portion of the vertebrae, which occurs most commonly at the fifth lumbar or first sacral level but can occur anywhere along the spinal canal.
Spina Bifida Occulta Signs and Symptoms
- Spinal cord and tissue don’t protrude.
- There may be a dimpling or birthmark at the point of poor fusion.
- Abnormal tufts of hair or discolored skin may be present.
- Typically, there are no signs or symptoms due to the fact the spinal nerves aren't involved.
Spina Bifida Occulta Incidence
- It is a benign disorder, occurring as frequently as in one out of every four children.
- Problems from spina bifida occulta are rare during adulthood.
- The spinal cord may become fastened to the backbone and cause the nerves of the spinal cord to become stretched when growth spurt of adolescence begins.
- Resulting difficulties can include weakness, numbness in the legs, bladder infections, and incontinence (lack of bladder and bowel control). Surgery may be needed to relieve these symptoms by reducing the tension on the spinal cord.
Spina Bifida Treatment
- The spinal cord must become unfettered along the back bone
- The spinal cord must be able to move so symptoms from the stretching of the spinal chord discontinue
- No surgical correction is needed in most cases.
- No tissue will be seen extruding from the vertebrae.
Meningocele
- It is the least common type of spina bifida.
- The spinal cord is normally protected by three layers of meninges (pia mater, arachnoid, and dura mater).
- Protective membranes (meninges) push out (or herniate) through the spine (unformed vertebrae), causing a circular mass, lump, or sac on the back, about the size of an orange, and covered by a layer of skin.
Meningocele Facts
- Protrusion usually occurs in the lumbar region, but is possible anywhere along the spinal canal.
- The protrusion mostly contains clear dura mater.
- Sensory or motor deficits do not accompany the disorder unless the membrane sac ruptures, wherein damage to the cord or infection could occur.
Meningocele Treatment
- Includes immediate surgery to replace meninges and to close the gap in the skin to prevent infection.
- Surgery should be done within 24 to 48 hours of birth, so infection of the meninges does not occur.
Myelomeningocele (Meningomyelocele)
- Also known as "Open Spina Bifida.”
- It is the most severe type of spina bifida.
- Also the most complicated birth defect and yet compatible with survival.
- A permanent disability.
- Most common in the lower thoracic, lumbar, or sacral region, these defects usually extend for three to six vertebral segments.
Myelomeningocele Particulars
- The baby's spinal canal remains open along several vertebrae in the back.
- Spinal cord and protective membranes form a sac in the baby's back.
- Prone to life-threatening infections.
- The meninges protrude through the vertebrae, and the spinal cord ends at the point of protrusion.
- Motor or sensory function will decrease or be absent beyond the point of damage.
- The higher the anomaly, the greater the paralysis.
- Can include Loss of Sensation plus partial or complete paralysis below the damaged site.
- Partial or complete lack of sensation/movement in lower extremities is typical.
Further Myelomeningocele Symptoms
- Loss of bowel and bladder control.
- Seizures may occur.
- Infant legs appear lax and unable to move.
- Urine and stools may continually dribble due to lack of sphincter control.
- Accompanying leg and foot disabilities, such as talipes (club foot) and DDH (Developmental Hip Dysplasia).
- 90% develop hydrocephalus because of lack of subarachnoid membrane for CSF absorption and obstruction of CSF circulation from the spinal deformity.
Myelomeningocele Treatment
- Shunting is required in the first 72 hours to decrease hospital stay length, decrease loss of and infection rates of CSF, and lessen damage from progressive ventricular dilation.
- Treatment includes early closure of NTD to prevent compromise of the spinal cord and nerve roots.
- Surgery is done to return meninges to the spinal cord and close the gap in the surface.
- Caesarean birth decreases the chance of pressure and injury to the spinal cord.
- The child will likely continue to have partial or complete paralysis of the lower extremities.
- Lesion can be repaired but cannot replace the absent lower cord.
Encephalocele
- Covered fully by skin, although they may be open or covered only by the dura.
- Originates in the occipital area of the skull but can be a nasal or nasopharyngeal disorder.
Encephalocele Diagnosis
- Transillumination of the sac reveals brain tissue.
- CT, UTZ, and MRI reveal size of the skull disorder and extent of the surgery.
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may be trapped in the protruding meninges or around any brain tissue that has protruded.
Encephalocele Treatment
- Includes immediate surgery as soon as after birth (within 24 to 48 hours).
- Surgery’s aim is to replace meninges and to close the gap in the skin to prevent infection in meninges.
- Accompanying brain disorder means the child’s cognitive potential may be impaired if a large portion of meninges have needed removal.
- Removal limits the rate of CSF absorption.
Risk Factors for Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
- Folate deficiency increases the risk.
- A family history of NTDs increases the chance of having another baby with the same defect.
- Anti-seizure medications, such as valproic acid, when taken during pregnancy seem to cause NTDs.
- Diabetes, obesity, and increased body temperature in early pregnancy also increase risk.
More Neural Tube Defect Risk Factors
- The rate to giving birth to a child with spina bifida is greater in women born with a NTD.
- A first child with spinal cord disorder means a MAFD assay is done in the 2nd pregnancy.
- Higher risk occurs with maternal age under 20 or over 40.
- Other factors include maternal education below the 12th grade level and low socioeconomic status.
NTD Incidence
- Is between 1 to 10 cases per 1,000 births worldwide.
- In the US, the rate has fallen since the government mandated the inclusion of folic acid.
- 600μg of folic acid in prenatal vitamins and cereal and grain products resulted in a reduction to two in 10,000 live births.
Diagnosing NTDs
- Fetoscopy
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- AFP Levels
- Amniocentesis
- Ultrasonography
- Computer tomography
- Plain X-Rays
Assessing and Observing for NTDs
- Observe and record whether an infant born with a neural tube disorder has spontaneous movement of the lower extremities.
- Assess the nature and pattern of voiding and defecation.
- Also note an infant without motor or sphincter control voids continually.
Clinical Manifestations of NTDs
- Paralysis
- Cognitive Symptoms
- Arnold-Chiari Malformation
- Birthmark
Signs and Symptoms of NTDs
- Many children with minor defects are asymptomatic.
- Neurologic Signs – Paralysis and sensory deficits below the involved lesion of spinal cord or lumbosacral nerve roots. Decreased rectal tone.
- Neurology with brain involvement – stridor, swallowing difficulties, intermittent apnea.
ORTHOPEDIC & UROLOGIC SIGNS; COMPLICATIONS & PROGNOSIS
- Orthopedic Signs- paralysis occurs in the fetus and can have orthopedic problems at birth includes clubfoot and a dislocated hip.
- Orthopedic signs include Scoliosis, muscle, innervation, Kyphosis
- Urologic signs include paralysis and bladder function, occasionally leading to a neurogenic bladder along with frequent UTIs.
- Complications from NTDs include problems walking and mobility, the accumulation of fluid in the brain.
- Prognosis varies by the level of cord involvement and severity of associated anomalies.
Post Natal- Nursing Intervention
- Prevent and detect infection
- Monitor and record new born’s vital signs, neurological signs
- Administer medications as per doctors
- Proper hygiene must be maintained while providing care
- Keep sac and wounds clean and sterile
- Maintain proper positioning of the new born
- Prevent any further injuries if possible
- Teach and educate the family members about necessary information
Arnold-Chiari (Chiari II) Malformation
- This is a structural variance in the cerebellum and skull base.
- There are four categories.
- Type I means there downward herniation of the caudal end.
- This disorder and the upper motor neuron involve gagging and swallowing.
- Sonogram assists early diagnosis.
- Never perform a back puncture as there is risk to the brain
- MRI can assist with the chronic headaches.
- Those with disorder risk for aspiration
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.