Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the structure of sensory ganglia neurons?
What is the structure of sensory ganglia neurons?
- Multiple dendrites and no axon
- Two processes, both axons
- Two independent axon terminals
- Single process divided into two branches, a dendrite and axon (correct)
Which type of neuron has a star-shaped body?
Which type of neuron has a star-shaped body?
- Neurons in the olfactory epithelium (correct)
- Anterior horn cells of spinal cord
- Neurons in sympathetic ganglia
- Bipolar neurons of the retina
Which term refers to the cytoplasm of a nerve cell's axon?
Which term refers to the cytoplasm of a nerve cell's axon?
- Cytomembrane
- Neurolemma
- Axoplasm (correct)
- Axolemma
Which feature is characteristic of naked fibers?
Which feature is characteristic of naked fibers?
What role do nodes of Ranvier play in nerve fibers?
What role do nodes of Ranvier play in nerve fibers?
Which layer of connective tissue surrounds the entire nerve trunk?
Which layer of connective tissue surrounds the entire nerve trunk?
What is the primary function of the myelin sheath?
What is the primary function of the myelin sheath?
What occurs at a synapse?
What occurs at a synapse?
What is the primary function of specialized cells in the nervous system?
What is the primary function of specialized cells in the nervous system?
What structures are responsible for carrying nerve impulses away from the cell body?
What structures are responsible for carrying nerve impulses away from the cell body?
Which organelle is NOT typically found in the cytoplasm of a neuron?
Which organelle is NOT typically found in the cytoplasm of a neuron?
What characterizes dendrites in a typical neuron?
What characterizes dendrites in a typical neuron?
What type of ganglia is associated with the autonomic nervous system?
What type of ganglia is associated with the autonomic nervous system?
What are the main components of a neuron?
What are the main components of a neuron?
Which basic stain is commonly used in histology for neuronal assessment?
Which basic stain is commonly used in histology for neuronal assessment?
What is one feature that distinguishes the axon from dendrites?
What is one feature that distinguishes the axon from dendrites?
What is the primary function of neurovesicles in the presynaptic neuron?
What is the primary function of neurovesicles in the presynaptic neuron?
Which part of the neuron does the synaptic cleft connect?
Which part of the neuron does the synaptic cleft connect?
Which type of synapse allows for the rapid transmission of electrical signals?
Which type of synapse allows for the rapid transmission of electrical signals?
What is the approximate width of the synaptic cleft?
What is the approximate width of the synaptic cleft?
Which of the following cells in the nervous system can transform into macrophages?
Which of the following cells in the nervous system can transform into macrophages?
Which cell type is responsible for supporting neurons by connecting them to blood vessels?
Which cell type is responsible for supporting neurons by connecting them to blood vessels?
What is primarily delivered to the synapse by the terminal button of an axon?
What is primarily delivered to the synapse by the terminal button of an axon?
Which type of glial cell is primarily found in the peripheral nervous system?
Which type of glial cell is primarily found in the peripheral nervous system?
What is the primary function of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS)?
What is the primary function of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS)?
Which cells are responsible for myelination in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Which cells are responsible for myelination in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
How many neurons can one oligodendrocyte myelinate?
How many neurons can one oligodendrocyte myelinate?
What type of neuronal cell is commonly described as having a central nucleus and numerous processes?
What type of neuronal cell is commonly described as having a central nucleus and numerous processes?
What distinguishes Schwann cells from oligodendrocytes in their myelination process?
What distinguishes Schwann cells from oligodendrocytes in their myelination process?
What characteristic distinguishes pseudounipolar neurons from other neuron types?
What characteristic distinguishes pseudounipolar neurons from other neuron types?
Which statement accurately describes the relationship of neuron cells in the context of their organization?
Which statement accurately describes the relationship of neuron cells in the context of their organization?
What role do astrocytes perform within the nervous system?
What role do astrocytes perform within the nervous system?
Which type of neuron is characterized by having two processes: a dendrite and an axon?
Which type of neuron is characterized by having two processes: a dendrite and an axon?
In terms of axon structure, what does the term 'axoplasmic' refer to?
In terms of axon structure, what does the term 'axoplasmic' refer to?
Which type of fibers is characterized as being non-myelinated and lacking neurolemma?
Which type of fibers is characterized as being non-myelinated and lacking neurolemma?
What is the primary role of the nodes of Ranvier in myelinated nerve fibers?
What is the primary role of the nodes of Ranvier in myelinated nerve fibers?
What tissue structure provides insulation to nerve impulses, specifically in myelinated fibers?
What tissue structure provides insulation to nerve impulses, specifically in myelinated fibers?
Which connective tissue type divides the nerve trunk into bundles?
Which connective tissue type divides the nerve trunk into bundles?
What characterizes the structure of neurons in sympathetic ganglia?
What characterizes the structure of neurons in sympathetic ganglia?
At what anatomical point does the transmission of a nervous impulse occur between neurons?
At what anatomical point does the transmission of a nervous impulse occur between neurons?
Which part of a neuron increases the surface area for receiving impulses?
Which part of a neuron increases the surface area for receiving impulses?
What is the primary role of the spinal cord within the nervous system?
What is the primary role of the spinal cord within the nervous system?
Which structure within a neuron is responsible for carrying impulses away from the cell body?
Which structure within a neuron is responsible for carrying impulses away from the cell body?
What characteristics distinguish the cytoplasm of a neuron?
What characteristics distinguish the cytoplasm of a neuron?
Which type of impulse is characterized by moving toward the cell body?
Which type of impulse is characterized by moving toward the cell body?
What distinguishes the structure of a neuron from other cells?
What distinguishes the structure of a neuron from other cells?
Which type of ganglia is structured to relay sensory and autonomic signals respectively?
Which type of ganglia is structured to relay sensory and autonomic signals respectively?
What does the term 'basophilic granules' refer to in a neuron?
What does the term 'basophilic granules' refer to in a neuron?
What is the primary role of neurotransmitters within the synaptic cleft?
What is the primary role of neurotransmitters within the synaptic cleft?
Which glial cells are primarily involved in providing support and nutrition to neurons?
Which glial cells are primarily involved in providing support and nutrition to neurons?
What is the function of neurovesicles in the terminal button of an axon?
What is the function of neurovesicles in the terminal button of an axon?
Which type of synapse is characterized by the direct connection of electrical signals between neurons?
Which type of synapse is characterized by the direct connection of electrical signals between neurons?
What structural feature primarily differentiates astrocytes from other glial cells?
What structural feature primarily differentiates astrocytes from other glial cells?
What is the approximate width of the synaptic cleft, allowing neurotransmitter passage?
What is the approximate width of the synaptic cleft, allowing neurotransmitter passage?
Which neural structure is directly responsible for connecting the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of another?
Which neural structure is directly responsible for connecting the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of another?
What type of synaptic transmission occurs when an impulse travels through a thin space connecting two neurons?
What type of synaptic transmission occurs when an impulse travels through a thin space connecting two neurons?
Which statement accurately describes the function of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system?
Which statement accurately describes the function of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system?
Which characteristic distinguishes Schwann cells from oligodendrocytes when it comes to myelination?
Which characteristic distinguishes Schwann cells from oligodendrocytes when it comes to myelination?
What structural feature of pseudounipolar neurons contributes to their function in the nervous system?
What structural feature of pseudounipolar neurons contributes to their function in the nervous system?
What significant role do the flat cells forming a tube around nerve fibers serve?
What significant role do the flat cells forming a tube around nerve fibers serve?
In the central nervous system, what distinguishes oligodendrocytes in terms of their structure?
In the central nervous system, what distinguishes oligodendrocytes in terms of their structure?
What is a common feature of the cells surrounding neurons in sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic ganglia?
What is a common feature of the cells surrounding neurons in sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic ganglia?
Which aspect of nerve fibers is most affected by the presence of myelin?
Which aspect of nerve fibers is most affected by the presence of myelin?
What is the classification of neurons based on the central position of their nucleus?
What is the classification of neurons based on the central position of their nucleus?
What is the role of specialized cells in the nervous system?
What is the role of specialized cells in the nervous system?
Describe the significance of Nissl granules in neurons.
Describe the significance of Nissl granules in neurons.
What key feature allows dendrites to receive more impulses?
What key feature allows dendrites to receive more impulses?
Explain the difference in directionality of impulse transmission between dendrites and axons.
Explain the difference in directionality of impulse transmission between dendrites and axons.
What structural characteristic is common in neurons of the spinal cord?
What structural characteristic is common in neurons of the spinal cord?
In terms of signal processing, what occurs when integrating sensory information in the nervous system?
In terms of signal processing, what occurs when integrating sensory information in the nervous system?
How do the neuron processes, particularly axons, differ from each other structurally?
How do the neuron processes, particularly axons, differ from each other structurally?
What role do cranial and spinal nerves play within the nervous system?
What role do cranial and spinal nerves play within the nervous system?
Describe the structure and function of nodes of Ranvier in myelinated nerve fibers.
Describe the structure and function of nodes of Ranvier in myelinated nerve fibers.
What distinguishes myelinated fibers with neurolemma from those without?
What distinguishes myelinated fibers with neurolemma from those without?
How is the structure of bipolar neurons in the retina specifically adapted for its function?
How is the structure of bipolar neurons in the retina specifically adapted for its function?
Explain the role of axolemma in neuron structure.
Explain the role of axolemma in neuron structure.
What is the significance of having a dense connective tissue layer surrounding nerve trunks?
What is the significance of having a dense connective tissue layer surrounding nerve trunks?
In how many ways can non-myelinated fibers be categorized based on their structural characteristics?
In how many ways can non-myelinated fibers be categorized based on their structural characteristics?
Identify a key feature of spinal ganglia neurons and its role in their functionality.
Identify a key feature of spinal ganglia neurons and its role in their functionality.
What typically differentiates the axon from the dendrites in terms of structure?
What typically differentiates the axon from the dendrites in terms of structure?
What initiates the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron?
What initiates the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron?
Describe the role of astrocytes in the nervous system.
Describe the role of astrocytes in the nervous system.
Explain the significance of the synaptic cleft in neurotransmission.
Explain the significance of the synaptic cleft in neurotransmission.
What distinguishes gap junctions from chemical synapses?
What distinguishes gap junctions from chemical synapses?
Identify the approximate width of a typical synaptic cleft.
Identify the approximate width of a typical synaptic cleft.
What type of synapse is characterized by the connection of an axon to a dendrite?
What type of synapse is characterized by the connection of an axon to a dendrite?
How do ependymal cells contribute to the nervous system?
How do ependymal cells contribute to the nervous system?
What chemical messengers are typically found in neurovesicles?
What chemical messengers are typically found in neurovesicles?
What is the primary function of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
What is the primary function of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
How do oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells differ in their roles within the nervous system?
How do oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells differ in their roles within the nervous system?
In which part of the nervous system are pseudounipolar neurons predominantly found?
In which part of the nervous system are pseudounipolar neurons predominantly found?
What characteristic of oligodendrocytes allows them to myelinate multiple neurons?
What characteristic of oligodendrocytes allows them to myelinate multiple neurons?
What histological feature distinguishes the arrangement of cells in sympathetic ganglia compared to spinal nerve roots?
What histological feature distinguishes the arrangement of cells in sympathetic ganglia compared to spinal nerve roots?
How are the myelination processes of Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes related to the pathology of certain neurological diseases?
How are the myelination processes of Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes related to the pathology of certain neurological diseases?
Describe the implications of having thinly myelinated fibers in the nervous system.
Describe the implications of having thinly myelinated fibers in the nervous system.
What histological distinctive feature is observed in the nerve fibers of dorsal roots of spinal nerves?
What histological distinctive feature is observed in the nerve fibers of dorsal roots of spinal nerves?
What specialized structure in the nervous system is responsible for the transmission of electrical impulses?
What specialized structure in the nervous system is responsible for the transmission of electrical impulses?
How do dendrites differ from axons in structure and function?
How do dendrites differ from axons in structure and function?
What organelles in the neuron are involved in maintaining cell survival and processing metabolic functions?
What organelles in the neuron are involved in maintaining cell survival and processing metabolic functions?
What distinctive feature characterizes the cell body of neurons?
What distinctive feature characterizes the cell body of neurons?
What is the role of basophilic granules in the cytoplasm of a neuron?
What is the role of basophilic granules in the cytoplasm of a neuron?
What is meant by the terms 'centripetal' and 'centrifugal' in relation to nerve impulses?
What is meant by the terms 'centripetal' and 'centrifugal' in relation to nerve impulses?
How do the functions of ganglia differ in the peripheral nervous system?
How do the functions of ganglia differ in the peripheral nervous system?
What common histological stains are used to identify neuronal structures?
What common histological stains are used to identify neuronal structures?
What are neurovesicles and what is their main content?
What are neurovesicles and what is their main content?
Explain the role of the synaptic cleft in neuronal communication.
Explain the role of the synaptic cleft in neuronal communication.
Describe the function of astrocytes in the nervous system.
Describe the function of astrocytes in the nervous system.
What type of synaptic connection is facilitated by gap junctions?
What type of synaptic connection is facilitated by gap junctions?
Identify one type of glial cell present in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Identify one type of glial cell present in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
How do neurotransmitters affect the postsynaptic neuron?
How do neurotransmitters affect the postsynaptic neuron?
What structural feature distinguishes microglia among glial cells?
What structural feature distinguishes microglia among glial cells?
What are the key components involved in the release of neurotransmitters?
What are the key components involved in the release of neurotransmitters?
What is the role of oligodendrocytes in the CNS?
What is the role of oligodendrocytes in the CNS?
How do Schwann cells differ in their function compared to oligodendrocytes?
How do Schwann cells differ in their function compared to oligodendrocytes?
What structural characteristic is typical of pseudounipolar neurons?
What structural characteristic is typical of pseudounipolar neurons?
Describe the myelination process of nerve fibers in the PNS.
Describe the myelination process of nerve fibers in the PNS.
What types of cells are primarily responsible for secretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
What types of cells are primarily responsible for secretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
What is one major difference in the arrangement of myelinated fibers in groups of neurons?
What is one major difference in the arrangement of myelinated fibers in groups of neurons?
How does the structure of neurons in sympathetic ganglia differ from those in sensory ganglia?
How does the structure of neurons in sympathetic ganglia differ from those in sensory ganglia?
What role do small cells surrounding neurons play within the nervous system?
What role do small cells surrounding neurons play within the nervous system?
Describe the structure of the axon and its surrounding membranes.
Describe the structure of the axon and its surrounding membranes.
What is the function of the myelin sheath in nerve fibers?
What is the function of the myelin sheath in nerve fibers?
Explain the significance of nodes of Ranvier in myelinated fibers.
Explain the significance of nodes of Ranvier in myelinated fibers.
What is the composition and function of the connective tissue surrounding the nerve trunk?
What is the composition and function of the connective tissue surrounding the nerve trunk?
Describe the differences between myelinated and non-myelinated fibers.
Describe the differences between myelinated and non-myelinated fibers.
What types of neurons are described as having a fusiform shape?
What types of neurons are described as having a fusiform shape?
Identify the structural characteristics of bipolar neurons in the retina.
Identify the structural characteristics of bipolar neurons in the retina.
What distinguishes the synapse as a point of signal transmission?
What distinguishes the synapse as a point of signal transmission?
Flashcards
Neuron
Neuron
A specialized cell transmitting electrical impulses in the nervous system.
Dendrites
Dendrites
Branching extensions from a neuron that receive nerve impulses.
Axon
Axon
A long, thin extension of a neuron that transmits nerve impulses away from the cell body.
Nissl granules
Nissl granules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrifugal nerve impulse
Centrifugal nerve impulse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centripetal nerve impulse
Centripetal nerve impulse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuron structure
Neuron structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous System Function
Nervous System Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bipolar Neuron Structure
Bipolar Neuron Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axon Structure
Axon Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelin Sheath Function
Myelin Sheath Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nodes of Ranvier
Nodes of Ranvier
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nerve Impulse Transmission
Nerve Impulse Transmission
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Ganglia
Sensory Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axolemma
Axolemma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axoplasm
Axoplasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synapse
Synapse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synaptic Cleft
Synaptic Cleft
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurovesicles
Neurovesicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presynaptic Neuron
Presynaptic Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postsynaptic Neuron
Postsynaptic Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Astrocytes
Astrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glial cells
Glial cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuroglia Function
Neuroglia Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelin Sheath: CNS vs PNS
Myelin Sheath: CNS vs PNS
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Ganglia?
What are Ganglia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Nerves
Spinal Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomic Nerves
Autonomic Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudounipolar Neuron
Pseudounipolar Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multipolar Neuron
Multipolar Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelination and Nerve Size
Myelination and Nerve Size
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are neurons?
What are neurons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of dendrites?
What is the function of dendrites?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the axon?
What is the function of the axon?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Nissl granules?
What are Nissl granules?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a bipolar neuron?
What is a bipolar neuron?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a multipolar neuron?
What is a multipolar neuron?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between centrifugal and centripetal nerve impulses?
What is the difference between centrifugal and centripetal nerve impulses?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the nervous system?
What is the role of the nervous system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory ganglia neuron
Sensory ganglia neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bipolar neuron
Bipolar neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory neuron
Olfactory neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic ganglion neuron
Sympathetic ganglion neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelin sheath
Myelin sheath
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurolemma
Neurolemma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synaptic Cleft: What is it?
Synaptic Cleft: What is it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitter Release
Neurotransmitter Release
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synaptic Transmission: How does it work?
Synaptic Transmission: How does it work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Synapse: Axodendritic
Types of Synapse: Axodendritic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Synapse: Axosomatic
Types of Synapse: Axosomatic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Synapse: Axo-axonic
Types of Synapse: Axo-axonic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Astrocytes: What are they?
Astrocytes: What are they?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Satellite Cells
Satellite Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuroglia
Neuroglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Schwann Cell
Schwann Cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocyte
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ganglia
Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bipolar Neurons of Retina
Bipolar Neurons of Retina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Olfactory Epithelium Neurons
Olfactory Epithelium Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuron's Function
Neuron's Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axon vs. Dendrite
Axon vs. Dendrite
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the Nervous system do?
What does the Nervous system do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Ganglia
Types of Ganglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Peripheral Nerves?
What are Peripheral Nerves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelination's Role
Myelination's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the types of synapses?
What are the types of synapses?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Difference between Axons and Dendrites
Difference between Axons and Dendrites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Nerves
Peripheral Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Synapses?
What are Synapses?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Synapses
Types of Synapses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Naked Nerve Fiber
Naked Nerve Fiber
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ensheathed Nerve Fiber
Ensheathed Nerve Fiber
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelination: CNS vs PNS
Myelination: CNS vs PNS
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Nervous System
- Classification:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): brain, spinal cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): peripheral nerves (cranial or spinal), ganglia (spinal or autonomic)
Nervous System Functions
- Sensory: Receives changes (stimuli) from inside and outside the body.
- Input: Sensory receptors capture stimuli.
- Integration: Nervous system interprets sensory information and decides if any action is needed.
- Motor: A response is created.
- Output: The response activates muscles or glands.
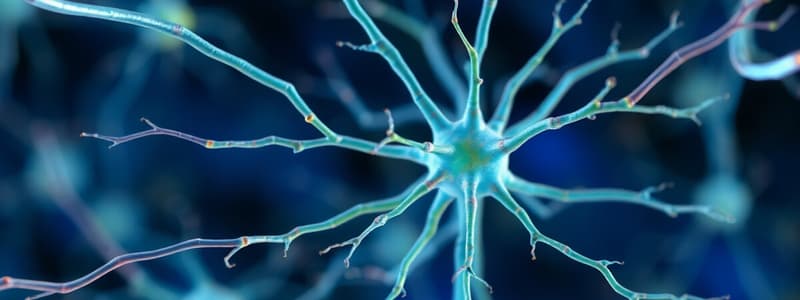
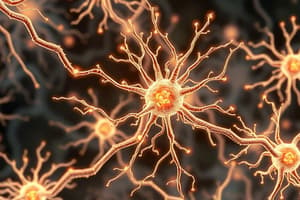
Neuron (Nerve Cell)
- Definition: Specialized cells for transmitting electrical impulses within the nervous system.
- Structure:
- Cell body (perikaryon/soma): Contains nucleus, cytoplasm with organelles (Nissl granules, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria) for cell maintenance.
- Processes: Dendrites (receive impulses) and axon (carries impulses away from the cell body).
- Axon: Contains Nissl granules throughout the cytoplasm except for around the nucleus and the axon.
- Myelin Sheath (in some): Provides insulation and faster impulse transmission.
- Nissl granules: Basophilic granules in the cytoplasm, critical for protein synthesis.
Neuron (Nerve Cell) Structure Further Details:
- Number: Single axon, many dendrites.
- Length: Axons are long, threadlike; dendrites are branched and short.
- Diameter: Uniform in axon diameter, tapering in dendrites.
- Content: Axons lack Nissl granules, dendrites do have Nissl granules.
- Branching: Dendrites are highly branched, axons branch only at their terminal ends (terminal arborization).
- Conduction of Nerve Impulses:
- Axons carry impulses away from the cell body (centrifugal).
- Dendrites carry impulses towards the cell body (centripetal).
Classification of Neurons (Based on the Number of Processes)
- Unipolar: One process
- Pseudounipolar: One process that quickly divides into two branches
- Bipolar: Two processes (one axon, one dendrite)
- Multipolar: Many dendrites and one axon (most common)
Classification of Neurons (Based on Function)
- Sensory neurons: Cells of spinal ganglia; transmit impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS.
- Motor neurons: Anterior horn cells of spinal cord; transmit impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands).
- Interneurons: Neurons connecting sensory and motor neurons; involved in information processing within the CNS.
Nerve Fiber
- Definition: The axon of a nerve cell with its surrounding membranes (axolemma and axoplasm).
- Structure: May be naked (non-myelinated) or ensheathed (with myelin sheath or neurolemma, or both).
- Types:
- Naked fibers: Non-myelinated, e.g., fibers in gray matter
- Myelinated fibers: With myelin sheath; found in white matter and peripheral nerves.
- Non-myelinated fibers: With neurolemma; found in sympathetic nerve fibers
Myelin Sheath
- Histology: White, tubular covering interrupted by nodes of Ranvier (gaps in the myelin sheath).
- Function: Insulates the nerve impulses. Formed by concentric layers derived from the cell membrane of Schwann cells.
Neurolemmal Sheath (Schwann Cells)
- Histology: Chain of cells forming a tube around the myelin sheath.
- Function: Insulation, regeneration of peripheral nerve fibers after injury, myelin formation
Nerve Trunk
- Structure:
- Nervous component: Bundles of myelinated nerve fibers.
- Connective tissue (CT) component:
- Epineurium: Surrounds the whole trunk.
- Perineurium: Divides the trunk into bundles.
- Endoneurium: Surrounds individual nerve fibers.
Synapse
- Definition: The point where a nerve impulse passes from one neuron to another neuron or an effector cell.
- Structure:
- Presynaptic membrane: Terminal button of the axon.
- Postsynaptic membrane: Dendrite or cell body of the other neuron.
- Synaptic cleft: Thin space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes.
- Types (based on transmission):
- Chemical synapses: Neurotransmitters cross the gap, triggering a response.
- Electrical synapses: Direct transmission of electrical signals.
Classification of Synapses
- Axo-dendritic: Axo ending on dendrite
- Axo-somatic: Axo ending on cell body
- Axo-axonic: Axo ending on another axon
Neuroglia
- Definition: Supporting tissue of the nervous system; non-neuronal cells.
- Types (in CNS):
- Astrocytes: Star-shaped cells providing nutrition and support.
- Oligodendrocytes: Form myelin sheaths around axons.
- Microglia: Small, phagocytic cells; immune defense.
- Ependymal cells: Line ventricles and help produce CSF.
- Types (in PNS):
- Satellite cells.
- Schwann cells.
Nerve Ganglia
- Definition: Collections of nerve cells and nerve fibers outside the CNS, covered by a connective tissue capsule.
- Types (Location):
- Spinal ganglia: Associated with spinal nerves.
- Autonomic ganglia: Part of the autonomic nervous system.
- Structure: Nerve cells (neurons), nerve fibers, and connective tissue (CT) capsule.
- Features: Size, shape, arrangement of nerve cells varies across types.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.