Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which part of the nervous system processes information and creates a response?
Which part of the nervous system processes information and creates a response?
- Autonomic nervous system
- Somatic nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
- Central nervous system (correct)
Motor neurons carry impulses from muscles and glands to the brain.
Motor neurons carry impulses from muscles and glands to the brain.
False (B)
What is the role of sodium ions in propagating a nerve impulse?
What is the role of sodium ions in propagating a nerve impulse?
Sodium ions flow into the cell, temporarily making the inside of the cell membrane more positive, causing an action potential.
The insulating membrane that surrounds a single axon in some neurons is called the _________.
The insulating membrane that surrounds a single axon in some neurons is called the _________.
Match the following parts of the nervous system with their functions:
Match the following parts of the nervous system with their functions:
Which part of the brain is the site of intelligence, learning, and judgment?
Which part of the brain is the site of intelligence, learning, and judgment?
The thalamus controls hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature.
The thalamus controls hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature.
What is the function of the sensory division of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the function of the sensory division of the peripheral nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic and ________ nervous systems.
The autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic and ________ nervous systems.
Match the part of the brain to its function.
Match the part of the brain to its function.
Flashcards
Peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
The part of the nervous system that collects information from the body's environment.
Central nervous system
Central nervous system
The part of the nervous system that processes information received from the environment and creates a response.
Sensory neurons
Sensory neurons
Neurons that carry impulses from sensory organs (like eyes) to the spinal cord and brain.
Motor neurons
Motor neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Threshold of a neuron
Threshold of a neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebrum
Cerebrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebellum
Cerebellum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thalamus
Thalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Stem
Brain Stem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Nervous System
- The nervous system has two main parts: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system
- The peripheral nervous system gathers information about the body's environment
- The central nervous system processes this information, creates a response, and sends it through the peripheral nervous system
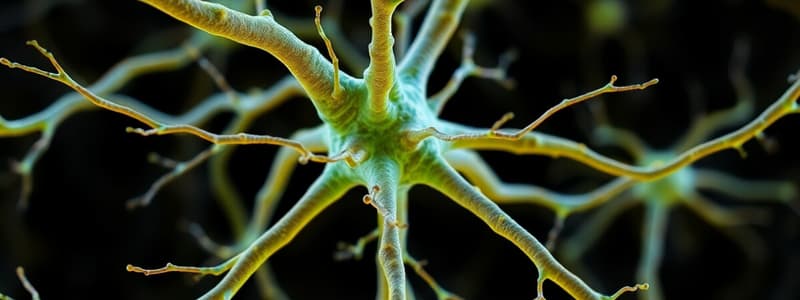
Neuron Structures
- Dendrites: Short, branched extensions that receive impulses from other neurons
- Nucleus: Located within the cell body
- Cell body: Contains the nucleus and other cellular components
- Axon: A long, slender extension that transmits impulses away from the cell body
- Myelin sheath: An insulating membrane around some axons
- Axon terminal: The end of the axon
Neuron Functions
- Sensory neurons: Carry impulses from the eyes to the spinal cord and brain
- Motor neurons: Carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
- Cell body: Has short, branched extensions called dendrites that receive impulses from other neurons.
- Axons and dendrites are often clustered in bundles called nerves
Nervous System Functions
- Collects information about the body's internal and external environment
- Processes this information
- Responds to this information
Nerve Impulse Propagation
- Sodium ions flow into the cell, temporarily making the inside of the cell membrane more positive than the outside
- This reversal of charges causes an action potential
Threshold of a Neuron
- The minimum level of stimulus needed to trigger an impulse in a neuron
Brain and Spinal Cord
- Spinal cord: Main link between the brain and the rest of the body
- Brain stem: Controls vital functions like blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, and swallowing
- Cerebrum: Controls intelligence, learning, and judgment
- Cerebellum: Coordinates muscle actions
- Thalamus: Receives and relays messages from the sense organs
- Hypothalamus: Controls hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature
Peripheral Nervous System
- The sensory division transmits impulses from sense organs to the central nervous system
- The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary activities
- The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for activity
- The parasympathetic nervous system prepares the body for relaxation
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.