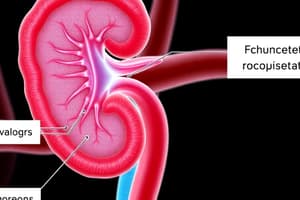
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What percentage of the filtered load is reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)?
What percentage of the filtered load is reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)?
- 67% (correct)
- 3%
- 5%
- 25%
Which section of the nephron is primarily involved in the process of glomerular filtration?
Which section of the nephron is primarily involved in the process of glomerular filtration?
- Collecting Tubule
- Glomerulus (correct)
- Distal Convoluted Tubule
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule
What function does the Macula Densa serve in the nephron?
What function does the Macula Densa serve in the nephron?
- Reabsorbs water
- Regulates blood pressure
- Facilitates tubular secretion
- Signals the distal tubule (correct)
What is the fate of the remaining 0.4% of filtered load in the kidneys?
What is the fate of the remaining 0.4% of filtered load in the kidneys?
Which nephron segment reabsorbs 25% of the filtered load?
Which nephron segment reabsorbs 25% of the filtered load?
Which membrane faces the lumen of the tubular system?
Which membrane faces the lumen of the tubular system?
What percentage of filtered load can be reabsorbed at the Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)?
What percentage of filtered load can be reabsorbed at the Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)?
Why is reabsorption essential for kidney function?
Why is reabsorption essential for kidney function?
What hormone increases sodium reabsorption by inserting sodium channels in the collecting tubule's apical membrane?
What hormone increases sodium reabsorption by inserting sodium channels in the collecting tubule's apical membrane?
How does arginine vasopressin (AVP) enhance water reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
How does arginine vasopressin (AVP) enhance water reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of calcium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of calcium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
What impact does Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) have on sodium reabsorption?
What impact does Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) have on sodium reabsorption?
What characterizes the collecting tubule's ability to reabsorb water?
What characterizes the collecting tubule's ability to reabsorb water?
What is the primary role of intercalated cells in the collecting tubule?
What is the primary role of intercalated cells in the collecting tubule?
Which statement best describes the interaction between the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and the macula densa?
Which statement best describes the interaction between the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and the macula densa?
What is the effect of dehydration on kidney function as it relates to AVP?
What is the effect of dehydration on kidney function as it relates to AVP?
What is the primary function of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in sodium reabsorption?
What is the primary function of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in sodium reabsorption?
Which of the following substances is completely reabsorbed in a normal individual in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Which of the following substances is completely reabsorbed in a normal individual in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Which part of the loop of Henle is permeable to water but not ions?
Which part of the loop of Henle is permeable to water but not ions?
What is the primary role of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
What is the primary role of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
Which mechanism allows sodium and glucose to be reabsorbed together in the PCT?
Which mechanism allows sodium and glucose to be reabsorbed together in the PCT?
What happens in the thick ascending loop of Henle with regards to sodium reabsorption?
What happens in the thick ascending loop of Henle with regards to sodium reabsorption?
How does the countercurrent system work in the loop of Henle?
How does the countercurrent system work in the loop of Henle?
What is a significant effect of loop diuretics in the nephron?
What is a significant effect of loop diuretics in the nephron?
What occurs at the macula densa in response to decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
What occurs at the macula densa in response to decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
What typically happens to water as it follows sodium during its reabsorption?
What typically happens to water as it follows sodium during its reabsorption?
How much sodium is typically reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
How much sodium is typically reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
What is the effect of using both loop and thiazide diuretics together?
What is the effect of using both loop and thiazide diuretics together?
What role does the sodium-hydrogen exchanger play in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
What role does the sodium-hydrogen exchanger play in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Flashcards
Glomerular filtration
Glomerular filtration
The process by which substances from the blood are filtered into the nephron.
Secretion
Secretion
The movement of substances from the blood into the tubular lumen.
Reabsorption
Reabsorption
The movement of substances from the tubular lumen back into the blood.
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macula Densa
Macula Densa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apical membrane
Apical membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basolateral membrane
Basolateral membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
LAB
LAB
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the DCT?
What is the function of the DCT?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is sodium reabsorbed in the DCT?
How is sodium reabsorbed in the DCT?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is calcium reabsorption regulated in the DCT?
How is calcium reabsorption regulated in the DCT?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the collecting tubule?
What is the function of the collecting tubule?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do intercalated cells contribute to acid-base balance in the collecting tube?
How do intercalated cells contribute to acid-base balance in the collecting tube?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does AVP affect water reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
How does AVP affect water reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does aldosterone influence sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
How does aldosterone influence sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the countercurrent system work with AVP to concentrate urine?
How does the countercurrent system work with AVP to concentrate urine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium Reabsorption
Sodium Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium-Potassium ATPase Pump
Sodium-Potassium ATPase Pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
PCT Functions
PCT Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
PCT Reabsorption Mechanisms
PCT Reabsorption Mechanisms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle
Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle Function
Loop of Henle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle: Permeabilities
Loop of Henle: Permeabilities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Countercurrent System
Countercurrent System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
DCT Reabsorption
DCT Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renin-Angiotensin System
Renin-Angiotensin System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop Diuretics
Loop Diuretics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide Diuretics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Combined Diuretic Use
Combined Diuretic Use
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Nephron Segments and Reabsorption Mechanisms
-
Three Biological Processes: Glomerular filtration, secretion, and reabsorption are fundamental to kidney function.
-
Filtration and Tubular System: The lecture traces the filtrate through nephron segments, highlighting reabsorption percentages at specific locations.
-
Reabsorption Locations (and percentages):
- Glomerulus: Filtration
- Bowman's capsule: Filtrate collection
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): 67% reabsorption
- Descending Loop of Henle: Water reabsorption
- Thick Ascending Loop of Henle: 25% reabsorption
- Macula Densa: Tubuloglomerular feedback
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): 5% reabsorption
- Collecting Tubule: 3% reabsorption
-
Kidney Function Overview:
- Kidneys receive 20% of cardiac output.
- Filter almost everything except large components (like RBCs and proteins).
- Reabsorption is vital to retain necessary substances.
- Excretion only of waste.
- Kidney performs filtration, reabsorption, & secretion.
Reabsorption Process and Terminology
- Reabsorption: Substances move from the tubular system to the vasculature.
- Fish Analogy: Used to visualize substance movement.
- Tubular and Capillary System: A cross-section illustrates the process.
- Lumen: Hollow space in the tubular system.
- Apical membrane: Tubule side.
- Basolateral membrane: Opposite to the lumen
- LAB (Acronym): Lumen, Apical membrane, Basolateral membrane.
Sodium Reabsorption
- Sodium Movement: Sodium moves from lumen to the tubular cell across the apical membrane.
- Sodium-Potassium ATPase Pump: Located on the basolateral membrane, it pumps sodium out of the cell (requiring ATP). This creates a negative intracellular environment, drawing sodium in from the tubule.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- Location: First segment after Bowman's capsule.
- Function: Major site of fluid and solute reabsorption (67%).
- PCT Reabsorbates: Sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, water, calcium, monohydrogen phosphate, sulfate, glucose, and amino acids.
- Glucose: Completely reabsorbed under normal conditions; therefore, no glucose in urine
- Other functions: Sodium reabsorption, glucose reabsorption, maintaining acid-base balance, and regulating calcium and phosphate.
- Secretes: Hydrogen ions.
- Excretes: Endogenous and exogenous solutes, including drugs.
Reabsorption Mechanisms (PCT)
- Glucose & Sodium: Reabsorbed into the vasculature.
- Hydrogen: Secreted in exchange for sodium.
- Water: Follows sodium osmotic pressure.
- Aquaporins: Water channels allow water to enter cells.
Loop of Henle
- U-shaped segment following the PCT
- Two parts:
- Descending Loop: Permeable to water but not ions.
- Thick Ascending Loop: Permeable to ions but not water.
- Function: Create hyperosmotic interstitium in the medulla.
- Thick Ascending Loop Reabsorption: 25% filtered sodium. Active transport of sodium into interstitium.
- Countercurrent System: Opposite flow of blood and filtrate.
- Sodium Gradient: Concentrates sodium at the bottom; essential for urine concentration.
- Thin Descending Loop of Henle: only permeable to water.
- Thick Ascending Loop of Henle:
-Sodium-potassium ATPase on the basolateral membrane.
-Sodium Potassium Chloride co-transporter in the apical membrane pulls in 3 ions.
- Chloride is a limiting component for this transporter. -Sodium is pumped into vasculature. -K+ channel on apical membrane returns K+. -Cl- channel on basolateral membrane returns Cl- to vasculature.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- Location: After the loop of Henle, at macula densa to connecting tubule.
- Function: Active regulation of calcium excretion.
- Fine control of salt and water excretion.
- Reabsorption: 5-8% filtered sodium and chloride through the sodium-chloride co-transporter.
- Role in blood pressure regulation
- Combined diuretics: loop and thiazides can be used for conditions such as heart failure. Careful monitoring is necessary.
Tubuloglomerular Feedback (TGF)
- Macula Densa: Monitoring of sodium & chloride delivery.
- Decreased GFR: less sodium and chloride to macula densa leads to: -Prostaglandin & renin production. -Angiotensin II stimulated vasoconstriction of efferent arteriole. -Increase in hydraulic pressure and GFR.
Detailed Look at the DCT
- Sodium-potassium ATPase: On the basolateral membrane.
- Sodium-chloride co-transporter: On apical membrane; inhibited by thiazide diuretics.
- Calcium reabsorption: Regulated by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D.
- Calcium-binding protein: Aids calcium reabsorption.
Collecting Tubule
- Final segment: Receives filtrate from multiple nephron segments.
- Intercalated cells: Secrete hydrogen ions & bicarbonate; reabsorb potassium.
- Reabsorption: 3-4% filtrate.
- Water permeability: Relatively impermeable to water unless aquaporins present (controlled by arginine vasopressin (AVP).
- Sodium channels: Inserted by aldosterone.
- ANP (Atrial Natriuretic Peptide): Inhibits sodium reabsorption.
- AVP (arginine vasopressin): Increases water reabsorption by inserting aquaporins.
Water Reabsorption in the Collecting Tubule
- Countercurrent System: Creates sodium gradient (highest in medulla).
- AVP: Inserts aquaporins, promoting water movement to the interstitium, concentrating urine during dehydration or low blood pressure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.