Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following muscles has its origin from the body of the hyoid bone?
Which of the following muscles has its origin from the body of the hyoid bone?
- Omohyoid muscle
- Thyrohyoid muscle
- Sternohyoid muscle (correct)
- Sternothyroid muscle
Which muscle group is subdivided into medial or prevertebral group and lateral group?
Which muscle group is subdivided into medial or prevertebral group and lateral group?
- The lateral group
- Infrahyoid muscles
- The posterior group (correct)
- The anterior group
What is the function of the Omohyoid muscle?
What is the function of the Omohyoid muscle?
- Elevates the hyoid bone
- Depresses the hyoid bone (correct)
- Elevates the larynx
- Depresses the larynx
Which nerve supply all infrahyoid muscles?
Which nerve supply all infrahyoid muscles?
Where does the Sternothyroid muscle insert?
Where does the Sternothyroid muscle insert?
What is the function of the Sternothyroid muscle?
What is the function of the Sternothyroid muscle?
Where does the Thyrohyoid muscle originate?
Where does the Thyrohyoid muscle originate?
What is the function of the Thyrohyoid muscle?
What is the function of the Thyrohyoid muscle?
Which muscle forms the lateral boundary of the submandibular triangle?
Which muscle forms the lateral boundary of the submandibular triangle?
What is the name of the triangle bounded by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, omohyoid muscle, and digastric muscle?
What is the name of the triangle bounded by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, omohyoid muscle, and digastric muscle?
Which nerve is found in the occipital triangle?
Which nerve is found in the occipital triangle?
What is the name of the muscle that forms the floor of the submandibular triangle?
What is the name of the muscle that forms the floor of the submandibular triangle?
Which structure is not found in the carotid triangle?
Which structure is not found in the carotid triangle?
Which muscle forms the lateral boundary of the omotracheal triangle?
Which muscle forms the lateral boundary of the omotracheal triangle?
What is the name of the triangle that contains the thyroid gland?
What is the name of the triangle that contains the thyroid gland?
Which nerve is found in the submandibular triangle?
Which nerve is found in the submandibular triangle?
At what level does the external carotid artery pass through the parotid gland and terminate?
At what level does the external carotid artery pass through the parotid gland and terminate?
Which nerve does the superior laryngeal artery pierce the thyrohyoid membrane with?
Which nerve does the superior laryngeal artery pierce the thyrohyoid membrane with?
What is the relation of the external carotid artery to the internal jugular vein in the carotid triangle?
What is the relation of the external carotid artery to the internal jugular vein in the carotid triangle?
Which artery supplies the middle part of the larynx?
Which artery supplies the middle part of the larynx?
What is the relation of the external carotid artery to the pharynx in the carotid triangle?
What is the relation of the external carotid artery to the pharynx in the carotid triangle?
Which muscle is the external carotid artery deep to within the parotid gland?
Which muscle is the external carotid artery deep to within the parotid gland?
What is the main artery that supplies the brain and spinal cord?
What is the main artery that supplies the brain and spinal cord?
How many branches does the external carotid artery give off?
How many branches does the external carotid artery give off?
Which artery supplies the thyroid gland?
Which artery supplies the thyroid gland?
Which nerve does the superior thyroid artery descend with?
Which nerve does the superior thyroid artery descend with?
What is the main vein of the neck?
What is the main vein of the neck?
What is the branch of the thyrocervical trunk that supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the branch of the thyrocervical trunk that supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the branch of the costocervical trunk that supplies the intercostal region?
What is the branch of the costocervical trunk that supplies the intercostal region?
What is the vein that is formed by the union of the internal jugular vein and the subclavian vein?
What is the vein that is formed by the union of the internal jugular vein and the subclavian vein?
Which artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk?
Which artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk?
What is the origin of the internal jugular vein?
What is the origin of the internal jugular vein?
What is the origin of the stylohyoid muscle?
What is the origin of the stylohyoid muscle?
What is the function of the muscle that originates from the mastoid process of the temporal bone?
What is the function of the muscle that originates from the mastoid process of the temporal bone?
What is the innervation of the mylohyoid muscle?
What is the innervation of the mylohyoid muscle?
What is the insertion of the muscle that originates from the mastoid process of the temporal bone?
What is the insertion of the muscle that originates from the mastoid process of the temporal bone?
What is the function of the middle group of muscles when acting together?
What is the function of the middle group of muscles when acting together?
What is the origin of the muscle that inserts into the body of the hyoid bone?
What is the origin of the muscle that inserts into the body of the hyoid bone?
What is the innervation of the muscle that originates from the mastoid process of the temporal bone?
What is the innervation of the muscle that originates from the mastoid process of the temporal bone?
What is the function of the mylohyoid muscle?
What is the function of the mylohyoid muscle?
What is the pathway of lymph collected from the deep cervical nodes?
What is the pathway of lymph collected from the deep cervical nodes?
What is the relation of the pharynx to the alimentary and the respiratory systems?
What is the relation of the pharynx to the alimentary and the respiratory systems?
What is the branch that supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the branch that supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the course of the pharynx?
What is the course of the pharynx?
What is the length of the pharynx?
What is the length of the pharynx?
What is the relationship between the external carotid artery and the internal jugular vein in the carotid triangle?
What is the relationship between the external carotid artery and the internal jugular vein in the carotid triangle?
Which branch of the thyrocervical trunk supplies the thyroid gland?
Which branch of the thyrocervical trunk supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the course of the superior laryngeal artery?
What is the course of the superior laryngeal artery?
What is the main vein of the neck?
What is the main vein of the neck?
What is the relationship between the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus?
What is the relationship between the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus?
What is the course of the subclavian artery?
What is the course of the subclavian artery?
Which of the following is a branch of the neck?
Which of the following is a branch of the neck?
What is the relation of the cranial nerves to the neck?
What is the relation of the cranial nerves to the neck?
What is the organization of the lymphatic drainage of the neck?
What is the organization of the lymphatic drainage of the neck?
Which cervical fascia gives off septa that can be subdivided into five parts?
Which cervical fascia gives off septa that can be subdivided into five parts?
What is the relationship between the pretracheal fascia and the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia?
What is the relationship between the pretracheal fascia and the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia?
Which muscle is enclosed by the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia?
Which muscle is enclosed by the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia?
What is the composition of the superficial cervical fascia?
What is the composition of the superficial cervical fascia?
How many parts can the septa of the deep cervical fascia be subdivided into?
How many parts can the septa of the deep cervical fascia be subdivided into?
What is the level at which the internal carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery?
What is the level at which the internal carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery?
What is the relationship between the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery in the neck?
What is the relationship between the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery in the neck?
What is the course of the internal carotid artery within the carotid canal?
What is the course of the internal carotid artery within the carotid canal?
What is the relationship between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein in the neck?
What is the relationship between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein in the neck?
What is the termination of the internal carotid artery?
What is the termination of the internal carotid artery?
What is the function of the auricular nerve?
What is the function of the auricular nerve?
What is the relation of the vagus nerve to the internal jugular vein in the neck?
What is the relation of the vagus nerve to the internal jugular vein in the neck?
What is the course of the vagus nerve in the neck?
What is the course of the vagus nerve in the neck?
What is the branch of the vagus nerve that arises from the superior vagal ganglion?
What is the branch of the vagus nerve that arises from the superior vagal ganglion?
What is the structure that the vagus nerve leaves the skull through?
What is the structure that the vagus nerve leaves the skull through?
What type of joint is the cricothyroid joint?
What type of joint is the cricothyroid joint?
What is the function of the conus elasticus?
What is the function of the conus elasticus?
What is the relation between the quadangular membrane and the aryepiglottic fold?
What is the relation between the quadangular membrane and the aryepiglottic fold?
What is the function of the thyrohyoid membrane?
What is the function of the thyrohyoid membrane?
What is the course of the cricothyroid joint?
What is the course of the cricothyroid joint?
What is the relation between the conus elasticus and the vocal fold?
What is the relation between the conus elasticus and the vocal fold?
What is the type of joint that the crico-arytenoid joint is?
What is the type of joint that the crico-arytenoid joint is?
What is the function of the quadangular membrane?
What is the function of the quadangular membrane?
What is the relation between the thyrohyoid membrane and the hyoid bone?
What is the relation between the thyrohyoid membrane and the hyoid bone?
What is the course of the quadangular membrane?
What is the course of the quadangular membrane?
What is the boundary of the Supraclavicular triangle?
What is the boundary of the Supraclavicular triangle?
Which of the following structures is found in the Anterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
Which of the following structures is found in the Anterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
What is the muscle that forms the posterior boundary of the Anterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
What is the muscle that forms the posterior boundary of the Anterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
Which of the following structures is found in the Supraclavicular triangle?
Which of the following structures is found in the Supraclavicular triangle?
What is the boundary of the Posterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
What is the boundary of the Posterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
What is the location of the groove for the subclavian vein?
What is the location of the groove for the subclavian vein?
What is the relation of the internal carotid artery to the external carotid artery in the neck?
What is the relation of the internal carotid artery to the external carotid artery in the neck?
What is the boundary of the Anterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
What is the boundary of the Anterior fissure of the scalene muscles?
Which nerve hooks around the external carotid artery?
Which nerve hooks around the external carotid artery?
Which of the following nerves is a cutaneous branch from the cervical plexus?
Which of the following nerves is a cutaneous branch from the cervical plexus?
What is the branch of the external carotid artery that supplies the middle ear?
What is the branch of the external carotid artery that supplies the middle ear?
What is the level at which the external carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery?
What is the level at which the external carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery?
What is the branch of the posterior auricular artery that supplies the middle ear?
What is the branch of the posterior auricular artery that supplies the middle ear?
What is the direction in which the external carotid artery runs?
What is the direction in which the external carotid artery runs?
What is the region through which the internal carotid artery passes?
What is the region through which the internal carotid artery passes?
What is the branch of the external carotid artery that supplies the scalp?
What is the branch of the external carotid artery that supplies the scalp?
What is the primary tributary of the sigmoid sinus?
What is the primary tributary of the sigmoid sinus?
Which vein is formed by the union of the posterior branch of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein?
Which vein is formed by the union of the posterior branch of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein?
What is the destination of the anterior jugular vein?
What is the destination of the anterior jugular vein?
What is the function of the jugular arch?
What is the function of the jugular arch?
Which of the following veins is not a tributary of the internal jugular vein?
Which of the following veins is not a tributary of the internal jugular vein?
What is the relationship between the vertebral vein and the deep cervical vein?
What is the relationship between the vertebral vein and the deep cervical vein?
Which of the following veins drains into the subclavian vein?
Which of the following veins drains into the subclavian vein?
What is the primary function of the posterior auricular vein?
What is the primary function of the posterior auricular vein?
What is the main difference between the left and right jugular trunks?
What is the main difference between the left and right jugular trunks?
What is the location of the deep cervical nodes in relation to the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
What is the location of the deep cervical nodes in relation to the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
What is the length of the pharynx?
What is the length of the pharynx?
What is the width of the pharynx at its upper part?
What is the width of the pharynx at its upper part?
What is the level at which the pharynx becomes the upper part of the oesophagus?
What is the level at which the pharynx becomes the upper part of the oesophagus?
What is the function of the pharynx?
What is the function of the pharynx?
What is the direction of the pharynx?
What is the direction of the pharynx?
What is the greatest width of the pharynx?
What is the greatest width of the pharynx?
What is the primary purpose of a cricothyrotomy?
What is the primary purpose of a cricothyrotomy?
What type of muscle is found in the posterior wall of the trachea?
What type of muscle is found in the posterior wall of the trachea?
Which nerve branch supplies the mucous membrane of the infraglottic portion of the larynx?
Which nerve branch supplies the mucous membrane of the infraglottic portion of the larynx?
What is the anatomical landmark at which the trachea begins?
What is the anatomical landmark at which the trachea begins?
What is the purpose of a tracheostomy?
What is the purpose of a tracheostomy?
What type of cartilage makes up the C-shaped rings of the trachea?
What type of cartilage makes up the C-shaped rings of the trachea?
Which structure lies posterior to the trachea in the neck?
Which structure lies posterior to the trachea in the neck?
What is the name of the muscle that is not supplied by the inferior laryngeal nerve?
What is the name of the muscle that is not supplied by the inferior laryngeal nerve?
Which of the following nuclei is responsible for visceral sensory function?
Which of the following nuclei is responsible for visceral sensory function?
What is the total number of nuclei of the vagal nerve?
What is the total number of nuclei of the vagal nerve?
Which type of fibers supply the heart, lungs, and the alimentary canal near to the splenic flexure?
Which type of fibers supply the heart, lungs, and the alimentary canal near to the splenic flexure?
What is the location of the superior parathyroid glands?
What is the location of the superior parathyroid glands?
What is the function of the special visceral motor fibers?
What is the function of the special visceral motor fibers?
What is the function of the general visceral sensory fibers?
What is the function of the general visceral sensory fibers?
What is the location of the inferior parathyroid glands?
What is the location of the inferior parathyroid glands?
How many types of fibers does the vagal nerve consist of?
How many types of fibers does the vagal nerve consist of?
What is the function of the special visceral sensory fibers?
What is the function of the special visceral sensory fibers?
What is the total number of pairs of parathyroid glands?
What is the total number of pairs of parathyroid glands?
Flashcards
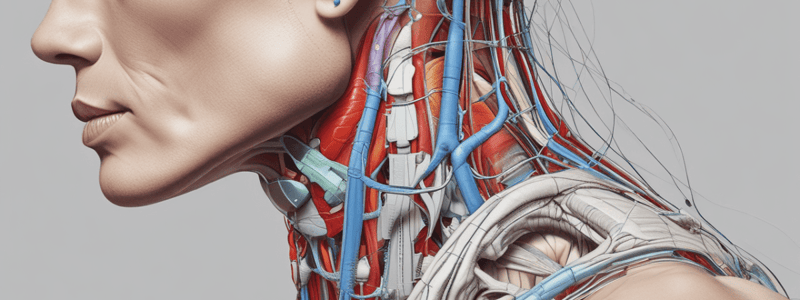
External Carotid Artery (ECA)
External Carotid Artery (ECA)
Divides into maxillary and superficial temporal arteries; located in carotid triangle and parotid gland.
Internal Carotid Artery (ICA)
Internal Carotid Artery (ICA)
Supplies the brain and orbit; originates from the common carotid artery bifurcation.
External Jugular Vein
External Jugular Vein
Formed by the union of the posterior branch of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein.
Cricothyrotomy
Cricothyrotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior Laryngeal Nerve
Inferior Laryngeal Nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea
Trachea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tracheostomy
Tracheostomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Jugular Vein
Anterior Jugular Vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital Artery
Occipital Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Auricular Artery
Posterior Auricular Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Triangle of the Neck
Anterior Triangle of the Neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Triangle of the Neck
Posterior Triangle of the Neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suprahyoid Muscles
Suprahyoid Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infrahyoid Muscles
Infrahyoid Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial Lymph Nodes of Neck
Superficial Lymph Nodes of Neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Lymph Nodes of Neck
Deep Lymph Nodes of Neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharynx
Pharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
External Carotid Artery (ECA)
- Divides into two terminal branches: maxillary and superficial temporal arteries at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage
- Located in the carotid triangle and within the parotid gland
- Laterally to the internal carotid artery (ICA) and medially to the CN VII and retromandibular vein
- Gives off eight branches, categorized into two groups:
- Anterior aspect:
- Superior thyroid artery
- Superior laryngeal artery
- Cricothyroid artery
- Posterior aspect:
- Vertebral artery
- Internal thoracic artery
- Thyrocervical trunk
- Costocervical trunk
- Anterior aspect:
Internal Carotid Artery (ICA)
- Supplies the greater part of the brain and the contents of the orbit
- Origin: bifurcation of the common carotid artery at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage (C6)
- End: terminates intracranially in the middle cranial fossa, medially to the anterior clinoid process of the sphenoid bone
- Course: ascends to the base of the skull, first located posterolaterally to the external carotid artery, then medially to that artery
- Relations:
- Within the neck: lies within the carotid sheath with the internal jugular vein laterally and the vagus nerve behind
- In the carotid triangle: lies laterally and posteriorly to the ECA, posteriorly and medially to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and anteriorly to the prevertebral fascia and the sympathetic trunk
Veins of the Neck
- Three main veins:
- Internal jugular vein
- External jugular vein
- Anterior jugular vein
- Internal jugular vein:
- Arises as the continuation of the sigmoid venous sinus
- Ascends through the neck and behind the medial end of the clavicle, where it is joined by the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein
- Relations:
- Laterally by the posterior belly of the digastric muscle
- Medially by the anterior belly of the digastric muscle
- Inferiorly by the mandible
- Floor: formed by the mylohyoid muscle, hyoglossus muscle, and the pharynx
Triangles of the Neck
- Anterior triangle of the neck:
- Submandibular triangle
- Carotid triangle
- Muscular triangle or omotracheal triangle
- Submental triangle
- Posterior triangle of the neck:
- Occipital triangle
- Supraclavicular triangle
- Omoclavicular triangle
- Greater supraclavicular fossa
- Relations:
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Omohyoid muscle
- Digastric muscle
- Scalene muscles
Muscles of the Neck
- Suprahyoid muscles:
- Mylohyoid muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Digastric muscle
- Infrahyoid muscles:
- Omohyoid muscle
- Sternohyoid muscle
- Sternothyroid muscle
- Thyrohyoid muscle
- Posterior group:
- Longus colli muscle
- Longus capitis muscle
- Rectus capitis anterior muscle
- Lateral group
Lymphatic Drainage of the Neck
- Groups of superficial nodes:
- Submandibular nodes
- Submental nodes
- Anterior cervical nodes
- Posterior cervical nodes
- Groups of deep nodes:
- Deep cervical nodes
- Jugular trunk
- Thoracic duct
- Right lymphatic duct
Pharynx
- Muscular tube extending from the base of the skull to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage of the larynx
- Subdivided into three regions:
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
- Relations:
- Base of the skull
- Lower border of the cricoid cartilage
- Level of the 6th cervical vertebra### Emergency Therapy for Asphyxiation
- In case of object entering the larynx, emergency therapy is required to supply air to the trachea and lungs
- A large needle should be inserted into the median cricothyroid ligament, a procedure called cricothyrotomy
Inferior Laryngeal Nerve
- Inferior laryngeal nerve (nervus laryngeus inferior) is a branch from the recurrent laryngeal nerve (branch of vagal nerve)
- Supplies mucous of infraglottic portion of the larynx and all intrinsic muscles (except cricothyroid muscle)
Trachea
- Cervical portion of trachea is a tube composed of cartilages and membranes
- Maintained by a series of C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage, incomplete posteriorly
- Posteriorly, across the gap of each cartilage, is a thin coat of unstriated muscle (trachealis), called membranous wall
- Cartilages united by fibro-elastic membranes, named anular ligaments
- Begins at the level of the 6th cervical vertebra (at the lower border of the cricoid cartilage)
- Anteriorly situated is the thyroid gland and posteriorly the trachea lies on the oesophagus
- Tracheostomy is a surgical procedure in which an opening in the trachea is made to allow patients in bad condition ventilation by respirator
Tributaries
- Sigmoid sinus (sinus sigmoideus)
- Occipital sinus (sinus occipitalis)
- Inferior petrosal sinus (sinus petrosus inferior)
- Occipital vein (vena occipitalis)
- Facial vein (vena facialis)
- Pharyngeal plexus (plexus pharyngeus)
- Lingual vein (vena lingualis)
- Superior and inferior thyroid veins (vena thyroidea superior et inferior)
- Thoracic duct (ductus thoracicus) on the left side
- Right lymphatic duct (ductus lymphaticus dexter) on the right side
External Jugular Vein
- A superficial vein formed behind the angle of the mandible by the union of the posterior branch of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein
- May enter either the internal jugular, brachiocephalic, or subclavian veins
- Tributaries:
- Posterior auricular vein (vena auricularis posterior)
- Occipital vein (vena occipitalis)
- Suprascapular vein (vena suprascapular)
- Transverse cervical vein (vena transversa colli)
Anterior Jugular Vein
- Begins below the hyoid bone to enter the external jugular or subclavian veins
- Jugular arch unites the two anterior jugular veins
Occipital Artery
- Relations:
- Arises at the same level as the facial artery
- Runs backwards across carotid sheath where the CN XII hooks around it
- Branches:
- Branches for muscles (neck and suboccipital)
- Mastoid branch
- Auricular branch
- Occipital branch
Posterior Auricular Artery
- Relations:
- Passes along the upper border of the posterior belly of the digastric
- Passes through the apical part of the parotid gland to the lateral aspect of the scalp
- Branches:
- Auricular branch
- Posterior tympanic artery - to the middle ear
- Branches to the muscles
- Stylomastoid artery
- Occipital branch
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.