Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which scalene muscle is primarily responsible for lateral flexion of the neck?
Which scalene muscle is primarily responsible for lateral flexion of the neck?
- Levator scapulae
- Anterior scalene
- Middle scalene (correct)
- Posterior scalene
Which group of muscles is involved in neck extension?
Which group of muscles is involved in neck extension?
- Superficial group (SCM)
- Prevertebral group
- Scalenes
- Suboccipital group (correct)
Which muscle is primarily responsible for neck flexion?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for neck flexion?
- Sternocleidomastoid (correct)
- Longus colli
- Platysma
- Digastric
The deep posterior neck muscles include which of the following?
The deep posterior neck muscles include which of the following?
What is the primary function of the suprahyoid muscles?
What is the primary function of the suprahyoid muscles?
Which scalene muscle assists in stabilization of the frontal plane?
Which scalene muscle assists in stabilization of the frontal plane?
Which muscle is classified as an infrahyoid muscle?
Which muscle is classified as an infrahyoid muscle?
Which muscle action is NOT performed by the splenius group?
Which muscle action is NOT performed by the splenius group?
Which of the following muscles is located superficial to the suboccipital group?
Which of the following muscles is located superficial to the suboccipital group?
What are the two bellies of the digastric muscle?
What are the two bellies of the digastric muscle?
What is the function of the anterior scalene muscle?
What is the function of the anterior scalene muscle?
The prevertebral muscles are located anterior to which structures?
The prevertebral muscles are located anterior to which structures?
Which of the following is NOT a muscle group found in the neck?
Which of the following is NOT a muscle group found in the neck?
Which of the following muscles contributes to ipsilateral rotation of the neck?
Which of the following muscles contributes to ipsilateral rotation of the neck?
Which function is associated with the platysma muscle?
Which function is associated with the platysma muscle?
Which nerve innervates the palatoglossus muscle?
Which nerve innervates the palatoglossus muscle?
What is a common feature shared by all vertebrae?
What is a common feature shared by all vertebrae?
Which cervical vertebra is characterized by having no body?
Which cervical vertebra is characterized by having no body?
What structure does the C2 vertebra, known as the Axis, possess that is significant in its anatomy?
What structure does the C2 vertebra, known as the Axis, possess that is significant in its anatomy?
Which term describes the bony projection that typically facilitates articulation with adjacent vertebrae?
Which term describes the bony projection that typically facilitates articulation with adjacent vertebrae?
What distinguishes cervical vertebrae from other types of vertebrae?
What distinguishes cervical vertebrae from other types of vertebrae?
Which part of a vertebra forms the central opening through which the spinal cord passes?
Which part of a vertebra forms the central opening through which the spinal cord passes?
How many cervical vertebrae are there in the human body?
How many cervical vertebrae are there in the human body?
What is a primary function of the transverse foramina found in cervical vertebrae?
What is a primary function of the transverse foramina found in cervical vertebrae?
What is the primary function of costal facets on thoracic vertebrae?
What is the primary function of costal facets on thoracic vertebrae?
Which vertebrae have mammillary processes that provide attachment for deep back muscles?
Which vertebrae have mammillary processes that provide attachment for deep back muscles?
What distinguishes the sacrum in terms of its structure?
What distinguishes the sacrum in terms of its structure?
Which part of the lumbar vertebrae is specifically associated with muscle attachment?
Which part of the lumbar vertebrae is specifically associated with muscle attachment?
In the thoracic vertebrae, where are the inferior costal facets located?
In the thoracic vertebrae, where are the inferior costal facets located?
Which of the following structures is NOT associated with the sacrum?
Which of the following structures is NOT associated with the sacrum?
What is the role of the posterior and anterior sacral foramina?
What is the role of the posterior and anterior sacral foramina?
Which vertebral group articulates directly with ribs?
Which vertebral group articulates directly with ribs?
What is the main function of the intervertebral discs?
What is the main function of the intervertebral discs?
Which region of the vertebral column consists of primary curvatures?
Which region of the vertebral column consists of primary curvatures?
What type of joint is found between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae?
What type of joint is found between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae?
Which vertebral joint permits gliding movements but limits flexion and extension?
Which vertebral joint permits gliding movements but limits flexion and extension?
What characteristic is true about the nucleus pulposus of an intervertebral disc?
What characteristic is true about the nucleus pulposus of an intervertebral disc?
How many fused coccygeal vertebrae are typically found in adults?
How many fused coccygeal vertebrae are typically found in adults?
Which of the following describes the lordosis curvature?
Which of the following describes the lordosis curvature?
What structure is located on the lateral aspect of the sacrum?
What structure is located on the lateral aspect of the sacrum?
Study Notes
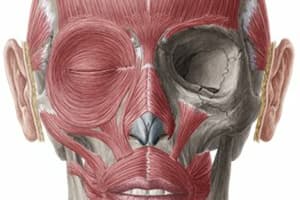
Superficial muscles
- The platysma muscle is a muscle of facial expression.
- The sternocleidomastoid is the primary neck flexor.
Suprahyoid muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles attach to the hyoid bone from above the hyoid bone.
- Suprahyoid muscles elevate the hyoid bone, depress the mandible, and act on the floor of the oral cavity.
- Suprahyoid muscles include the digastric, stylohoid, mylohyoid, and geniohyoid muscles.
- The digastric has both anterior and posterior bellies.
Infrahyoid muscles
- Infrahyoid muscles attach to the hyoid bone from below the hyoid bone.
- Infrahyoid muscles depress the hyoid bone and act on the larynx.
- Infrayoid muscles include the omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid, and thyrohyoid muscles.
- The omohyoid has both superior and interior bellies.
Prevertebral muscles
- Prevertebral muscles are deep muscles located immediately anterior to the vertebral bodies.
- Prevertebral muscles include the longus capitis, longus colli, rectus capitis anterior, and rectus capitis lateralis.
Muscles of the lateral neck
- The lateral neck contains three scalene muscles: anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene.
- The scalene muscles produce lateral flexion with ipsilateral action (same side of the body).
- The scalenes also stabilize in the frontal plane with bilateral action (both sides of the body).
Muscles in the posterior neck
- Muscles in the posterior neck extend the neck, including the trapezius, levator scapulae, splenius capitis/cervicis, semispenalis capitis/cervicis, and longissimus capitis/cervicis.
- These muscles also perform lateral flexion and rotation.
Suboccipital Muscles
- The suboccipital muscles are the deepest posterior neck muscles.
- The suboccipital muscles include the rectus capitis posterior major, rectus capitis posterior minor, obliquus capitis superior, and obliquus capitis inferior.
Summary of Muscle Actions in the Neck
- The muscles of the neck can be categorized depending on the plane of action.
- Action in the median plane includes flexion and extension.
- Action in the transverse plane includes ipsilateral and contralateral rotation.
- Action in the frontal plane includes lateral flexion.
Vertebrae
- All vertebrae are irregular bones sharing common features: body, transverse processes, spinous process, vertebral arch, vertebral foramen, and articular facets.
- The vertebral arch is composed of the lamina and the pedicle.
- Vertebral foramen is the hole in the center of the vertebra.
- Articular facets are the small, flat surfaces that connect the vertebrae together.
Cervical Vertebrae
- Cervical vertebrae contain transverse foramina and bifid spinous processes.
- The atlas (C1) has no body.
- The axis (C2) has a dens.
- The seventh cervical vertebra (C7) has a larger, non-bifid spinous process and the vertebral prominence.
Thoracic Vertebrae
- The thoracic vertebrae are characterized by costal facets which articulate with ribs.
- Each of the 12 thoracic vertebrae has superior, inferior, and transverse costal facets.
Lumbar Vertebrae
- Lumbar vertebrae are the largest vertebrae.
- Lumbar vertebrae contain mammillary processes which provide attachment sites for deep back muscles.
Sacrum & Coccyx
- The sacrum is composed of five fused sacral vertebrae.
- The sacrum contains lateral, intermediate, and medial crests, anterior and posterior sacral foramina, a sacral hiatus, a sacral horn, an ala, and an auricular surface.
- The coccyx is composed of four fused coccygeal vertebrae.
- The coccyx contains a coccygeal horn.
Vertebral Column
- The vertebral column has 33 stacked vertebrae.
- The cervical vertebrae are the seven most superior vertebrae.
- The thoracic vertebrae are the 12 vertebrae that connect to the ribs.
- The lumbar vertebrae are the five vertebrae located in the lower back.
- The sacrum is composed of five fused vertebrae.
- The coccyx is composed of four fused vertebrae.
- The vertebral column functions to supports body weight and provides bony protection for the spinal cord.
Curvatures
- The curves of the vertebral column aid in weight distribution, shock absorption, and stability.
- The thoracic and sacral regions of the vertebral column are concave anteriorly.
- The cervical and lumbar regions of the vertebral column are concave posteriorly.
- The thoracic and sacral curves are called kyphoses.
- The cervical and lumbar curves are called lordoses.
Intervertebral Joints
- The vertebral column is connected by intervertebral joints, which are categorized as intervertebral symphyses, zygapophyseal joints, atlantoaxial joints, and atlanto-occipital joints.
Intervertebral Symphyses
- Intervertebral symphyses connect the bodies of adjacent vertebrae.
- Intervertebral symphyses are characterized by the presence of an intervertebral disc, which is composed of the anulus fibrosus (outer fibrocartilage ring) and the nucleus pulposus (gelatinous central mass).
Zygapophyseal Joints
- Zygapophyseal joints are also known as facet joints.
- Zygapophyseal joints connect the superior and inferior articular facets of adjacent vertebrae.
- Zygapophyseal joints permit gliding moments but limit flexion and extension of the neck.
Atlantoaxial Joints
- The atlantoaxial joint is between C1 and C2.
Atlanto-occipital Joints
- The atlanto-occipital joint is between C1 and the occipital bone.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the superficial, suprahyoid, infrahyoid, and prevertebral muscles of the head and neck. Test your knowledge on muscle functions, attachments, and classifications, including key muscles such as the sternocleidomastoid and digastric. Perfect for anatomy students seeking to reinforce their understanding.