Podcast
Questions and Answers
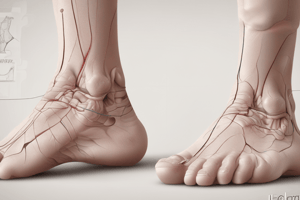
What is Pes Planus Distortion Syndrome?
What is Pes Planus Distortion Syndrome?
- A muscle strain in the calf
- An injury to the anterior tibialis
- A condition characterized by foot supination
- A postural distortion syndrome with flat feet and knock knees (correct)
What is the Gastrocnemius?
What is the Gastrocnemius?
Short muscle
What is the Soleus?
What is the Soleus?
Short muscle
What does the term 'Peroneals' refer to?
What does the term 'Peroneals' refer to?
What are Adductors?
What are Adductors?
What is the Iliotibial Head?
What is the Iliotibial Head?
What is the Hip Flexor Complex?
What is the Hip Flexor Complex?
What is the Biceps Femoris?
What is the Biceps Femoris?
What is the Anterior Tibialis?
What is the Anterior Tibialis?
What is the Posterior Tibialis?
What is the Posterior Tibialis?
What is the Vastus Medialis?
What is the Vastus Medialis?
What are Gluteus Medius/Maximus?
What are Gluteus Medius/Maximus?
What are Hip External Rotators?
What are Hip External Rotators?
What does increased 'Knee Adduction' indicate?
What does increased 'Knee Adduction' indicate?
What does increased 'Foot Pronation' lead to?
What does increased 'Foot Pronation' lead to?
What is 'Ankle Dorsiflexion'?
What is 'Ankle Dorsiflexion'?
What does 'Plantar Fasciitis' refer to?
What does 'Plantar Fasciitis' refer to?
What is the condition referred to as 'Patellar Tendonitis'?
What is the condition referred to as 'Patellar Tendonitis'?
What does 'Low-back Pain' signify?
What does 'Low-back Pain' signify?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Pes Planus Distortion Syndrome
- Characterized by flat feet and knock knees.
- Involves foot pronation, adducted, and internally rotated knees.
Short Muscles Involved
- Gastrocnemius: A muscle located in the calf.
- Soleus: Also a calf muscle, contributes to foot movement.
- Peroneals: Group of muscles on the outer side of the lower leg.
- Adductors: Muscles located in the inner thigh, responsible for adducting the leg.
- Iliotibial Head: Part of the iliotibial band, which stabilizes the knee.
- Hip Flexor Complex: Includes several muscles that help flex the hip.
- Biceps Femoris: One of the hamstring muscles located at the back of the thigh.
Lengthened Muscles Involved
- Anterior Tibialis: Located at the front of the lower leg, responsible for ankle dorsiflexion.
- Posterior Tibialis: Supports the arch of the foot, often lengthened in pes planus.
- Vastus Medialis: Portion of the quadriceps, involved in knee stability.
- Gluteus Medius/Maximus: Key muscles for hip abduction and stability.
- Hip External Rotators: Muscles that assist in rotating the hip outward.
Increased Movement Patterns
- Knee Adduction: Tendency for the knees to move toward each other.
- Knee Internal Rotation: Increased inward rotation of the knee joint.
- Foot Pronation: Increased flattening of the foot arch during movement.
- Foot External Rotation: Adjustment of foot positioning outward.
Decreased Movement Patterns
- Ankle Dorsiflexion: Limited ability to bring the top of the foot toward the shin.
- Ankle Inversion: Reduced movement of the foot twisting inward.
Possible Injuries Associated
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the tissue connecting the heel to the toes.
- Posterior Tibialis Injury: Often associated with overuse or dysfunction in pes planus.
- Patellar Tendonitis: Also known as jumper's knee, inflammation of the patellar tendon.
- Low-back Pain: Common injury due to altered gait and posture from pes planus.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.