Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of skeletal muscles?
What is the primary function of skeletal muscles?
- Enhancing respiratory function
- Facilitating digestion
- Regulating blood flow
- Producing movement and stabilizing joints (correct)
Which type of muscle fibers are primarily involved in endurance activities and slow movements?
Which type of muscle fibers are primarily involved in endurance activities and slow movements?
- Fast-twitch fibers
- Red fibers (correct)
- White fibers
- Pinnate fibers
What characterizes tonic muscles?
What characterizes tonic muscles?
- They are primarily composed of white fibers.
- They are located exclusively in the lower body.
- They are responsible for explosive movements.
- They demonstrate continuous low level of contractile activity. (correct)
Which of the following statements about muscle elasticity is true?
Which of the following statements about muscle elasticity is true?
What type of muscle architecture is designed for strength?
What type of muscle architecture is designed for strength?
Which type of muscle is primarily located in the walls of visceral organs and blood vessels?
Which type of muscle is primarily located in the walls of visceral organs and blood vessels?
Which characteristic distinguishes skeletal muscle from smooth muscle?
Which characteristic distinguishes skeletal muscle from smooth muscle?
What are the layers of fibrous fascia that surround muscle fibers in order from smallest to largest?
What are the layers of fibrous fascia that surround muscle fibers in order from smallest to largest?
What primarily composes muscular fascia?
What primarily composes muscular fascia?
Which property allows skeletal muscle to respond to stimuli?
Which property allows skeletal muscle to respond to stimuli?
Flashcards
Muscle Irritability
Muscle Irritability
The ability of a muscle to respond to a stimulus, like an electrical nerve impulse.
Muscle Contractility
Muscle Contractility
The capacity of a muscle to generate tension between its ends, essentially to become shorter and thicker.
Muscle Relaxation
Muscle Relaxation
The opposite of contraction, where a muscle passively returns to its resting length and tension decreases.
Muscle Distensibility
Muscle Distensibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscular Fascia
Muscular Fascia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Elasticity
Muscle Elasticity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pennate Muscles
Pennate Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parallel Muscles
Parallel Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tonic Muscles
Tonic Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Muscle Classification
- Three types of muscles exist:
- Cardiac muscle tissue is located in the heart.
- Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of visceral organs and blood vessels.
- Skeletal muscle tissue is within skeletal muscles.
- Skeletal muscle makes up approximately 40% to 45% of total body weight.
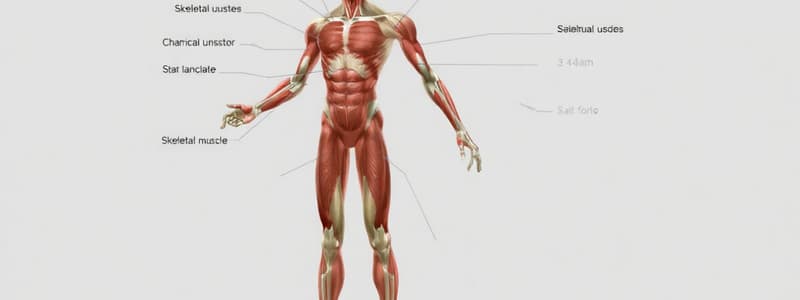
Skeletal Muscle Characteristics
- Skeletal and cardiac muscle appear striated under a microscope, while smooth muscle does not.
- Skeletal muscle is under voluntary control.
- Smooth and cardiac muscle are not under voluntary control.
- A skeletal muscle connects to two bones, crossing the joint between them.
- Most skeletal muscles connect to two bones, but some connect to more than two, or to soft tissue instead of bone.
- Muscle contraction pulls on bony attachments, causing movement.
Muscle Function
- Skeletal muscles are the primary movers of the human body.
- Humans have 640 skeletal muscles, ranging in size and shape from the stapedius in the middle ear to the gluteus maximus.
- Muscles are positioned across joints and connected to bony levers.
- Specific muscles are adapted for appropriate range, direction, and force to meet needs.
- Functions of skeletal muscles include:
- Producing movement
- Stabilizing joints
- Shaping body segments
- Maintaining posture
- Forming supportive walls
Muscular Fascia
- Muscular/deep fascia is the tough fibrous connective tissue that structurally organizes muscles.
- Collagen fibers are the major component, with elastin fibers present in smaller amounts.
- Fascia is consistently composed of collagen, but regions receive specific names based on location.
- Endomysium surrounds individual muscle fibers.
- Perimysium surrounds groups of muscle fibers, creating fascicles.
- Epimysium surrounds the entire muscle.
- Fascia blends, continuing beyond the muscle to connect it to bones.
- Fascial attachments transfer muscle contraction force to bones.
Muscle Fiber Interior
- Muscles are composed of fibers.
- Inner structures include nerves, blood vessels, and the sarcolemma, and various parts of the cytoplasm.
- Fibrous attachments, like tendons, connect muscles to bones.
Skeletal Muscle Properties
- Irritability: The muscle's ability to respond to stimuli.
- Contractility: The muscle's ability to produce tension between its ends.
- Relaxation: The opposite of contraction, releasing tension.
- Distensibility: The muscle's ability to stretch or lengthen up to a physiological limit without damage.
- Elasticity: The muscle's ability to return to its original length after stretching, as long as it hasn't been overstretched.
Muscle Classification
- 2 ways to classify muscles:
- By myoglobin content
- Red: contain more red fibers and are responsible for slow, sustained movements. - An example is anti-gravity muscles.
- White: contain more white fibers and are responsible for rapid, short-duration movements.
- By contractile activity
- Tonic: low-level, prolonged contractions for posture maintenance.
- Phasic: rapid, powerful contractions, involved in movement.
- By the orientation of the pull to the joint structure: - Anterior vs. posterior - Possible axes of motion
- By the number of joints crossed
- One joint muscle
- Two joint muscle
- Multi-joint muscle
- By myoglobin content
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.