Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the anatomy of seminiferous tubules?
What is the anatomy of seminiferous tubules?
Seminiferous tubules are located in the testis, made up of columnar Sertoli cells surrounded by spermatogenic cells on the epithelial interior and stem cells exteriorly.
What is the function of seminiferous tubules?
What is the function of seminiferous tubules?
The seminiferous tubules function to produce sperm, maintain sperm, and store the sperm.
Where is semen produced?
Where is semen produced?
Semen is produced in the seminiferous tubules located inside the testes.
What are the contents of sperm?
What are the contents of sperm?
What is the structure of the epididymis?
What is the structure of the epididymis?
What is the function of the epididymis?
What is the function of the epididymis?
What is the function of estrogen?
What is the function of estrogen?
What is the function of progesterone?
What is the function of progesterone?
What are the chromosome aspects of the sperm and eggs?
What are the chromosome aspects of the sperm and eggs?
What arteries supply the ovaries with blood?
What arteries supply the ovaries with blood?
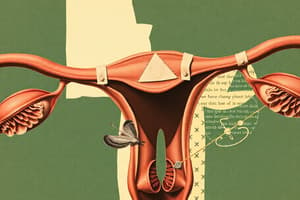
What are the uterine tubes also called?
What are the uterine tubes also called?
What are the three layers of the uterine walls?
What are the three layers of the uterine walls?
What are the three regions of the uterus?
What are the three regions of the uterus?
What is the vagina?
What is the vagina?
What makes up the female external genitalia?
What makes up the female external genitalia?
What do the reproductive organs consist of?
What do the reproductive organs consist of?
What covers the male and female gonads?
What covers the male and female gonads?
What do male gonads (testes) produce?
What do male gonads (testes) produce?
What do female gonads (ovaries) produce?
What do female gonads (ovaries) produce?
What are the functions of the male reproductive system?
What are the functions of the male reproductive system?
What are the functions of the female reproductive system?
What are the functions of the female reproductive system?
What are the male secondary/accessory sex organs?
What are the male secondary/accessory sex organs?
What are the two main types of cells within the seminiferous tubules?
What are the two main types of cells within the seminiferous tubules?
What are the three mechanisms that assist in temperature regulation of the testes?
What are the three mechanisms that assist in temperature regulation of the testes?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Anatomy of Seminiferous Tubules
- Seminiferous tubules located in the testes consist of columnar Sertoli cells and spermatogenic cells.
- Two layers exist: inner epithelial layer (spermatogenic cells) and outer layer (stem cells).
Function of Seminiferous Tubules
- Responsible for the production, maintenance, and storage of sperm.
- Sertoli cells undergo differentiation during meiosis to produce mature sperm.
Semen Production
- Sperm develop within coiled seminiferous tubules in the testes.
- Developmental stages occur from peripheral (least-developed) to lumen (fully-developed) within the tubules.
Contents of Sperm
- Includes citrate, amino acids, flavins, enzymes, fructose, vitamins (C, B12), minerals (calcium, magnesium), and various sugars and acids.
Structure of the Epididymis
- A long, coiled tube that stores and transports sperm from the testes.
- Composed of three sections: head, body, and tail; located at the posterior margin of each testis.
Function of the Epididymis
- Matures and stores immature sperm produced in the testes.
- During arousal, contractions push sperm into the vas deferens.
Function of Estrogen
- Promotes development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as breasts and regulates the menstrual cycle.
- In males, aids in sperm maturation and maintaining libido.
Function of Progesterone
- Thickens the uterine lining to prepare for a fertilized egg.
- Produced by the placenta during pregnancy, maintaining elevated levels throughout.
Chromosome Aspects of Sperm and Eggs
- Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (XX in females, XY in males).
Ovulation
- Release of a mature egg from the ovary, typically around days 14-16 in a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- If unfertilized, the egg is shed during menstruation.
Arteries Supplying the Ovaries
- Ovarian arteries reach the ovaries through the suspensory ligament.
Uterine Tubes (Fallopian Tubes)
- Connect the ovaries to the uterus; approximately 4 inches long.
- Comprise three sections: isthmus, ampulla, infundibulum, and fimbriae.
Layers of Uterine Walls
- Three distinct layers: Perimetrium, Myometrium, and Endometrium.
Regions of the Uterus
- Consists of three regions: Fundus, Body, and Cervix.
Vagina Structure
- A thin-walled tube about 4 inches long, located between the rectum and bladder.
- Contains various structures including vaginal fornix, orifice, rugae, and hymen.
Female External Genitalia
- Composed of the mons pubis, labia (majora and minora), clitoris, and vestibule structures.
Reproductive Organs Composition
- Comprised of primary sex organs (gonads) and accessory (secondary) organs.
Gonads Connective Tissue
- Male and female gonads are covered by tunica albuginea, a connective tissue.
Male Gonadal Production
- Testes produce sperm and testosterone, key for male reproductive function.
Female Gonadal Output
- Ovaries produce eggs, estrogen, and progesterone critical for female reproduction.
Male Reproductive System Functions
- Produces sperm (gametes), expels and delivers them to the female system, and secretes testosterone.
Female Reproductive System Functions
- Produces eggs, secretes estrogen and progesterone, houses and nurtures the embryo, and delivers the fetus.
Male Secondary/Accessory Sex Organs
- Includes the scrotum, male duct system (vas deferens), penis, and accessory glands (prostate, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral glands).
Types of Cells in Seminiferous Tubules
- Contains germ cells (sperm precursors) and sustentocytes (Sertoli cells).
Testes Temperature Regulation
- Regulated by the dartos muscle, cremaster muscles, and pampiniform venous plexus to maintain optimal sperm production conditions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.