Podcast
Questions and Answers
What significant event highlighted the strategic importance of the Middle East during World War One?
What significant event highlighted the strategic importance of the Middle East during World War One?
- Discovery of oil (correct)
- Creation of independent states
- Versailles Treaty
- Treaty of Seves
Which treaty in 1920 resulted in the creation of independent states like Armenia and Hatay?
Which treaty in 1920 resulted in the creation of independent states like Armenia and Hatay?
- Sykes-Picot Agreement
- Treaty of Lausanne
- Treaty of Seves (correct)
- Versailles Treaty
What major geographical challenge does Iraq face due to its reliance on the Tigris and Euphrates rivers?
What major geographical challenge does Iraq face due to its reliance on the Tigris and Euphrates rivers?
- Political instability
- Landlocked status (correct)
- Control over water headwaters
- Oil reserves depletion
What conflict arose from the British creation of a Jewish state in Palestine after World War I?
What conflict arose from the British creation of a Jewish state in Palestine after World War I?
Who led a secular Arab nationalist movement and nationalized the Suez Canal, leading to conflicts with European powers and Israel?
Who led a secular Arab nationalist movement and nationalized the Suez Canal, leading to conflicts with European powers and Israel?
Why was the Middle East strategically important to the British in the 19th century?
Why was the Middle East strategically important to the British in the 19th century?
What was the Sykes-Picot Agreement of 1916 about?
What was the Sykes-Picot Agreement of 1916 about?
What led to the decline of the Ottoman Empire by the 19th century?
What led to the decline of the Ottoman Empire by the 19th century?
Why did the British Empire start acquiring protectorates in the Middle East?
Why did the British Empire start acquiring protectorates in the Middle East?
Which empires were involved in the division and partition of the Ottoman lands?
Which empires were involved in the division and partition of the Ottoman lands?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
- The Middle East has been synonymous with warfare, instability, and conflict for nearly a century, with major wars being fought in Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Yemen since the turn of the 21st century.
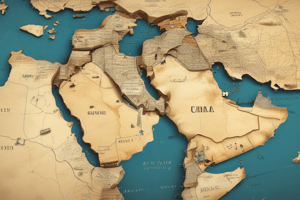
- The region, which spans from Hungary to Yemen, has been dominated by the Turkish Ottoman Empire for many centuries, with diverse ethnicities, languages, and religions.
- The Ottoman Empire, which had no tolerance for nationalism or separatism, began a long period of decline by the 19th century, attracting the interest of the British Empire.
- The Middle East was strategically important to the British due to its geographic location between India and the British home islands, and the Suez Canal, which granted the quickest possible journey time between the two.
- The British began acquiring protectorates in the Middle East, starting with the modern United Arab Emirates, to safeguard their access to the Suez Canal.
- The Ottoman Empire joined the first world war on the side of Imperial Germany, and the British and French decided to completely destroy the Ottoman Empire and partition its lands.
- The Sykes-Picot Agreement, negotiated in 1916, outlined the division and partition of the Ottoman Empire's lands between Britain and France, creating artificial borders that ignored ethnic, linguistic, and religious boundaries.
- The initial political lines drawn by the British and French in 1916 also paid little attention to the complex real borders of the Middle East, with further complications arising from British promises and guarantees.
- The discovery of oil in the Middle East during World War One highlighted its strategic importance, and the British were incentivized to acquire influence and control over as much of the region as possible to secure future oil supplies.
- The Versailles Treaty in 1919 shifted the borders of the Middle East once again, transferring the Ottoman province of Mosul from the French zone of influence to the British zone.- The Treaty of Seves (1920) resulted in significant territorial changes in the Middle East, including the creation of independent states of Armenia and Hatay (later annexed by Turkey), Italian control over several Aegean Islands, Greek annexation of Eastern Thrace and Izmir, and international control over the Turkish Straits.
- The treaty's terms outraged the Turkish government, leading to a two-year rebellion and negotiations that resulted in the more favorable 1923 Treaty of Lausanne.
- The Middle East map created in the 1920s left many unresolved issues, including the lack of an independent Kurdish state and disputed territories between Turkey, Syria, Iraq, and Lebanon.
- The Ottoman provinces of Basra, Masul, and Baghdad contained different people with varying identities and interests. Shia Arabs populated Basra and Masul, while Sunni Arabs dominated Baghdad.
- The discovery of oil and gas reserves across the Middle East has been a significant source of conflict between various ethnic, religious, and political groups.
- Iraq, a landlocked country, is heavily reliant on the Tigris and Euphrates rivers for its civilization but lacks control over their headwaters, which are located in Turkey.
- The French mandates in Lebanon and Syria were also internally fragmented, leading to territorial disputes and various conflicts.
- The British created a Jewish state in Palestine following World War I, which led to the ongoing Arab-Israeli conflict.
- Egypt's Gamal Abdel Nasser led a secular Arab nationalist movement and nationalized the Suez Canal, leading to conflicts with European powers and Israel.
- The Six Day War in 1967 resulted in significant Israeli territorial gains, leading to increased tensions between Israel and the Arab and Islamic worlds.
- The United States took on a more prominent role in securing oil supplies in the Middle East following the British withdrawal.
- Egypt and Syria attempted to retake the Golan Heights and the Sinai Peninsula from Israel in the 1973 Yom Kippur War, leading to peace agreements between Israel and Egypt and Egypt's expulsion from the Arab League.
- Lebanon's complex demographics led to a 15-year civil war, which ended in 1990.
- Syria invaded Lebanon in 1976 to annex the country, and Israel invaded to fight Palestinian forces, resulting in direct conflicts between the two.
- The Israeli occupation of Lebanon ended in 2000, and the Syrian occupation ended in 2005.- In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Israel unilaterally annexed East Jerusalem and the Syrian Golan Heights, escalating tensions with Syria.
- During this time, a revolution took place in Iran, leading to the establishment of a theocratic government under the Ayatollah Khomeini.
- The new Iranian regime sought to unite all Islamic territories under Islamic rule and export its revolution to other countries, particularly in the Middle East.
- Israel and Iran became bitter enemies, with Iran viewing Israel as an occupier of rightfully Islamic lands.
- Iraq, which had just undergone a revolution led by Saddam Hussein, also saw the Iranian Revolution as a threat due to its large Shia population and oil reserves.
- In response, Iraq invaded Iran in 1980, leading to an eight-year-long war that claimed hundreds of thousands of lives.
- The war drained both countries' resources and ultimately ended in a stalemate.
- In the late 1980s and early 1990s, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia, fearing the spread of the Iranian Revolution, lent billions of dollars to Iraq to keep it fighting.
- In 1990, Saddam Hussein invaded Kuwait, leading to the Gulf War and the restoration of the Sykes-Picot map of the Middle East.
- The United States emerged as the primary security guarantor of the Persian Gulf and its oil supplies.
- In the 1990s, a new brand of Sunni Islamism emerged in the Arab world, led by organizations like Al Qaeda and later ISIS, seeking to overturn the Sykes-Picot map and establish a new Islamic state.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.