Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for the functional part of the endometrial cycle?
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for the functional part of the endometrial cycle?
- Myometrium
- Basal layer
- Serosa
- Endometrium (correct)
What anatomical part of the uterus is located at the upper portion?
What anatomical part of the uterus is located at the upper portion?
- Fundus (correct)
- Cervix
- Isthmus
- Body/corpus
What is the primary function of FSH in the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary function of FSH in the menstrual cycle?
- Stimulates growth of ovarian follicles (correct)
- Regulates progesterone levels
- Triggers ovulation
- Initiates menstrual shedding
During which phase of the menstrual cycle do estrogen levels significantly rise due to follicular growth?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle do estrogen levels significantly rise due to follicular growth?
Which arteries supply the myometrium of the uterus?
Which arteries supply the myometrium of the uterus?
How does blood flow in the uterine arteries change during the secretory phase compared to the proliferative phase?
How does blood flow in the uterine arteries change during the secretory phase compared to the proliferative phase?
What triggers the LH surge that leads to ovulation?
What triggers the LH surge that leads to ovulation?
What is the fate of the corpus luteum if fertilization occurs?
What is the fate of the corpus luteum if fertilization occurs?
What is the maximum diameter of a follicle before ovulation occurs?
What is the maximum diameter of a follicle before ovulation occurs?
Which structure is replaced with a yellowish fatty substance after ovulation?
Which structure is replaced with a yellowish fatty substance after ovulation?
What is the sonographic appearance of the endometrium during the secretory phase?
What is the sonographic appearance of the endometrium during the secretory phase?
What sign indicates ovulation may occur within 24 hours?
What sign indicates ovulation may occur within 24 hours?
Which hormone surge leads to the rupture of the follicle?
Which hormone surge leads to the rupture of the follicle?
What is the typical size range of an ovary in a premenopausal woman?
What is the typical size range of an ovary in a premenopausal woman?
What is the appearance of the endometrium at the end of the menstrual phase?
What is the appearance of the endometrium at the end of the menstrual phase?
What does the presence of a corpus albicans indicate?
What does the presence of a corpus albicans indicate?
How should the endometrium be measured for evaluation?
How should the endometrium be measured for evaluation?
During which phase is the endometrial appearance described as a triple layer sign?
During which phase is the endometrial appearance described as a triple layer sign?
Which pelvic ligament connects the lateral ovary to the posterolateral pelvic wall?
Which pelvic ligament connects the lateral ovary to the posterolateral pelvic wall?
How does the endometrium typically appear in a post-menopausal woman not on HRT?
How does the endometrium typically appear in a post-menopausal woman not on HRT?
What is menorrhagia characterized by?
What is menorrhagia characterized by?
Which pelvic space is most likely to have fluid accumulation?
Which pelvic space is most likely to have fluid accumulation?
What condition does oligomenorrhea indicate?
What condition does oligomenorrhea indicate?
Which muscle is most likely to be mistaken for an ovary during an examination?
Which muscle is most likely to be mistaken for an ovary during an examination?
What is the primary purpose of having a full bladder during transabdominal scanning?
What is the primary purpose of having a full bladder during transabdominal scanning?
What part of the fallopian tubes is most commonly the site of fertilization?
What part of the fallopian tubes is most commonly the site of fertilization?
What are the anterior pelvic compartments primarily housing?
What are the anterior pelvic compartments primarily housing?
Which statement correctly describes metrorrhagia?
Which statement correctly describes metrorrhagia?
What is a common consequence of pregnancy regarding kidney function?
What is a common consequence of pregnancy regarding kidney function?
Which condition describes the cessation of menses in women who previously menstruated?
Which condition describes the cessation of menses in women who previously menstruated?
Which of the following structures lies between the pubic symphysis and the urinary bladder?
Which of the following structures lies between the pubic symphysis and the urinary bladder?
What is the size measurement range for a normal uterus?
What is the size measurement range for a normal uterus?
Which of the following conditions is not a contraindication for endovaginal ultrasound?
Which of the following conditions is not a contraindication for endovaginal ultrasound?
What is the primary purpose of hCG in fertility treatments?
What is the primary purpose of hCG in fertility treatments?
Which procedure involves the placement of zygotes into the fallopian tubes?
Which procedure involves the placement of zygotes into the fallopian tubes?
What does ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome commonly result from?
What does ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome commonly result from?
What is the sonographic appearance of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome?
What is the sonographic appearance of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome?
What defines true precocious puberty?
What defines true precocious puberty?
Which condition is hydrocolpos commonly associated with in pediatric patients?
Which condition is hydrocolpos commonly associated with in pediatric patients?
In post-menopausal women, what happens to the endometrial stripe measurements?
In post-menopausal women, what happens to the endometrial stripe measurements?
How can the endometrial thickness vary for women undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT)?
How can the endometrial thickness vary for women undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT)?
What is a common indicator for performing a pelvic ultrasound in pediatric patients?
What is a common indicator for performing a pelvic ultrasound in pediatric patients?
What is hematocolpos?
What is hematocolpos?
What might severe cases of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome require?
What might severe cases of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome require?
What characterizes precocious pseudo puberty?
What characterizes precocious pseudo puberty?
What does the acronym IVF stand for?
What does the acronym IVF stand for?
What is the primary purpose of using a probe cover during an ultrasound examination?
What is the primary purpose of using a probe cover during an ultrasound examination?
Which of the following is NOT an indication for performing a pelvic ultrasound?
Which of the following is NOT an indication for performing a pelvic ultrasound?
How do combined oral contraceptive pills primarily prevent pregnancy?
How do combined oral contraceptive pills primarily prevent pregnancy?
What is the sonographic appearance of an intrauterine device (IUD)?
What is the sonographic appearance of an intrauterine device (IUD)?
Which type of IUD utilizes natural progesterone and is effective for one year?
Which type of IUD utilizes natural progesterone and is effective for one year?
What hormonal IUD is known for its long-term effectiveness of up to five years?
What hormonal IUD is known for its long-term effectiveness of up to five years?
What is a common reason for referring a patient for an ultrasound when they have an IUD?
What is a common reason for referring a patient for an ultrasound when they have an IUD?
Which of the following is a complication that can occur with an IUD?
Which of the following is a complication that can occur with an IUD?
Which factor is NOT a male factor contributing to infertility?
Which factor is NOT a male factor contributing to infertility?
What is the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of infertility?
What is the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of infertility?
What is the primary use of Clomiphene Citrate in infertility treatment?
What is the primary use of Clomiphene Citrate in infertility treatment?
What characteristic does the endometrium typically exhibit when altered by oral contraceptives?
What characteristic does the endometrium typically exhibit when altered by oral contraceptives?
What hormonal mechanism does a device like Mirena utilize to affect the menstrual cycle?
What hormonal mechanism does a device like Mirena utilize to affect the menstrual cycle?
Which of the following is a sign indicating potential complications with an IUD that warrants an ultrasound evaluation?
Which of the following is a sign indicating potential complications with an IUD that warrants an ultrasound evaluation?
What is the most common cause of post-menopausal bleeding without hormone replacement therapy (HRT)?
What is the most common cause of post-menopausal bleeding without hormone replacement therapy (HRT)?
What does a thin endometrium measuring 4 mm or less typically indicate?
What does a thin endometrium measuring 4 mm or less typically indicate?
What is one of the primary uses of Doppler ultrasound in evaluating endometrial thickening?
What is one of the primary uses of Doppler ultrasound in evaluating endometrial thickening?
What is Tamoxifen primarily used for?
What is Tamoxifen primarily used for?
What is CA-125 known to signal when elevated?
What is CA-125 known to signal when elevated?
Why is it important to perform both transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound in post-menopausal evaluation?
Why is it important to perform both transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound in post-menopausal evaluation?
What indicates the presence of Nabothian cysts in the cervix?
What indicates the presence of Nabothian cysts in the cervix?
What typically complicates visualization of the ovaries in post-menopausal patients?
What typically complicates visualization of the ovaries in post-menopausal patients?
What does hydrosalpinx represent?
What does hydrosalpinx represent?
What condition is most commonly associated with the occurrence of endometrial carcinoma?
What condition is most commonly associated with the occurrence of endometrial carcinoma?
What can increase the risk of endometrial carcinoma related to Tamoxifen use?
What can increase the risk of endometrial carcinoma related to Tamoxifen use?
What is considered an abnormal echotexture in the myometrium during an ultrasound?
What is considered an abnormal echotexture in the myometrium during an ultrasound?
What is one of the indications for sonography in a post-menopausal patient?
What is one of the indications for sonography in a post-menopausal patient?
What is the significance of obtaining lab values before performing an OB ultrasound in the first trimester?
What is the significance of obtaining lab values before performing an OB ultrasound in the first trimester?
What hormone is primarily produced by trophoblastic tissues to support early pregnancy?
What hormone is primarily produced by trophoblastic tissues to support early pregnancy?
Which of the following conditions can a lower than expected hCG level indicate?
Which of the following conditions can a lower than expected hCG level indicate?
What is a potential indicator of higher than expected hCG levels?
What is a potential indicator of higher than expected hCG levels?
What is the earliest intra-gestational sac anatomy typically visualized during an ultrasound?
What is the earliest intra-gestational sac anatomy typically visualized during an ultrasound?
How is gestational age typically determined in obstetric practice?
How is gestational age typically determined in obstetric practice?
Which statement accurately describes conceptual age?
Which statement accurately describes conceptual age?
When does the heart of the embryo typically begin to beat?
When does the heart of the embryo typically begin to beat?
What does the trophoblast form after implantation?
What does the trophoblast form after implantation?
Which layer of the embryo will develop into the digestive system?
Which layer of the embryo will develop into the digestive system?
What might vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy indicate?
What might vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy indicate?
What primarily contributes to the fetal part of the placenta?
What primarily contributes to the fetal part of the placenta?
Why might a patient report vaginal bleeding prior to receiving a positive pregnancy test?
Why might a patient report vaginal bleeding prior to receiving a positive pregnancy test?
When should the yolk sac be visualized transvaginally?
When should the yolk sac be visualized transvaginally?
What is the gestational sac's expected growth rate per day?
What is the gestational sac's expected growth rate per day?
What is the most accurate method of dating a pregnancy sonographically?
What is the most accurate method of dating a pregnancy sonographically?
At what measurement should the embryo be visualized sonographically?
At what measurement should the embryo be visualized sonographically?
What is the significance of a calcified yolk sac?
What is the significance of a calcified yolk sac?
When should cardiac activity be visualized in an embryo?
When should cardiac activity be visualized in an embryo?
What is the primary function of the yolk sac?
What is the primary function of the yolk sac?
What signifies a physiologic omphalocele?
What signifies a physiologic omphalocele?
What happens to the yolk sac by 12 weeks of pregnancy?
What happens to the yolk sac by 12 weeks of pregnancy?
What does a small gestational sac (GS) indicate regarding the risk of spontaneous abortion?
What does a small gestational sac (GS) indicate regarding the risk of spontaneous abortion?
What is the role of the trophoblastic tissue during early pregnancy?
What is the role of the trophoblastic tissue during early pregnancy?
What is the expected appearance of the gestational sac (GS)?
What is the expected appearance of the gestational sac (GS)?
What is the measurement method for the mean sac diameter (MSD)?
What is the measurement method for the mean sac diameter (MSD)?
What should be expected during the middle of the first trimester regarding the amnion and chorion?
What should be expected during the middle of the first trimester regarding the amnion and chorion?
Which of the following is a sign of an inevitable abortion?
Which of the following is a sign of an inevitable abortion?
What is the primary characteristic of a threatened abortion?
What is the primary characteristic of a threatened abortion?
What old term refers to an anembryonic pregnancy?
What old term refers to an anembryonic pregnancy?
Which symptom is commonly associated with ectopic pregnancy?
Which symptom is commonly associated with ectopic pregnancy?
What distinguishes a heterotopic pregnancy?
What distinguishes a heterotopic pregnancy?
What is a key sonographic finding indicative of a septic abortion?
What is a key sonographic finding indicative of a septic abortion?
Which measurement indicates an anembryonic pregnancy on sonography?
Which measurement indicates an anembryonic pregnancy on sonography?
In the context of ectopic pregnancy, what does the 'ring of fire' refer to?
In the context of ectopic pregnancy, what does the 'ring of fire' refer to?
What is a clinical sign indicative of ectopic pregnancy?
What is a clinical sign indicative of ectopic pregnancy?
Which of the following is NOT a clinical sign of an inevitable abortion?
Which of the following is NOT a clinical sign of an inevitable abortion?
What is a common risk factor contributing to the increase in ectopic pregnancies?
What is a common risk factor contributing to the increase in ectopic pregnancies?
What does a pseudo gestational sac indicate?
What does a pseudo gestational sac indicate?
What sonographic finding is common in an ectopic pregnancy?
What sonographic finding is common in an ectopic pregnancy?
What distinguishes monochorionic-diamniotic twins from other types of twins?
What distinguishes monochorionic-diamniotic twins from other types of twins?
What indicates a normal finding when observing an echogenic area protruding from the fetal abdomen at around 9 weeks?
What indicates a normal finding when observing an echogenic area protruding from the fetal abdomen at around 9 weeks?
Which of the following best describes dizygotic twins?
Which of the following best describes dizygotic twins?
Which factor is NOT considered a common teratogen?
Which factor is NOT considered a common teratogen?
What is the definition of a chromosomal abnormality?
What is the definition of a chromosomal abnormality?
What does the term 'euploid' refer to?
What does the term 'euploid' refer to?
What is the main purpose of nuchal translucency screening?
What is the main purpose of nuchal translucency screening?
How do maternal diseases like diabetes affect fetal development?
How do maternal diseases like diabetes affect fetal development?
What distinguishes autosomal dominant inheritance patterns from autosomal recessive patterns?
What distinguishes autosomal dominant inheritance patterns from autosomal recessive patterns?
What is a characteristic of chemical teratogens?
What is a characteristic of chemical teratogens?
Which maternal risk factor is related to the likelihood of producing offspring with genetic anomalies?
Which maternal risk factor is related to the likelihood of producing offspring with genetic anomalies?
What condition results from the presence of an extra chromosome?
What condition results from the presence of an extra chromosome?
What increases the risk of congenital malformations during pregnancy?
What increases the risk of congenital malformations during pregnancy?
What is the significance of an abnormal nuchal translucency (NT) measurement when combined with a normal karyotype?
What is the significance of an abnormal nuchal translucency (NT) measurement when combined with a normal karyotype?
What does a low level of PAPP-A and Beta-HCG generally indicate?
What does a low level of PAPP-A and Beta-HCG generally indicate?
What is the outcome of autosomal recessive inheritance patterns?
What is the outcome of autosomal recessive inheritance patterns?
At what gestational age is chorionic villus sampling (CVS) typically performed?
At what gestational age is chorionic villus sampling (CVS) typically performed?
Which markers are included in a quad screen test?
Which markers are included in a quad screen test?
What is the primary purpose of amniocentesis?
What is the primary purpose of amniocentesis?
How does the presence of trophoblastic vascular waveforms relate to a complete abortion?
How does the presence of trophoblastic vascular waveforms relate to a complete abortion?
What does an elevated MSAFP indicate in a pregnancy?
What does an elevated MSAFP indicate in a pregnancy?
What characterizes a missed abortion?
What characterizes a missed abortion?
What are the expected marker levels in a fetus with Trisomy 21?
What are the expected marker levels in a fetus with Trisomy 21?
When is the use of dye during amniocentesis most critical?
When is the use of dye during amniocentesis most critical?
What markers are typically decreased in a fetus diagnosed with Trisomy 18?
What markers are typically decreased in a fetus diagnosed with Trisomy 18?
What is the main reason for performing cell-free DNA testing?
What is the main reason for performing cell-free DNA testing?
What does the presence of chromosomal abnormalities typically lead to?
What does the presence of chromosomal abnormalities typically lead to?
What contributes to the insufficiency of visualizing an intrauterine pregnancy to rule out ectopic pregnancy?
What contributes to the insufficiency of visualizing an intrauterine pregnancy to rule out ectopic pregnancy?
How does the pseudo gestational sac differ from a true gestational sac?
How does the pseudo gestational sac differ from a true gestational sac?
What structure allows the majority of blood in the fetal right atrium to bypass the lungs?
What structure allows the majority of blood in the fetal right atrium to bypass the lungs?
Why is the fetal liver's demand for oxygenated blood lower compared to after birth?
Why is the fetal liver's demand for oxygenated blood lower compared to after birth?
What is one potential consequence of excessive ultrasound energy exposure to fetal tissues?
What is one potential consequence of excessive ultrasound energy exposure to fetal tissues?
What is the significance of the thermal index in ultrasound imaging?
What is the significance of the thermal index in ultrasound imaging?
When is an ultrasound examination considered potentially harmful in terms of temperature elevation?
When is an ultrasound examination considered potentially harmful in terms of temperature elevation?
What is the primary characteristic of gestational trophoblastic disease?
What is the primary characteristic of gestational trophoblastic disease?
What happens to the mechanical index as the frequency of an ultrasound beam increases?
What happens to the mechanical index as the frequency of an ultrasound beam increases?
Which treatment is commonly used for a complete hydatiform mole?
Which treatment is commonly used for a complete hydatiform mole?
What is a significant risk following treatment for a hydatiform mole?
What is a significant risk following treatment for a hydatiform mole?
Which structural change does the left umbilical vein undergo after birth?
Which structural change does the left umbilical vein undergo after birth?
What characteristic distinguishes a partial mole from a complete mole?
What characteristic distinguishes a partial mole from a complete mole?
What is a recommended practice to minimize exposure during ultrasound examinations?
What is a recommended practice to minimize exposure during ultrasound examinations?
What is the main role of the Ductus Venosus in fetal circulation?
What is the main role of the Ductus Venosus in fetal circulation?
What is an invasive mole also known as?
What is an invasive mole also known as?
Which factor influences how ultrasound can lead to cavitation effects in tissues?
Which factor influences how ultrasound can lead to cavitation effects in tissues?
What typically triggers the appearance of theca lutein cysts in patients?
What typically triggers the appearance of theca lutein cysts in patients?
What is a common finding for choriocarcinoma on ultrasound?
What is a common finding for choriocarcinoma on ultrasound?
What is the typical focus of ultrasound energy when attempting to decrease the mechanical index?
What is the typical focus of ultrasound energy when attempting to decrease the mechanical index?
What defines a complete abortion?
What defines a complete abortion?
What is the most common outcome of women who have a molar pregnancy?
What is the most common outcome of women who have a molar pregnancy?
How does choriocarcinoma differ from an invasive mole?
How does choriocarcinoma differ from an invasive mole?
What is associated with an elevated hCG level in gestational trophoblastic disease?
What is associated with an elevated hCG level in gestational trophoblastic disease?
What differentiates a mole with a coexisting normal fetus from gestational trophoblastic disease?
What differentiates a mole with a coexisting normal fetus from gestational trophoblastic disease?
What is a common clinical finding in gestational trophoblastic disease?
What is a common clinical finding in gestational trophoblastic disease?
In cases of ectopic pregnancy, what increases the likelihood of recurrence?
In cases of ectopic pregnancy, what increases the likelihood of recurrence?
Which type of ovarian tumor is most common in postmenopausal women and primarily produces estrogen?
Which type of ovarian tumor is most common in postmenopausal women and primarily produces estrogen?
What is a characteristic feature of Sertoli-Leydig tumors?
What is a characteristic feature of Sertoli-Leydig tumors?
What type of cyst arises from the broad ligament and typically has thin walls?
What type of cyst arises from the broad ligament and typically has thin walls?
What is the primary source of metastatic ovarian tumors?
What is the primary source of metastatic ovarian tumors?
What is a common clinical presentation of patients with androgen-producing tumors?
What is a common clinical presentation of patients with androgen-producing tumors?
Which of the following tumors is characterized by the presence of mucin-filled signet-ring cells?
Which of the following tumors is characterized by the presence of mucin-filled signet-ring cells?
Which type of ovarian tumor has a high percentage of malignancy and is primarily seen in women under 30 years of age?
Which type of ovarian tumor has a high percentage of malignancy and is primarily seen in women under 30 years of age?
Which tumor is most likely associated with endometrial hyperplasia due to excess estrogen production?
Which tumor is most likely associated with endometrial hyperplasia due to excess estrogen production?
What distinguishes transitional cell tumors in the ovaries?
What distinguishes transitional cell tumors in the ovaries?
What is the typical sonographic appearance of Krukenberg tumors?
What is the typical sonographic appearance of Krukenberg tumors?
What is the maximum Thermal Index (TI) that should be maintained during ultrasound procedures?
What is the maximum Thermal Index (TI) that should be maintained during ultrasound procedures?
Which uterine anomaly is characterized by having two completely separate uteri and cervixes?
Which uterine anomaly is characterized by having two completely separate uteri and cervixes?
What condition is likely suggested by the presence of heavy menstrual bleeding, frequent urination, and may involve leiomyomas?
What condition is likely suggested by the presence of heavy menstrual bleeding, frequent urination, and may involve leiomyomas?
What is a common characteristic of a T-shaped uterus, often associated with DES syndrome?
What is a common characteristic of a T-shaped uterus, often associated with DES syndrome?
Which type of uterine fibroid occurs within the wall of the uterus?
Which type of uterine fibroid occurs within the wall of the uterus?
In which condition might you find a fluid collection in the uterus, potentially detected after menarche?
In which condition might you find a fluid collection in the uterus, potentially detected after menarche?
What is a common sign of cervical cancer in women?
What is a common sign of cervical cancer in women?
What type of cyst is commonly asymptomatic and results from an obstructed transcervical gland?
What type of cyst is commonly asymptomatic and results from an obstructed transcervical gland?
In the context of ultrasound, how should the Mechanical Index (MI) be maintained?
In the context of ultrasound, how should the Mechanical Index (MI) be maintained?
What is the term for the congenital absence of the vagina?
What is the term for the congenital absence of the vagina?
What imaging finding might suggest the presence of endometrial hyperplasia?
What imaging finding might suggest the presence of endometrial hyperplasia?
Which condition might present as a vascular plexus of arteries and veins without an intervening capillary network?
Which condition might present as a vascular plexus of arteries and veins without an intervening capillary network?
What is a rare tumor derived from smooth muscle of the uterus and might mimic leiomyomas?
What is a rare tumor derived from smooth muscle of the uterus and might mimic leiomyomas?
What is a common treatment method for heavy vaginal bleeding due to uterine AVM?
What is a common treatment method for heavy vaginal bleeding due to uterine AVM?
What is the most common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding?
What is the most common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding?
In postmenopausal women, when is an endometrial thickness greater than 5mm considered significant?
In postmenopausal women, when is an endometrial thickness greater than 5mm considered significant?
Which clinical sign is characteristic of endometrial carcinoma?
Which clinical sign is characteristic of endometrial carcinoma?
Which of the following statements about endometrial polyps is true?
Which of the following statements about endometrial polyps is true?
What appearance do intrauterine synechiae or adhesions typically have on imaging?
What appearance do intrauterine synechiae or adhesions typically have on imaging?
What does the presence of small cystic areas in the endometrium indicate?
What does the presence of small cystic areas in the endometrium indicate?
Which factor is typically associated with ovarian torsion?
Which factor is typically associated with ovarian torsion?
Which hormone imbalance is commonly observed in patients with PCOS?
Which hormone imbalance is commonly observed in patients with PCOS?
How can sonohysterography be beneficial in evaluating uterine conditions?
How can sonohysterography be beneficial in evaluating uterine conditions?
What is a characteristic sonographic appearance of a corpus luteum cyst?
What is a characteristic sonographic appearance of a corpus luteum cyst?
What percentage of serous and mucinous tumors are classified as borderline?
What percentage of serous and mucinous tumors are classified as borderline?
Which type of epithelial tumor accounts for the majority of malignant ovarian tumors?
Which type of epithelial tumor accounts for the majority of malignant ovarian tumors?
Which statement about hemorrhagic cysts is true?
Which statement about hemorrhagic cysts is true?
What is the condition described by the triad of pleural effusion, ascites, and benign ovarian tumors?
What is the condition described by the triad of pleural effusion, ascites, and benign ovarian tumors?
What is the appearance of a normal physiologic cyst on ultrasound?
What is the appearance of a normal physiologic cyst on ultrasound?
What condition is characterized by multiple tiny cysts around the periphery of the ovaries?
What condition is characterized by multiple tiny cysts around the periphery of the ovaries?
What is the typical age range for women who develop transitional cell tumors?
What is the typical age range for women who develop transitional cell tumors?
Which type of ovarian tumor is identified as having complex but predominantly cystic appearance?
Which type of ovarian tumor is identified as having complex but predominantly cystic appearance?
What clinical sign is associated with intrauterine synechiae?
What clinical sign is associated with intrauterine synechiae?
What is the 5-year survival rate for dysgerminomas, the most common malignant germ cell tumor?
What is the 5-year survival rate for dysgerminomas, the most common malignant germ cell tumor?
Which type of tumor arises from primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonads?
Which type of tumor arises from primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonads?
What is the most common benign germ cell tumor of the ovary, also known as a dermoid cyst?
What is the most common benign germ cell tumor of the ovary, also known as a dermoid cyst?
What percentage of endometrioid tumors are malignant, generally having a better prognosis than serous or mucinous carcinomas?
What percentage of endometrioid tumors are malignant, generally having a better prognosis than serous or mucinous carcinomas?
Which benign ovarian tumor may lead to Meig's syndrome by causing ascites and pleural effusion?
Which benign ovarian tumor may lead to Meig's syndrome by causing ascites and pleural effusion?
Which tumor type is described as having irregular borders, loss of definition, and likely to present with pelvic pressure and abdominal pain when ruptured?
Which tumor type is described as having irregular borders, loss of definition, and likely to present with pelvic pressure and abdominal pain when ruptured?
What type of neoplasm is classified under sex cord-stromal tumors?
What type of neoplasm is classified under sex cord-stromal tumors?
In which type of tumor would you expect to see areas of hemorrhage and necrosis present?
In which type of tumor would you expect to see areas of hemorrhage and necrosis present?
What is the sonographic appearance of a benign cystic teratoma?
What is the sonographic appearance of a benign cystic teratoma?
Flashcards
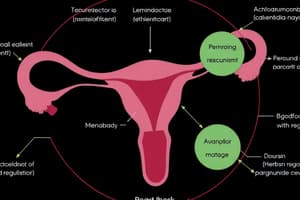
Uterine Layers
Uterine Layers
The uterus is composed of three layers: endometrium (inner lining), myometrium (muscle layer), and serosa (outer layer).
Uterine Anatomy
Uterine Anatomy
The uterus has distinct parts: fundus (top), body/corpus (main part), isthmus (narrowing), and cervix (lower part).
Uterine Arterial Blood Supply
Uterine Arterial Blood Supply
Uterine arteries supply blood to the uterus, branching into arcuate, radial, and basal arteries, with spiral arteries supplying the endometrium.
Ovarian Blood Supply
Ovarian Blood Supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH Role in Menstrual Cycle
FSH Role in Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH Role in Menstrual Cycle
LH Role in Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicular Phase
Follicular Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Regulation (hCG)
Menstrual Regulation (hCG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicle Growth Rate
Follicle Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Threshold
Ovulation Threshold
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Timing (Sonographic)
Ovulation Timing (Sonographic)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Timing (Cumulus)
Ovulation Timing (Cumulus)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Day
Ovulation Day
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum Function
Corpus Luteum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum Regression
Corpus Luteum Regression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium Thickness (Menstrual)
Endometrium Thickness (Menstrual)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium Proliferative Phase
Endometrium Proliferative Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium Secretory Phase
Endometrium Secretory Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium Measurement
Endometrium Measurement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum Sonographic Appearance
Corpus Luteum Sonographic Appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Symptoms
Ovulation Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Contraceptives & Endometrium
Oral Contraceptives & Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Menopausal Endometrium
Post-Menopausal Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metrorrhagia
Metrorrhagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menometrorrhagia
Menometrorrhagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polymenorrhea
Polymenorrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multiparous
Multiparous
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nulliparous
Nulliparous
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior cul-de-sac
Posterior cul-de-sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior cul-de-sac
Anterior cul-de-sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary amenorrhea
Primary amenorrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary amenorrhea
Secondary amenorrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelvic Compartments
Pelvic Compartments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian tube fertilization
Fallopian tube fertilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Probe Prep
Probe Prep
Signup and view all the flashcards
Probe Removal
Probe Removal
Signup and view all the flashcards
EndoVaginal Scanning Planes
EndoVaginal Scanning Planes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indications for Pelvic Ultrasound
Indications for Pelvic Ultrasound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Oral Contraceptives
Types of Oral Contraceptives
Signup and view all the flashcards
How Oral Contraceptives Prevent Pregnancy
How Oral Contraceptives Prevent Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic Appearance of IUD
Sonographic Appearance of IUD
Signup and view all the flashcards
IUD Mechanism of Action
IUD Mechanism of Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of IUDs
Types of IUDs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormonal IUDs and their Applications
Hormonal IUDs and their Applications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mirena and Ovarian Cycle
Mirena and Ovarian Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reasons for Ultrasound with IUD
Reasons for Ultrasound with IUD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complications of IUD
Complications of IUD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infertility Factors
Infertility Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrasound's Role in Infertility
Ultrasound's Role in Infertility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infertility Drugs and their Roles
Infertility Drugs and their Roles
Signup and view all the flashcards
hCG's Role
hCG's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parlodel and Dostinex
Parlodel and Dostinex
Signup and view all the flashcards
IVF
IVF
Signup and view all the flashcards
ZIFT
ZIFT
Signup and view all the flashcards
GIFT
GIFT
Signup and view all the flashcards
IUI
IUI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
OHSS Sonographic Appearance
OHSS Sonographic Appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infant Uterus
Infant Uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Childhood Uterus
Childhood Uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pediatric Pelvic Ultrasound Indications
Pediatric Pelvic Ultrasound Indications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precocious Puberty
Precocious Puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
True Precocious Puberty
True Precocious Puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precocious Pseudopuberty
Precocious Pseudopuberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemato-, Pyo-, Hydro-, Metro-, Colpos-
Hemato-, Pyo-, Hydro-, Metro-, Colpos-
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrocolpos
Hydrocolpos
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic Appearance of Hydrocolpos
Sonographic Appearance of Hydrocolpos
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Menopausal Pelvic Ultrasound Findings
Post-Menopausal Pelvic Ultrasound Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postmenopausal Bleeding
Postmenopausal Bleeding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrial Atrophy
Endometrial Atrophy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrial Carcinoma
Endometrial Carcinoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tamoxifen & Endometrium
Tamoxifen & Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Artery Doppler
Uterine Artery Doppler
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postmenopausal Ovaries
Postmenopausal Ovaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
CA-125
CA-125
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrial Atrophy Bleeding
Endometrial Atrophy Bleeding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nabothian Cysts
Nabothian Cysts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Calcifications
Uterine Calcifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transvaginal & Transabdominal Exams
Transvaginal & Transabdominal Exams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrosalpinx
Hydrosalpinx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Fluid in Postmenopausal Pelvis
Free Fluid in Postmenopausal Pelvis
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Trimester Ultrasound
First Trimester Ultrasound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gestational Age
Gestational Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conceptual Age
Conceptual Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
hCG Levels: Doubling Time
hCG Levels: Doubling Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
hCG Plateau
hCG Plateau
Signup and view all the flashcards
hCG Production
hCG Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Qualitative hCG Test
Qualitative hCG Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quantitative hCG Test
Quantitative hCG Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
hCG Level for Gestational Sac Visualization
hCG Level for Gestational Sac Visualization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastocyst
Blastocyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophoblast
Trophoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk Sac
Yolk Sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua Basalis
Decidua Basalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorionic Villi
Chorionic Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placental Formation
Placental Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monochorionic-diamniotic twins
Monochorionic-diamniotic twins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monochorionic-monoamniotic twins
Monochorionic-monoamniotic twins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dizygotic twins
Dizygotic twins
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a teratogen?
What is a teratogen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensitive period concept
Sensitive period concept
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical agents (teratogens)
Physical agents (teratogens)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical agents (teratogens)
Chemical agents (teratogens)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maternal factors (teratogens)
Maternal factors (teratogens)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Euploid
Euploid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aneuploid
Aneuploid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trisomy
Trisomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triploidy
Triploidy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genotype
Genotype
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phenotype
Phenotype
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk sac visualization
Yolk sac visualization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk sac function
Yolk sac function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitelline duct
Vitelline duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorion differentiation
Chorion differentiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amnion formation
Amnion formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double decidual sign
Double decidual sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophoblastic tissue flow
Trophoblastic tissue flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
First sonographic evidence of pregnancy
First sonographic evidence of pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal gestational sac appearance
Normal gestational sac appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mean sac diameter (MSD)
Mean sac diameter (MSD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk sac abnormalities
Yolk sac abnormalities
Signup and view all the flashcards
CRL measurement
CRL measurement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac activity visualization
Cardiac activity visualization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD)
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complete Hydatiform Mole
Complete Hydatiform Mole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Partial Mole
Partial Mole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Invasive Mole
Invasive Mole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Theca Lutein Cysts
Theca Lutein Cysts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Methotrexate
Methotrexate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic Surgery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laparotomy
Laparotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expectant Management
Expectant Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic Findings in GTD
Sonographic Findings in GTD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for GTD
Treatment for GTD
Signup and view all the flashcards
GTD Recurrence
GTD Recurrence
Signup and view all the flashcards
GTD and Pregnancy
GTD and Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural Effusion
Pleural Effusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thecoma
Thecoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Granulosa Cell Tumor
Granulosa Cell Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sertoli-Leydig Tumor
Sertoli-Leydig Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metastatic Ovarian Tumors
Metastatic Ovarian Tumors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Krukenberg Tumor
Krukenberg Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paraovarian Cyst
Paraovarian Cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiological Cysts
Physiological Cysts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the signs of an inevitable abortion?
What are the signs of an inevitable abortion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the sonographic findings of an inevitable abortion?
What are the sonographic findings of an inevitable abortion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a threatened abortion?
What is a threatened abortion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic findings of a threatened abortion?
Sonographic findings of a threatened abortion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anembryonic pregnancy
Anembryonic pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical signs of Anembryonic pregnancy
Clinical signs of Anembryonic pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic findings of an anembryonic pregnancy
Sonographic findings of an anembryonic pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a septic abortion?
What is a septic abortion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic findings of a septic abortion
Sonographic findings of a septic abortion
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is ectopic pregnancy?
What is ectopic pregnancy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is ectopic pregnancy increasing?
Why is ectopic pregnancy increasing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sites of ectopic pregnancy
Sites of ectopic pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Clinical symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonographic findings of an ectopic pregnancy
Sonographic findings of an ectopic pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a heterotopic pregnancy?
What is a heterotopic pregnancy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a pseudo gestational sac?
What is a pseudo gestational sac?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thermal Index (TI)
Thermal Index (TI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical Index (MI)
Mechanical Index (MI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus didelphys
Uterus didelphys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bicornuate uterus
Bicornuate uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Septate uterus
Septate uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gartner's duct cyst
Gartner's duct cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
DES syndrome/t-shaped uterus
DES syndrome/t-shaped uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leiomyoma (Fibroid)
Leiomyoma (Fibroid)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Leiomyosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrometra
Hydrometra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine AVM
Uterine AVM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Ovarian Tumors
Epithelial Ovarian Tumors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serous Ovarian Tumor
Serous Ovarian Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucinous Ovarian Tumor
Mucinous Ovarian Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrioid Ovarian Tumor
Endometrioid Ovarian Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clear Cell Ovarian Tumor
Clear Cell Ovarian Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Cell Ovarian Tumor (Brenner Tumor)
Transitional Cell Ovarian Tumor (Brenner Tumor)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Germ Cell Ovarian Tumor
Germ Cell Ovarian Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cystic Teratoma (Dermoid Cyst)
Cystic Teratoma (Dermoid Cyst)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk Sac or Endodermal Sinus Tumor
Yolk Sac or Endodermal Sinus Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sex Cord Stromal Ovarian Tumor
Sex Cord Stromal Ovarian Tumor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibroma
Fibroma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meig's Syndrome
Meig's Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Increased NT
Increased NT
Signup and view all the flashcards
NT Caliper Placement
NT Caliper Placement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Low PAPP-A and Beta-HCG
Low PAPP-A and Beta-HCG
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell-free DNA Testing
Cell-free DNA Testing
Signup and view all the flashcards
CVS (Chorionic Villus Sampling)
CVS (Chorionic Villus Sampling)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quad Screen
Quad Screen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alpha-feto Protein (AFP)
Alpha-feto Protein (AFP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elevated Alpha-Feto Protein
Elevated Alpha-Feto Protein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased Alpha-Feto Protein
Decreased Alpha-Feto Protein
Signup and view all the flashcards
hCG and uE3 in Trisomy 21
hCG and uE3 in Trisomy 21
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhibin A and Trisomy 21
Inhibin A and Trisomy 21
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dye in Amniocentesis
Dye in Amniocentesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complete Abortion
Complete Abortion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Missed Abortion
Missed Abortion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectopic Pregnancy Sonographic Appearance
Ectopic Pregnancy Sonographic Appearance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is visualizing an IUP insufficient for ruling out ectopic pregnancy?
Why is visualizing an IUP insufficient for ruling out ectopic pregnancy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differentiate Gestational Sac and Pseudo Gestational Sac
Differentiate Gestational Sac and Pseudo Gestational Sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Blood Flow: Umbilical Vein
Fetal Blood Flow: Umbilical Vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Blood Flow: Liver
Fetal Blood Flow: Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Blood Flow: Pulmonary Circulation
Fetal Blood Flow: Pulmonary Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Blood Flow: Aorta
Fetal Blood Flow: Aorta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Blood Flow: Foramen Ovale
Fetal Blood Flow: Foramen Ovale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Thermal Effects
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Thermal Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Mechanical Effects
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Mechanical Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Mechanical Index
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Mechanical Index
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Thermal Index
Ultrasound Bioeffects: Thermal Index
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minimizing Ultrasound Bioeffects
Minimizing Ultrasound Bioeffects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Power vs. Intensity
Power vs. Intensity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Relationship between Intensity and Focus
Relationship between Intensity and Focus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrial Polyp
Endometrial Polyp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrauterine Synechiae
Intrauterine Synechiae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicular Cyst
Follicular Cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum Cyst
Corpus Luteum Cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemorrhagic Cyst
Hemorrhagic Cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian Torsion
Signup and view all the flashcards
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome)
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sono Hysterography
Sono Hysterography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Uterus Anatomy and Layers
- The uterus has three layers: endometrium, myometrium, and serosa.
- Anatomic parts include the fundus, body (corpus), isthmus, and cervix.
Uterine and Ovarian Arterial Vascularity
- Uterine arteries supply the perimetrium/serosa, arcuate arteries supply the myometrium, radial arteries supply the myometrium.
- Basal arteries supply the basal layer, spiral arteries supply the functional layer of the endometrium.
- Ovarian arteries (gonadal arteries) are lateral branches of the aorta, anastomosing with uterine arteries.
- Flow velocity and resistance in arcuate and radial arteries vary through the menstrual cycle and with age (e.g., high resistance in proliferative phase, postmenopausal women).
Venous Drainage
- Right gonadal vein drains into the inferior vena cava (IVC)
- Left gonadal vein drains into the left renal vein.
FSH and LH Roles in Menstrual Cycle
- FSH: Stimulates follicle growth and development. Theca cells produce estrogen, stimulating endometrial growth. Only one follicle typically matures (Graafian follicle).
- LH: Triggers follicle maturation and rupture (ovulation). Stimulates progesterone production which peaks after ovulation. LH surge (days 10 to 12 before ovulation) triggers ovulation. Progesterone maintenance triggers shedding if fertilization does not occur. hCG signals corpus luteum to continue progesterone production if fertilization occurs.
Ovarian Phases
- Follicular Phase (days 1-14): FSH stimulates follicle expansion and movement to the ovary's surface. Follicles grow (2-3 mm/day). A follicle over 11 mm likely ovulates (max 15-30 mm). Decreased reflectivity around a follicle suggests impending ovulation (within 24 hours). Presence of cumulus oophorus suggests ovulation within 36 hours.
- Ovulation (day 14): LH surge causes follicle rupture. Findings post-ovulation include decreased follicle size, free fluid in posterior cul-de-sac; mittelschmerz (mid-cycle pain) may be present.
- Luteal Phase (days 15-28): Expelled ovum site becomes corpus luteum. Produces progesterone for endometrial maintenance for implantation. In the absence of hCG, corpus luteum regresses. Corpus albicans will appear as small, rounded, hyperechoic areas.
Pelvic Ligaments
- Broad ligament extends from uterus to lateral pelvic wall.
- Round ligament is anterior and inferior, connecting uterine cornua to anterior pelvic wall.
- Infundibulopelvic ligament connects lateral ovary to posterolateral pelvic wall. Contains ovarian vessels and nerves.
Ovary Anatomy
- Almond-shaped, approximately 3 cm long (premenopausal), 2 x 0.5 cm (postmenopausal).
- Posterior to uterus near cornua.
- Medial to external iliac vessels, anterior to internal iliac vessels and ureter.
- Supported by ovarian ligaments and suspensory (infundibulopelvic) ligament.
- Layers: outer cortex, inner medulla (blood vessels, connective tissue), hilum (vessels, nerves).
Corpus Luteum
- A yellowish fatty substance replacing ruptured follicle; filled with fluid; thick-walled; anechoic cyst appearance.
- Regresses to Corpus albicans if not maintained by hCG. Corpus albicans appears as small rounded hyperechoic areas.
Pelvic Muscles
- Pelvic muscles appear as hyperechoic striations, forming pelvic space borders.
- Rectus abdominis (anterior wall), iliopsoas (can mimic ovary), iliacus (lateral margins), obturator internus (triangular), levator ani (anterior/middle pelvic floor).
Pelvic Bones
- Sacrum, coccyx, ilium, ischium, pubis compose the pelvis.
Endometrium Changes (Contraceptives/Post-Menopause)
- Oral Contraceptives: Anovulatory endometrium, thin and echogenic throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Post-Menopause: < 5mm (no HRT), ≤ 8mm (with HRT). Endometrium appearance similar to premenopausal with HRT, thickening may occur.
IUD Sonographic Appearance
- Highly reflective and echogenic with reverberation and shadow casting.
Amenorrhea
- Primary: Delayed menarche (before 16 yrs in some sources) due to congenital factors or ovarian dysfunction. Secondary: Cessation of prior menstruation due to infection, trauma, ovarian dysfunction, or endocrine disturbances such as pituitary disease.
Pelvic Spaces
- Posterior cul-de-sac (Rectouterine space/Pouch of Douglas): Deepest space, posterior to uterus, anterior to rectum. Fluid normal, especially with menstruation or post-ovulation.
- Anterior cul-de-sac (Utero-vesicle pouch): Between posterior bladder and anterior uterus.
- Space of Retzius: Between pubic symphysis and anterior bladder.
Other Terms
- Menorrhagia: Heavy or prolonged periods at usual times.
- Metrorrhagia: Bleeding between periods.
- Menometrorrhagia: Heavy bleeding at irregular intervals.
- Oligomenorrhea: Abnormally short or light periods (associated with PCOS, stress, chronic illness).
- Polymenorrhea: Frequent periods
- Dysmenorrhea: Painful periods (associated with endometriosis).
- Multiparous: Having given birth more than once.
- Nulliparous: Having given birth to no children.
- Nulligravida: Never pregnant.
- Gravidity: Number of pregnancies.
- Parity: Number of live births.
Ultrasound Techniques
- Transabdominal: Full bladder used for wider field of view, lower resolution.
- Transvaginal: Empty bladder, higher resolution, narrow field of view.
- Contraindications TV: Pregnant patients with premature rupture of membranes, vaginal conditions, patient consent, pediatric patients.
Pelvic Ultrasound Indications
- Pelvic pain, masses, endocrine abnormalities (PCOS), amenorrhea, abnormal bleeding, infertility, infections, congenital anomalies, etc.
Infertility Drugs
- Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid, Serophene): Tablets to induce ovulation, used for infrequent or long cycles.
- Gonadotropins (Repronex, Follistim, Pergonal, Bravelle, Fertinex, Metrodin, Gonal-F): Injections to induce egg release after follicle development.
- Metformin (Glucophage): Insulin-lowering medication, commonly used for PCOS.
- hCG (Pregnyl, Novarel, Ovidrel, Profasi): Triggers ovulation with other drugs.
- Parlodel and Dostinex: Reduce prolactin levels, used for pituitary tumors.
Infertility Procedures
- IVF (In-vitro fertilization): Ovarian stimulation, oocyte aspiration, sperm incubation, embryo catheterization in uterus.
- ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Tube Transfer): Zygote placed in fallopian tube.
- GIFT (Gamete Intrafallopian Tube Transfer): Sperm and ova placed in fallopian tube.
- IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): Ultrasound guidance for sperm placement in uterine fundus (useful for motility issues).
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
- Excessive ovarian stimulation (infertility drugs), often more severe in conceivers.
- Findings: large ovarian cysts (> 5 cm), bilateral, may resemble theca lutein cysts; ascites, pleural effusion, potential for fatal complications.
Pediatric Pelvic Ultrasound
- Infant: Cervix twice body length; echogenic endometrium; ~3 cm length, 0.5-1 cm AP diameter; ovaries in various locations.
- Childhood: Uterus regresses; endometrial stripe not easily outlined (until ~7 years). Follicular development occurs before menarche.
Pediatric Ultrasound Indications
- Ovarian cysts, PCOS, neoplasms, congenital anomalies, ambiguous genitalia, precocious puberty assessment.
Precocious Puberty
- Sexual characteristics before age 8 (true vs. pseudo puberty).
- True: Early but normal gonadotropin secretion, idiopathic (most common), congenital adrenal hyperplasia possible cause.
- Pseudo: Abnormal estrogen exposure, often a hormone-producing tumor.
Hormone/Fluid Terminology
- Hemato: Blood
- Pyo: Pus
- Hydro: Water
- Metro: Uterus
- Colpos: Vagina; e.g., hydrometrocolpos (fluid in uterus and vagina).
Hydrocolpos
- Fluid (blood/pus) collection in vagina, may involve cervix and uterus, usually imperforate hymen in children.
- Findings: hypoechoic, distended endometrial cavity/vagina; posterior acoustic enhancement; echoes may be present (severe obstruction); assess for genitourinary anomalies.
Post-Menopausal Pelvis
- Uterus decreases in size (rapidly first 5 years, gradually). Cervix may be larger than body later in life. Myometrium can have calcifications. Fluid in endometrial cavity is normal. Endometrial stripe < 8mm (asymptomatic).
HRT and Endometrial Thickness
- Normal endometrial values in HRT users are still being established.
- Imaging during estrogen phase is preferable.
- Endometrium ≤ 8 mm with estrogen-only HRT.
- Endometrium ≤ 12 mm during estrogen phase, decreasing during progesterone phase.
Post-Menopausal Bleeding Causes
- Exogenous estrogen (HRT), endometrial atrophy (common without HRT), endometrial carcinoma (common GYN cancer), cervical carcinoma, estrogen-producing ovarian tumor.
Tamoxifen
- Non-steroidal antiestrogen for breast cancer; can cause endometrial changes and increase risk of endometrial cancer.
- Ultrasound helpful for evaluating vaginal bleeding in Tamoxifen users; look for subendometrial cysts, cystic areas, endometrial hyperplasia, increased tissue growth.
Uterine Artery Doppler
- Low sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing benign/malignant endometrial thickening; not routinely used as a primary diagnostic tool.
Post-Menopausal Ovaries
- Difficult to visualize due to lack of follicles, small size.
- Use both transabdominal and transvaginal. Transabdominal for visualization of the high pelvis or hysterectomy patients. Applying pressure with the hand to help visualize.
- Avoid misinterpreting other structures as ovaries.
CA-125
- Serum marker for ovarian cancer, elevated in ~80% of epithelial ovarian cancers.
Endometrial Atrophy (Post-Menopausal Bleeding)
- Atrophied endometrium can be friable and bleed easily. Thin endometrium (< 4 mm) may reduce the need for biopsy.
Nabothian Cysts
- Common in postmenopausal cervix; likely secondary to prior infection; avoid confusing with adnexal disease.
Uterine Calcifications (Post-Menopause)
- Degenerated fibroids, arcuate artery calcification.
First Trimester Pelvic Ultrasound
- Fetus development, growth, & well-being.
- Fetal growth, position, gestational age estimation.
- Vaginal bleeding, suspected multiple pregnancies, hydatidiform mole, ectopic pregnancy, IUD evaluation.
First Trimester Lab Values
- Obtain LMP, GPA details, medications, clinical problems, previous pregnancy issues, and hCG levels.
Early Pregnancy Terminology
- Conceptual age: From conception.
- Gestational age: From first day of last menstrual period (LMP).
- Qualitative hCG: Detects presence (urine test).
- Quantitative hCG: Provides specific hCG blood levels.
- Gametes: Reproductive cells (sperm and egg).
- Zygote: Fertilized cell.
- Morula: Dividing cells in oviduct, entering uterus.
- Blastomere: Cells in 2/4 cell stages.
- Blastocyst: Collection of cells implanting in endometrium.
- Blastocele: Inner fluid cavity.
- Trophoblast: Outer layer, producing hCG.
- Inner cell mass: Differentiates to layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm).
- Decidua (basalis, capsularis, parietalis): Endometrial tissues related to implantation.
hCG Levels and Abnormal Findings
- Higher than expected: Incorrect dates, gestational trophoblastic disease, multiple gestations.
- Lower than expected: Incorrect dates, ectopic pregnancy, embryonic problems.
First Sonographic Evidence of Pregnancy
- Gestational sac. Seen transvaginally at hCG > 1000-2000 mIU (3rd IRP), transabdominally at 5+ weeks.
Gestational Sac Appearance
- Round, oval, or teardrop-shaped. Located mid- or near fundus. Double decidual sign. Intact borders. ~1 mm/day growth. Yolk sac seen when MSD ≥ 8 mm (TV).
Mean Sac Diameter (MSD)
- Measured from inner to inner in 3 planes and averaged. Calculated with formula: MSD = Length * Width * Height / 3.
- MSD + 30 = gestational age in days.
Yolk Sac Abnormalities
- Calcified yolk sac, large yolk sac or absent yolk sac indicates possible embryonic demise.
Embryo Visualization
- Seen transvaginally at 16 mm MSD or transabdominally at 25 mm MSD.
Crown-Rump Length (CRL)
- Most accurate dating method (first trimester), measured from head to rump excluding limbs. Accurate to about 3-5 days, inaccurate after 11 weeks.
- CRL (mm) + 42 ≈ Gestational age in days
Cardiac Activity Visualization
- Primordial heart begins beating around 6 weeks.
- Should be seen by 46 days or CRL > 4 mm (rates vary).
Fetal Brain Anatomy
- Visualizable at 9 weeks; cerebral hemispheres, choroid plexus filling ventricles.
Types of Twins
- Monozygotic (MZ): One ovum divides (identical).
- Monochorionic-diamniotic (MCDA): One chorion, two amnions; common.
- Monochorionic-monoamniotic (CMMA): Extremely high risk of problems; one chorion, one amniotic membrane.
- Dizygotic (DZ): Two ova (fraternal); two separate sacs.
Omphalocele
- Protruding midgut that usually returns to abdominal cavity by week 12.
First Trimester Abnormalities
- Threatened abortion: Bleeding, cramping, closed cervix.
- Missed abortion: Embryo without cardiac activity; closed cervix.
- Incomplete abortion: Some products retained after expulsion. Complete abortion: All products expelled.
- Anembryonic pregnancy: No embryo develops; gestation sac may enlarge slightly.
- Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, didelphys uterus, uterine AVM
Ectopic Pregnancy
- Implantation outside the uterus; most common in fallopian tubes.
- Clinical signs: Amenorrhea, positive pregnancy test, spotting/bleeding, adnexal tenderness/mass, pelvic pain, shoulder pain.
- Sonographic findings (grayscale & vascular): Empty uterus; extrauterine embryo, free fluid (possible), double decidual sign.
- Treatment: Laparoscopic surgery, expectant management, methotrexate.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD)
- Abnormal proliferation of trophoblast tissue.
- Complete hydatidiform mole: Most common GTD type; hydropic villi, no fetal tissue. Enlarged, echogenic mass in uterus.
- Partial hydatidiform mole: Mostly 1 maternal / 2 paternal chromosome sets; abnormal fetal tissue.
- Treatment: Suction curettage (D&C), hysterectomy.
Invasive mole and choriocarcinoma
- Invasive mole (chorioadenoma destruens): Mole penetrates myometrium; malignant, but not metastatic.
- Choriocarcinoma: Rare, infiltrates myometrium, highly vascular; malignant, metastatic.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.