Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of crossing-over during prophase I of meiosis in a diploid cell?
What is the significance of crossing-over during prophase I of meiosis in a diploid cell?
- It ensures that the resulting gametes have identical genetic material.
- It causes the zygote to have only maternal genes.
- It results in the exchange of genetic material between maternal and paternal chromatids. (correct)
- It prevents the completion of meiosis in the oocyte until fertilization occurs.
Why is the completion of meiosis II in the oocyte dependent on fertilization?
Why is the completion of meiosis II in the oocyte dependent on fertilization?
- To ensure there is no mixing of paternal and maternal genes.
- To allow the fusion of spermatic and oocyte pronucleus to form a diploid cell. (correct)
- To prevent the release of more than one ovum each cycle.
- To activate the zona pellucida and make it impenetrable to other sperm cells.
Where does fertilization typically occur in the female reproductive system?
Where does fertilization typically occur in the female reproductive system?
- Vagina
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Ampulla of the uterine tube (correct)
What is the role of zona pellucida in early embryo development?
What is the role of zona pellucida in early embryo development?
What occurs during zona 'hatching' in the process of implantation?
What occurs during zona 'hatching' in the process of implantation?
Which structure releases lytic enzymes that partially penetrate the zona pellucida during implantation?
Which structure releases lytic enzymes that partially penetrate the zona pellucida during implantation?
Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?
What is established by the syncytiotrophoblast eroding endometrial blood vessels during implantation?
What is established by the syncytiotrophoblast eroding endometrial blood vessels during implantation?
On which day does the blastocyst begin to embed in the endometrium during implantation?
On which day does the blastocyst begin to embed in the endometrium during implantation?
Which of the following describes the adaptation of endometrial tissues in preparation for implantation?
Which of the following describes the adaptation of endometrial tissues in preparation for implantation?
What is the term used to describe an organism that breathes no air, does not use the digestive tract, and lives in a sterile environment?
What is the term used to describe an organism that breathes no air, does not use the digestive tract, and lives in a sterile environment?
What is the term for a single generalized, totipotential cell that eventually develops into 100 trillion specialized cells in the human body?
What is the term for a single generalized, totipotential cell that eventually develops into 100 trillion specialized cells in the human body?
What term describes an air-breathing organism with a functional GI tract that quickly becomes colonized by microbial flora after birth?
What term describes an air-breathing organism with a functional GI tract that quickly becomes colonized by microbial flora after birth?
What is the main function of the uterus during the fertilization process?
What is the main function of the uterus during the fertilization process?
During ovulation, what is the main role of the uterine tube (Fallopian tube)?
During ovulation, what is the main role of the uterine tube (Fallopian tube)?
What is the significance of the placenta in the context of fertilization and implantation?
What is the significance of the placenta in the context of fertilization and implantation?
Which female reproductive organ is responsible for the production of progesterone and estrogens?
Which female reproductive organ is responsible for the production of progesterone and estrogens?
What is the outermost layer of an oocyte?
What is the outermost layer of an oocyte?
Which of the following is a spherical mass of cells that is composed of an inner cell mass surrounded by a trophoblast?
Which of the following is a spherical mass of cells that is composed of an inner cell mass surrounded by a trophoblast?
The first appearance of cytotrophoblast and synctiotrophoblast occurs after ______
The first appearance of cytotrophoblast and synctiotrophoblast occurs after ______
The endometrium expresses small apical processes known as _______ that aid in implantation of the blastocyst
The endometrium expresses small apical processes known as _______ that aid in implantation of the blastocyst
The trophoblast differentiates into 2 layers following ___________
The trophoblast differentiates into 2 layers following ___________
What is the term for the thickened area of columnar cells found in the cephalad region of the hypoblast at the end of week 2, acting as an organization area?
What is the term for the thickened area of columnar cells found in the cephalad region of the hypoblast at the end of week 2, acting as an organization area?
What prevents the formation of structures that belong at the caudal aspect of the embryo during week 2?
What prevents the formation of structures that belong at the caudal aspect of the embryo during week 2?
Which layer surrounds the umbilical vesicle(s) at the end of week 2?
Which layer surrounds the umbilical vesicle(s) at the end of week 2?
During the development at the end of week 2, what forms the wall of the chorionic sac?
During the development at the end of week 2, what forms the wall of the chorionic sac?
At the end of week 2, what is responsible for signaling 'episodes' that stimulate differentiation and development of local structures in the embryo?
At the end of week 2, what is responsible for signaling 'episodes' that stimulate differentiation and development of local structures in the embryo?
What is the role of the hypoblast during embryonic development in Week 2?
What is the role of the hypoblast during embryonic development in Week 2?
What is the function of amnioblasts in embryonic development?
What is the function of amnioblasts in embryonic development?
What happens to the decidual cells that syncytiotrophoblast contacts following complete implantation?
What happens to the decidual cells that syncytiotrophoblast contacts following complete implantation?
Which layer gives rise to amnioblasts during Week 2 of embryonic development?
Which layer gives rise to amnioblasts during Week 2 of embryonic development?
What role does the prechordal plate play during Week 2 of embryonic development?
What role does the prechordal plate play during Week 2 of embryonic development?
During Week 2, what significant event occurs with the trophoblast?
During Week 2, what significant event occurs with the trophoblast?
What is the main function of the hypoblast during Week 2 of embryonic development?
What is the main function of the hypoblast during Week 2 of embryonic development?
What happens to the mesenchymal cells derived from the primitive streak during Week 2 of embryonic development?
What happens to the mesenchymal cells derived from the primitive streak during Week 2 of embryonic development?
During gastrulation, which germ layer forms the supporting tissues of the embryo?
During gastrulation, which germ layer forms the supporting tissues of the embryo?
What is the structure that appears in the median plane of the dorsal aspect of the embryonic disc at the beginning of Week 3?
What is the structure that appears in the median plane of the dorsal aspect of the embryonic disc at the beginning of Week 3?
Which embryonic cell type differentiates into mesenchyme during gastrulation?
Which embryonic cell type differentiates into mesenchyme during gastrulation?
What develops in the primitive streak as a result of the proliferation and movement of epiblast cells?
What develops in the primitive streak as a result of the proliferation and movement of epiblast cells?
At the beginning of Week 3, where do cells proliferate to form the primitive node in the embryo?
At the beginning of Week 3, where do cells proliferate to form the primitive node in the embryo?
What is the term used to describe the two layers of extraembryonic mesoderm separated by the fluid in the extraembryonic coelom?
What is the term used to describe the two layers of extraembryonic mesoderm separated by the fluid in the extraembryonic coelom?
What is the role of the prechordal plate at the end of Week 2 in embryonic development?
What is the role of the prechordal plate at the end of Week 2 in embryonic development?
What is the fate of the cells remaining in the epiblast during Week 3 of embryonic development?
What is the fate of the cells remaining in the epiblast during Week 3 of embryonic development?
What is the main role of mesenchymal cells derived from the primitive streak during Week 3 of embryonic development?
What is the main role of mesenchymal cells derived from the primitive streak during Week 3 of embryonic development?
Following gastrulation, which structure establishes the longitudinal axis of the embryo?
Following gastrulation, which structure establishes the longitudinal axis of the embryo?
What is the final fate of the primitive streak by the end of Week 4 in embryonic development?
What is the final fate of the primitive streak by the end of Week 4 in embryonic development?
During week 3, mesenchymal cells dive into the primitive pit and migrate cephalad to form the ___________
During week 3, mesenchymal cells dive into the primitive pit and migrate cephalad to form the ___________
Match the following structures with their significant role during Week 2 of embryonic development:
Match the following structures with their significant role during Week 2 of embryonic development:
Match the following events with their correct timing of embryonic development:
Match the following events with their correct timing of embryonic development:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Week 3 - Gastrulation
- Gastrulation: the process by which the three germ layers of the embryo are established
- Ectoderm, Mesoderm, and Endoderm
- Bilaminar embryonic disc becomes trilaminar embryonic disc
- Embryo may be referred to as a gastrula
Process of Gastrulation
- Formation of the primitive streak appears at the beginning of the 3rd week
- Thickened linear band in the median plane of the dorsal aspect of the embryonic disc
- Initiates in the caudal region of the epiblast
- Cells at the cephalad end of the primitive streak proliferate to form a primitive node
- A narrow groove, the primitive groove, develops in the primitive streak
- Continuous with a small depression in the primitive node, the primitive pit
Embryonic Mesoderm
- Cells leave the deep surface of the streak and form mesenchyme
- Embryonic connective tissue which forms the supporting tissues of the embryo
- Some mesenchyme forms mesoblastic cells (undifferentiated mesoderm)
- The mesoblasts form the intraembryonic, or embryonic, mesoderm
- Cells from the epiblast, as well as from the primitive node and other parts of the primitive streak, displace the hypoblast
- Form the embryonic endoderm in the roof of the umbilical vesicle
- The cells remaining in the epiblast form the embryonic ectoderm
- Mesenchymal cells derived from the primitive streak migrate widely
- Differentiate into diverse types of cells, such as fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts
Primitive Streak
- Later, the primitive streak diminishes in size and becomes an insignificant structure in the sacrococcygeal region
- Disappears by the end of the 4th week
Early Embryology Overview
- Week 1: appearance begins with fertilization, from zygote to blastocyst
- Inner cell mass (embryoblast), trophoblast, and blastocoel
- "Hatching" from zona pellucida, first appearance of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast
- Week 2: adhesion to endometrium (uterus) and beginning of implantation
- From a single cell to a "ball" of cells
- Trophoblast develops into syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast
- Embryo "sinks" beneath the endometrium
- Trophoblastic extensions begin to interface with maternal blood vessels
- Embryoblast develops into a bilaminar disk – epiblast + hypoblast
- Prechordal plate develops at the end of this week
- Umbilical vesicle, extraembryonic coelom develop
- Disk-shaped embryonic cells surrounded by extra-embryonic cavities
- Week 3: gastrulation, bilaminar disk to trilaminar disk
- Three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
- Notochord forms, and then the following develop: neural groove, neural plate, early neural tube
- Paraxial mesoderm + somites, tertiary chorionic villi, heart tube, primordial circulation develop
- Developing villi surround elongated, disk-shaped embryo with a few somites
Introduction to Embryology
- Why learn embryology?
- Fascinating field of biology
- We start out as one generalized, totipotential cell to 100 trillion cells
- Massive changes occur within minutes after birth
- Clinical relevance: essential to understanding developmental/congenital disorders
- Immune system, cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous system, reproductive system
- Infertility, referred pain
Implantation
- The zona pellucida degenerates (day 5)
- The blastocyst adheres to the endometrial epithelium (day 6)
- The trophoblast differentiates into two layers: syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast (day 7)
- The syncytiotrophoblast erodes endometrial tissues and the blastocyst begins to embed in the endometrium (day 8)
- Blood-filled lacunae appear in the syncytiotrophoblast (day 9)
- The blastocyst sinks beneath the endometrial epithelium and the defect is filled by a closing plug (day 10)
- Lacunar networks form by fusion of adjacent lacunae (days 10 and 11)
- The syncytiotrophoblast erodes endometrial blood vessels, allowing maternal blood to seep in and out of lacunar networks (days 11 and 12)
- The defect in the endometrial epithelium is repaired (days 12 and 13)
- Primary chorionic villi develop (days 13 and 14)
Week 2
- Rapid proliferation and differentiation of the trophoblast occurs as the blastocyst completes implantation in the uterine endometrium
- The endometrial changes resulting from the adaptation of these tissues in preparation for implantation are known as the decidual reaction### Meiosis and Fertilization
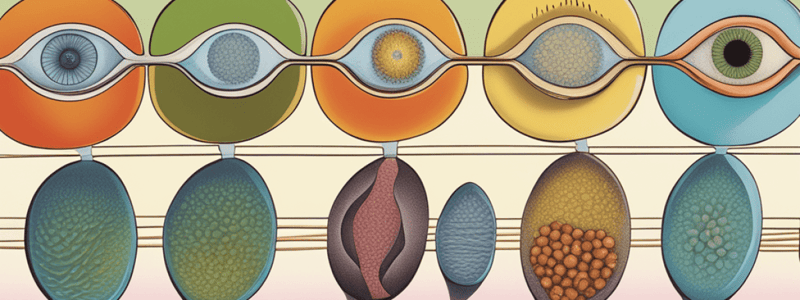
- A diploid cell (germ cell) undergoes meiosis to produce a unique haploid gamete
- Crossing-over between maternal and paternal chromatids during prophase I results in "mixed" chromatids with both paternal and maternal genes
- Meiosis is not completed in an oocyte until the sperm penetrates the oocyte
Fertilization
- Fertilization occurs when the spermatic pronucleus and the oocyte pronucleus fuse, resulting in a diploid cell
- The single diploid cell is known as a zygote
- Fertilization typically occurs in the ampulla of the uterine tube
Ovulation
- A person with ovaries is born with a certain number of diploid oocytes that have been "paused" during the first stage of meiosis
- After puberty, the ovaries release an ovum each cycle into the uterine tubes
- The oocyte will not complete meiosis II unless fertilization occurs
Early Embryology
- The blastocyst hatches from the zona pellucida and undergoes implantation in the uterine endometrium
- The blastocyst is composed of a trophoblast, an embryoblast, and a blastocoel
- The trophoblast develops into syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast
- The embryoblast develops into a bilaminar disk consisting of epiblast and hypoblast
Week 1
- Day 1-3: The zygote develops into a morula, a 12-32 cell stage
- Day 4-5: A fluid-filled cavity develops within the embryo, and four separate structures can be noted: trophoblast, embryoblast, blastocoel, and zona pellucida
- Day 5-6: The blastocyst hatches from the zona pellucida and undergoes implantation in the uterine endometrium
- Day 6-7: The syncytiotrophoblast invades into the endometrial stroma, and the embryoblast differentiates into two distinct layers: epiblast and hypoblast
Week 2
- Day 10: Implantation of the embryo is complete
- The embryo is completely embedded within the endometrium, surrounded by syncytiotrophoblast cells
- The stromal cells undergo decidualization, accumulating glycogen and lipids throughout the uterus
- The epiblast and hypoblast extend around the entire interior surface of the blastocoel
Week 3
- The epiblast enlarges and gives rise to amnioblasts
- The hypoblast extends around the entire interior surface of the blastocoel
- The mesoblasts form the intraembryonic, or embryonic, mesoderm
- Gastrulation occurs, resulting in the formation of three embryonic germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm
- The notochord forms, and then the following develop: neural groove, neural plate, early neural tube, paraxial mesoderm, and somites
Extra-Embryonic Structures
- The umbilical vesicle (yolk sac) forms from the hypoblast
- The amniotic cavity forms from the epiblast
- The extra-embryonic coelom forms from the fluid accumulation between the extra-embryonic mesodermal cells
- The chorion forms from the extraembryonic somatic mesoderm and trophoblast
- The chorionic sac encloses the embryo and its cavities, and is surrounded by the syncytiotrophoblast
Development of Chorionic Villi
- The cytotrophoblast sends extensions to the lacuna to form primary villi
- The primary villi are precursors of functional placental villi
- The syncytiotrophoblast contacts endometrial blood vessels, and the blood vessel deteriorates, forming "little lakes" or lacunar networks
- The oxygenated maternal blood and glycogen/lipids from deteriorating decidual cells nourish the embryo
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.