Podcast
Questions and Answers
What phase occurs from days 6 to 14 in the uterine cycle?
What phase occurs from days 6 to 14 in the uterine cycle?
- Menstrual phase
- Proliferative phase (correct)
- Luteal phase
- Secretory phase
What is the role of progesterone during the secretory phase?
What is the role of progesterone during the secretory phase?
- To build the stratum basalis
- To stimulate the release of eggs from the ovaries
- To maintain the stratum functionalis for potential embryo support (correct)
- To initiate menstruation
Which structure is NOT part of the layers of the vagina?
Which structure is NOT part of the layers of the vagina?
- Muscularis
- Adventitia
- Mucosa
- Epithelium (correct)
Which of the following is considered external genitalia?
Which of the following is considered external genitalia?
What is the primary function of the mammary glands in pregnant females?
What is the primary function of the mammary glands in pregnant females?
What stimulates the vagina's mucosa to maintain health?
What stimulates the vagina's mucosa to maintain health?
What is the primary function of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
During spermatogenesis, what is the outcome of the meiosis stage?
During spermatogenesis, what is the outcome of the meiosis stage?
What happens to spermatogonia during the first stage of spermatogenesis?
What happens to spermatogonia during the first stage of spermatogenesis?
Which hormone primarily signals sperm production in the testes?
Which hormone primarily signals sperm production in the testes?
What is the significance of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
What is the significance of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
What structural adaptations do sperm acquire during spermiogenesis?
What structural adaptations do sperm acquire during spermiogenesis?
What function do the accessory sex organs play in the male reproductive system?
What function do the accessory sex organs play in the male reproductive system?
Why is it important for the testicles to be located outside the abdominal cavity?
Why is it important for the testicles to be located outside the abdominal cavity?
What occurs immediately after the formation of spermatocytes in spermatogenesis?
What occurs immediately after the formation of spermatocytes in spermatogenesis?
What is the primary role of the acrosome in sperm?
What is the primary role of the acrosome in sperm?
Which of the following statements about the epididymis is correct?
Which of the following statements about the epididymis is correct?
What does the ductus deferens do?
What does the ductus deferens do?
Which gland is responsible for secreting mucous to lubricate and neutralize urine acid in the male urethra?
Which gland is responsible for secreting mucous to lubricate and neutralize urine acid in the male urethra?
What substance do seminal vesicles primarily secrete to help nourish sperm?
What substance do seminal vesicles primarily secrete to help nourish sperm?
What is the main function of the prostate gland?
What is the main function of the prostate gland?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the spermatic cords?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the spermatic cords?
What is the primary purpose of the urethra in males?
What is the primary purpose of the urethra in males?
Which erectile body is NOT found in the penis?
Which erectile body is NOT found in the penis?
What is the role of the nurse cells in the testicles?
What is the role of the nurse cells in the testicles?
What role does the corona radiata play in relation to the ovum?
What role does the corona radiata play in relation to the ovum?
During which phase of the ovarian cycle does the corpus luteum form?
During which phase of the ovarian cycle does the corpus luteum form?
What event must occur for the primary oocyte to complete meiosis II?
What event must occur for the primary oocyte to complete meiosis II?
What is the anatomical term for the uterine tubes?
What is the anatomical term for the uterine tubes?
What is the primary function of the uterus?
What is the primary function of the uterus?
What is the term for the layer of the uterine wall that undergoes changes during the uterine cycle?
What is the term for the layer of the uterine wall that undergoes changes during the uterine cycle?
What can result from an ectopic pregnancy?
What can result from an ectopic pregnancy?
Which layer of the uterine wall is primarily responsible for muscular contractions during childbirth?
Which layer of the uterine wall is primarily responsible for muscular contractions during childbirth?
What is the consequence of no implantation occurring after ovulation?
What is the consequence of no implantation occurring after ovulation?
What is the primary cause of cervical cancer related to the cervix?
What is the primary cause of cervical cancer related to the cervix?
What is the primary function of the erectile bodies in the penis?
What is the primary function of the erectile bodies in the penis?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for signaling the maturation of an ovum in the ovaries?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for signaling the maturation of an ovum in the ovaries?
What change occurs in the female reproductive system in response to the menstrual cycle?
What change occurs in the female reproductive system in response to the menstrual cycle?
What part of the ovary is responsible for holding vascular tissue?
What part of the ovary is responsible for holding vascular tissue?
During which phase of the ovarian cycle are primordial follicles activated?
During which phase of the ovarian cycle are primordial follicles activated?
What happens to the veins that normally drain the penis during arousal?
What happens to the veins that normally drain the penis during arousal?
What is the function of smooth muscle contraction along the reproductive tract?
What is the function of smooth muscle contraction along the reproductive tract?
How often is typically one egg released from an ovary?
How often is typically one egg released from an ovary?
Which structure forms a fluid-filled cavity that surrounds the oocyte during the maturation process?
Which structure forms a fluid-filled cavity that surrounds the oocyte during the maturation process?
What hormone surges to trigger the rupture of the follicle during ovulation?
What hormone surges to trigger the rupture of the follicle during ovulation?
Flashcards
Scrotum Function
Scrotum Function
The scrotum regulates the temperature of the testicles, keeping them 3 degrees Celsius cooler than the body's core temperature.
Spermatogenesis Stages
Spermatogenesis Stages
Spermatogenesis involves three main stages: spermatocytogenesis (formation of spermatocytes), meiosis (reduction division), and spermiogenesis (sperm maturation).
Seminiferous Tubules Function
Seminiferous Tubules Function
The seminiferous tubules are where sperm cells are produced. It's a key part of the male reproductive process.
Testicles' Role in Sperm Production
Testicles' Role in Sperm Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatogonia Division
Spermatogonia Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meiosis Role in Spermatogenesis
Meiosis Role in Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatid Maturation
Spermatid Maturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scrotum Structure
Scrotum Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Composition
Sperm Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromosome
Acromosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nurse cells
Nurse cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Deferens (Vas Deferens)
Ductus Deferens (Vas Deferens)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicles
Seminal Vesicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Glands
Bulbourethral Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatic Cords
Spermatic Cords
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semen
Semen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Phase
Menstrual Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proliferative Phase
Proliferative Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretory Phase
Secretory Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagina Function
Vagina Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Genitalia
External Genitalia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammary Gland Function
Mammary Gland Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corona Radiata
Corona Radiata
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fimbriae
Fimbriae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Luteal Phase
Luteal Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum
Corpus Luteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Oocyte
Primary Oocyte
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Tubes
Uterine Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristaltic Waves
Peristaltic Waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus Function
Uterus Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis Erection
Penis Erection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erection Triggers
Erection Triggers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ejaculation Control
Ejaculation Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Female Reproductive System Function
Female Reproductive System Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovaries: Location and Function
Ovaries: Location and Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oocyte Release
Oocyte Release
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Cycle: Follicular Phase
Ovarian Cycle: Follicular Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Cycle: Ovulation
Ovarian Cycle: Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primordial Follicles
Primordial Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Male Reproductive System
- The male reproductive system becomes active after puberty.
- Puberty causes reproductive organs to mature, creating a fertile individual.
- Primary sex organs produce sex cells (sperm) and sex hormones.
- Accessory sex organs support the sex cells and aid in fertilization.
- Scrotum: a sac outside the abdominal cavity.
- Scrotum structure: smooth and skeletal muscle and skin, divided into left and right compartments for testes.
- Scrotum function: maintains testes at 3 degrees cooler than body temperature.
- Muscles in scrotum contract/relax to adjust temperature.
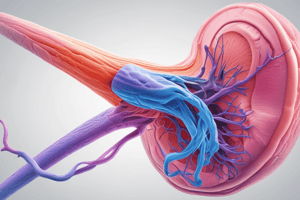
- Testes: oval-shaped organs with seminiferous tubules for sperm production.
- Testes respond to follicle-stimulating hormone.
- Sperm maturation in epididymis.
- Seminiferous tubules: composed of stratified epithelium surrounding a lumen.
- Spermatogenic cells mature into sperm.
- At puberty, seminiferous tubules produce approximately 400 million sperm.
- Spermatogenic cells (different stages): Spermatogonium, Primary spermatocyte, Secondary spermatocyte, Spermatid, and Sperm.
- Spermatogenesis stages: formation of spermatocytes, meiosis, and spermiogenesis.
- Spermatogonium divides by mitosis producing two daughter cells.
- Meiosis is reduction division producing 4 spermatids from one spermatogonium.
- Spermiogenesis: spermatids mature into sperm with flagella, mitochondria, nucleus (DNA), with a special structure at the head called the acrosome.
- Support cells in testicles help sperm mature and leave the scrotum.
- Muscle contractions help sperm exit the testes.
- Epidydimis: organ arching over posterior side of testicles, about 6 meters long when uncoiled.
- Epididymus function: Complete maturation and ability for sperm to swim and fertilize during 20 days.
- Ejaculation: smooth muscle causing mature sperm to move to the ductus deferens.
- Ductus deferens (vas deferens): carries sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory duct and prostatic urethra.
- Spermatic Cords: hold blood vessels, nerves, and ductus deferens to the testes.
- Urethra: carries sperm and urine; secretes lubricating solution before ejaculation.
- Semen consists of sperm plus secretions from accessory glands.
- Accessory Glands: these glands increase sperm's survival outside the body.
- Seminal vesicles: produce fructose (sugar), nutrients, prostaglandins to stimulate urethra contraction, and enzymes to thicken ejaculate.
- Prostate gland: secrete milky fluid enhancing sperm mobility and thickening ejaculate; prone to STDs and tumors.
- Bulbourethral glands: lubricate and neutralize the acid from urine in the male urethra.
- Penis: designed to deliver semen.
- Penis contains corpora spongiosum, corpora cavernosa and smooth muscle and connective tissues.
- Erectile bodies: spongy, blood vessel rich network, dilate during arousal.
- Veins that drain penis are compressed during erection.
- Vasodilation from parasympathetic branch causes erection.
- Ejaculation from sympathetic branch contracting smooth muscles along reproductive tract.
Female Reproductive System
- The female reproductive system produces ova (eggs) and sex hormones.
- These organs provide an environment for internal fertilization and development. The female reproductive system also goes through changes during the menstrual cycle.
- Mammary glands nourish the infant.
- Ovaries: paired organs suspended by ligaments.
- Ovaries structure: surrounded by a fibrous capsule, divided into cortex (ova) and medulla (vascular tissue).
- Ovaries function: oogenesis and female hormone production.
- Ovaries respond to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to mature ova, only one egg released each month.
- Estrogen and progesterone released by ovaries regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Ovarian Cycle stages: Follicular phase, Ovulation, Luteal phase
- Follicular phase-(first two weeks): follicles develop and mature, releasing eggs (oocytes.)
- Ovulation (midcycle): the mature follicle ruptures, releasing oocyte, due to Luteinizing Hormone (LH) release.
- Luteal phase-(second two weeks): ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum that produces progesterone.
- If pregnancy fails, corpus luteum degenerates, initiating the next cycle.
- Oogenesis (in fetal development): meiosis I begins but is not completed.
- Primary oocytes in ovaries remain in prophase I until puberty.
- At ovulation, primary oocyte completes meiosis I, starts meiosis II
- Meiosis II completed if fertilization occurs, resulting in ovum.
- Uterine/fallopian tubes: these tubes carry ova to uterus.
- Ciliated epithelium inside tubes guides ova towards the uterus.
- Muscles contraction (peristaltic waves) aids in movement.
- Non-ciliated cells along the tube nourish ova or the developing embryo.
- Uterus: pear-shaped muscular pouch superior to bladder, receives embryo.
- Uterus walls have 3 layers (perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium).
- The thick endometrium undergoes changes during menstrual cycle.
- Cervix: opening of the uterus, dilates during childbirth.
- Vagina: birth canal, the opening that leads to the cervix.
- Vagina structure: very flexible, composed of adventitia, muscularis, and mucosa layers.
- Vagina produces glycogen to support beneficial bacteria producing lactic acid.
- External genitalia (vulva): mons pubis, labia majora, clitoris, vestibule (vaginal and urethral orifices, vestibule glands), and labia minora.
- Mammary glands are modified sweat glands to produce milk after childbirth.
- Mammary glands appear as rudimentary structures in both genders; after puberty, ducts grow but glands do not fully develop, mainly adipose.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.