Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where are the sites of sperm production in the male?
Where are the sites of sperm production in the male?
- Seminal vesicle
- Ductus deferens
- Paired testes (correct)
- Epididymis
What is the function of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
- Stores sperm
- Regulates the temperature of the developing sperm (correct)
- Produces testosterone
- Facilitates urine excretion
What is the purpose of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
What is the purpose of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
- Sperm maturation and storage (correct)
- Hormone secretion
- Nutrient absorption
- Sperm production
What is the function of the ductus (vas) deferens in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the ductus (vas) deferens in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the seminal vesicle in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the seminal vesicle in the male reproductive system?
What is the purpose of the ejaculatory duct in the male reproductive system?
What is the purpose of the ejaculatory duct in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the seminiferous tubules in the testes?
What is the function of the seminiferous tubules in the testes?
What happens when the temperature within the scrotum falls below a certain point?
What happens when the temperature within the scrotum falls below a certain point?
What is the length of each testis in the male reproductive system?
What is the length of each testis in the male reproductive system?
What is the purpose of the smooth muscle in the scrotum?
What is the purpose of the smooth muscle in the scrotum?
What is the role of the testes in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the testes in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the scrotum in relation to the temperature of the developing sperm?
What is the function of the scrotum in relation to the temperature of the developing sperm?
Where does the process of sperm production occur?
Where does the process of sperm production occur?
What is the function of the epididymis in sperm development?
What is the function of the epididymis in sperm development?
What is the main function of the penis in the male reproductive system?
What is the main function of the penis in the male reproductive system?
What is contained in semen?
What is contained in semen?
What stimulates undifferentiated spermatogonia and Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?
What stimulates undifferentiated spermatogonia and Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?
What is the composition of a mature sperm?
What is the composition of a mature sperm?
What controls male reproductive tissues, behavior, and secondary sexual characteristics?
What controls male reproductive tissues, behavior, and secondary sexual characteristics?
What is the main role of testosterone in the male reproductive system?
What is the main role of testosterone in the male reproductive system?
What controls the production and secretion of testosterone in the male reproductive system?
What controls the production and secretion of testosterone in the male reproductive system?
What maintains a consistent blood concentration of testosterone and sperm production in the male reproductive system?
What maintains a consistent blood concentration of testosterone and sperm production in the male reproductive system?
How many sperm are typically produced daily after puberty?
How many sperm are typically produced daily after puberty?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
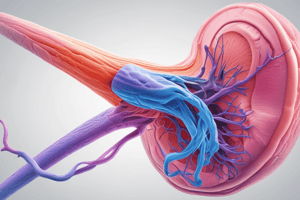
Male Reproductive System and Sperm Production
- Sperm are not fully mature upon leaving the seminiferous tubules; their ability to swim develops in the epididymis and ductus deferens.
- The penis is the male organ of sexual intercourse, delivering sperm internally to the female and containing erectile tissues for erection.
- Semen, a mixture of fluids, contains fructose and prostaglandins from the seminal vesicles, an alkaline fluid from the prostate gland, and mucus from the bulbourethral gland.
- The process of sperm production occurs in the seminiferous tubules, involving mitosis and meiosis to produce haploid cells.
- Spermatogonia, diploid cells with 46 chromosomes, divide by mitosis to ensure a constant supply of primary spermatocytes.
- Spermatids, haploid cells, mature slowly to become sperm, a process taking about 9-10 weeks and supported by Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules.
- A mature sperm has a head with DNA, an acrosome containing penetration enzymes, and a flagellum powered by mitochondria.
- Tens of millions of sperm are produced daily after puberty, and a typical ejaculation may contain 100-300 million sperm.
- Testosterone, produced by interstitial cells, controls male reproductive tissues, behavior, and secondary sexual characteristics, stimulating undifferentiated spermatogonia and Sertoli cells.
- The production and secretion of testosterone depend on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Negative feedback loops maintain a consistent blood concentration of testosterone and sperm production.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.