Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the seminal fluid added by the seminal vesicles?
What is the primary function of the seminal fluid added by the seminal vesicles?
- To neutralize acidic residues in the urethra
- To provide a protective barrier around sperm
- To stimulate sperm production in the testes
- To provide energy for sperm motility (correct)
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating Leydig cells to produce testosterone?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating Leydig cells to produce testosterone?
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Inhibin
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) (correct)
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
What role does the prostate fluid play in semen composition?
What role does the prostate fluid play in semen composition?
- It neutralizes the acidic environment of the epididymis
- It provides nutrients for sperm maturation
- It increases sperm motility and protects sperm from bacteria (correct)
- It stimulates the secretion of inhibin by Sertoli cells
Where does sperm maturation primarily occur?
Where does sperm maturation primarily occur?
What is the function of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in spermatogenesis?
What is the function of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in spermatogenesis?
Which gland adds fluid to semen that neutralizes any acidic residue in the urethra?
Which gland adds fluid to semen that neutralizes any acidic residue in the urethra?
During ejaculation, the final semen mixture is expelled through which structure?
During ejaculation, the final semen mixture is expelled through which structure?
What does Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) stimulate the release of?
What does Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) stimulate the release of?
What initiates the production of testosterone by Leydig cells?
What initiates the production of testosterone by Leydig cells?
How does dihydrotestosterone (DHT) differ from testosterone in terms of receptor binding?
How does dihydrotestosterone (DHT) differ from testosterone in terms of receptor binding?
What is the primary role of inhibin in male reproductive physiology?
What is the primary role of inhibin in male reproductive physiology?
What role does estrogen play in the male reproductive system?
What role does estrogen play in the male reproductive system?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)?
Which of the following correctly describes one of the functions of testosterone?
Which of the following correctly describes one of the functions of testosterone?
What physiological feedback mechanism does testosterone use to regulate its own levels?
What physiological feedback mechanism does testosterone use to regulate its own levels?
Which cell type is primarily responsible for converting small amounts of testosterone into estrogen?
Which cell type is primarily responsible for converting small amounts of testosterone into estrogen?
What happens to hormone levels if fertilization does not occur after ovulation?
What happens to hormone levels if fertilization does not occur after ovulation?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium continue to thicken and become more vascularized?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium continue to thicken and become more vascularized?
What role does estrogen play in the menstrual cycle during the follicular phase?
What role does estrogen play in the menstrual cycle during the follicular phase?
What occurs to the cervical mucus during the luteal phase?
What occurs to the cervical mucus during the luteal phase?
At what average age does menopause typically occur in women?
At what average age does menopause typically occur in women?
What is a significant effect of decreased estrogen during menopause?
What is a significant effect of decreased estrogen during menopause?
What marks the transition to menopause for women?
What marks the transition to menopause for women?
Which phase directly follows ovulation in the menstrual cycle?
Which phase directly follows ovulation in the menstrual cycle?
What is colostrum primarily known for?
What is colostrum primarily known for?
What causes constipation during pregnancy?
What causes constipation during pregnancy?
What role does corticotripin-releasing hormone (CRH) play during pregnancy?
What role does corticotripin-releasing hormone (CRH) play during pregnancy?
How does pregnancy affect insulin resistance?
How does pregnancy affect insulin resistance?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the enlargement of mammary glands during pregnancy?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the enlargement of mammary glands during pregnancy?
What are the main stages of parturition?
What are the main stages of parturition?
How does the basal metabolic rate (BMR) change during pregnancy?
How does the basal metabolic rate (BMR) change during pregnancy?
What physiological change may lead pregnant women to feel overheated?
What physiological change may lead pregnant women to feel overheated?
What initiates contractions during the first stage of labor?
What initiates contractions during the first stage of labor?
Which hormone increases receptor density in the uterus, making it more responsive during labor?
Which hormone increases receptor density in the uterus, making it more responsive during labor?
During the second stage of labor, what primarily assists in pushing the baby through the birth canal?
During the second stage of labor, what primarily assists in pushing the baby through the birth canal?
What is the expected duration of the second stage of labor?
What is the expected duration of the second stage of labor?
What role does relaxin play during childbirth?
What role does relaxin play during childbirth?
What causes uterine blood vessels to tear during the third stage of labor?
What causes uterine blood vessels to tear during the third stage of labor?
Which of the following is a cause of labor pain during contractions?
Which of the following is a cause of labor pain during contractions?
How long does it typically take for the placenta to be expelled after the birth of the baby?
How long does it typically take for the placenta to be expelled after the birth of the baby?
Study Notes
Male Reproductive System
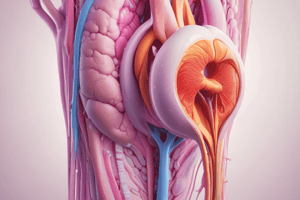
- Sperm maturation occurs in the epididymis where sperm gain motility and become capable of fertilizing an egg.
- Sperm transported from epididymis via the vas deferens.
- Seminal fluid added by seminal vesicles containing fructose for energy and substances aiding motility and protection against the female reproductive tract.
- Sperm and seminal fluid combine in the ejaculatory duct, which passes through the prostate.
- Prostate gland contributes fluid for protection against bacteria and increased sperm motility.
- Bulbourethral glands secrete an alkaline fluid to neutralize acidity in the urethra.
- Ejaculation expels the semen mixture through the urethra and out of the penis.
Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH), secreted from the hypothalamus, stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release LH and FSH.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) targets Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone, essential for spermatogenesis and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) targets Sertoli cells to support sperm development and maturation, while also stimulating inhibin secretion.
- Testosterone, produced by Leydig cells, initiates and maintains spermatogenesis, supports male reproductive organs, and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a more potent form of testosterone, binding more effectively to androgen receptors and further promoting sperm development.
- Estrogen, produced by Sertoli cells, is involved in regulating fluid reabsorption in the epididymis for sperm maturation.
- Inhibin, secreted by Sertoli cells, provides negative feedback to the pituitary gland, reducing FSH release to regulate spermatogenesis.
Feedback Loops
- Testosterone negatively feeds back to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, suppressing GnRH and LH secretion to stabilize testosterone levels.
- Inhibin provides negative feedback to the pituitary gland, inhibiting FSH release to maintain balanced sperm production.
Functions of Testosterone and DHT
- Testosterone and DHT are both androgens that play important roles in male development and reproductive function.
- Testosterone is essential for spermatogenesis and supports Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules.
- DHT is more potent than testosterone and plays a role in developing male secondary sex characteristics.
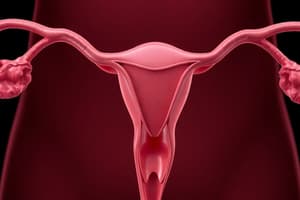
Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual cycle includes three phases:
- Menstrual phase: shedding of the endometrium causing bleeding.
- Proliferative phase: estrogen stimulates endometrial lining thickening.
- Secretory phase: progesterone prepares the endometrium for implantation.
- Follicular phase occurs during days 1-14, with the development of follicles in response to FSH, leading to the maturation of a dominant follicle.
- Luteal phase occurs during days 15-28 with the transformation of the dominant follicle into the corpus luteum, secreting progesterone.
Menopause
- Menopause marks the end of a woman's reproductive years typically occurring between ages 45-55.
- Production of eggs and hormones (estrogen and progesterone) decreases by the ovaries, resulting in the cessation of ovulation and menstruation.
- Decreased estrogen levels contribute to various physical and emotional changes and impact bone density, mood, and cardiovascular health.
Pregnancy
- Colostrum, the first milk produced, is rich in antibodies and provides passive immunity to the newborn.
- Gastrointestinal system:
- Constipation caused by progesterone relaxing smooth muscles and pressure from the enlarging uterus.
- Heartburn caused by the uterus pushing up on the stomach leading to acid reflux.
- Nausea and vomiting often associated with hCG produced early in pregnancy.
- Endocrine system:
- Pituitary gland: increases in size due to progesterone-stimulated prolactin production.
- Progesterone plays a role in mammary gland enlargement and milk synthesis preparation.
- Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH), released by the placenta, stimulates ACTH secretion, leading to increased cortisol levels.
- Insulin resistance increases maternal glucose levels ensuring glucose delivery to the fetus.
- Parathyroid Hormone-related Peptide (PTHrp), released from the placenta and breasts during lactation, promotes calcium absorption and bone mineralization in the fetus.
- Thyroid gland increases in size, stimulated by hCG to promote fetal growth and development.
- Metabolic changes:
- Increased nutrient requirements due to the demands of pregnancy and fetal growth.
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) increases contributing to an overall increased energy demand.
- Feeling overheated due to increased metabolic rate and carrying extra weight.
Parturition (Childbirth)
- Parturition is the process of delivering a baby involving coordinated events, including cervical dilation, uterine contractions, and expulsion of the fetus and placenta.
- Three stages of parturition:
- First stage: Contractions
- Cervical dilation: gradual opening of the cervical canal.
- Hormonal changes: high estrogen increases oxytocin receptor density, making the uterus more responsive to oxytocin, which stimulates contractions.
- Positive feedback cycle: cervical stretching triggers oxytocin release initiating contractions.
- Uterine contractions begin mild and infrequent, becoming stronger and more frequent.
- Second stage: Delivery of the baby
- Neural reflex activation: stretching of the cervix and uterine walls stimulates abdominal muscle contractions, leading to voluntary pushing.
- Pushing: active contraction of abdominal muscles pushes the baby through the birth canal.
- Umbilical cord: clamped, tied, and severed after delivery.
- Third stage: Delivery of the placenta
- Placenta separation: contractions after baby delivery separate the placenta from the uterine wall.
- Blood loss: detachment causes uterine blood vessel tearing, leading to blood loss, which is minimized by uterine contractions.
- Expulsion of the afterbirth: placenta is expelled, typically within 15-30 minutes.
- First stage: Contractions
- Relaxin softens and widens the cervix and inhibits uterine contractions during pregnancy.
- Labor pain is caused by:
- Hypoxia of the myometrium during contractions, restricting blood flow, leading to pain similar to angina.
- Pressure from the fetal head against the pelvic outlet.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the intricate details of the male reproductive system, including sperm maturation, transportation, and the roles of various glands. This quiz will delve into the hormonal control of spermatogenesis, highlighting key hormones and their functions. Test your understanding of how these processes contribute to male fertility.