Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a common symptom associated with BPH?
What is a common symptom associated with BPH?
- Severe back pain
- Rapid weight gain
- Frequent need to urinate (correct)
- Increased appetite
TURP is a surgery that reduces the size of the prostate.
TURP is a surgery that reduces the size of the prostate.
True (A)
Name one peripherally acting alpha-adrenergic blocker used in the treatment of BPH.
Name one peripherally acting alpha-adrenergic blocker used in the treatment of BPH.
Tamsulosin
The increase in prostate cell growth is primarily ____________ sensitive.
The increase in prostate cell growth is primarily ____________ sensitive.
Which of the following statements about 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors is true?
Which of the following statements about 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors is true?
What should be done before cataract surgery in patients taking alpha-adrenergic blockers?
What should be done before cataract surgery in patients taking alpha-adrenergic blockers?
Match the drug with its effect or classification:
Match the drug with its effect or classification:
Patients on 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can donate blood immediately after their last dose.
Patients on 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can donate blood immediately after their last dose.
Flashcards
BPH
BPH
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that occurs with aging, often affecting men over 80.
BPH Symptoms
BPH Symptoms
Frequent urination, small urine volume, incomplete bladder emptying.
BPH Cause
BPH Cause
Excessive growth of prostate cells, primarily driven by testosterone.
BPH Diagnosis
BPH Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripherally Acting Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers
Peripherally Acting Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers
Signup and view all the flashcards
5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors
5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors
Signup and view all the flashcards
TURP
TURP
Signup and view all the flashcards
TUNA
TUNA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
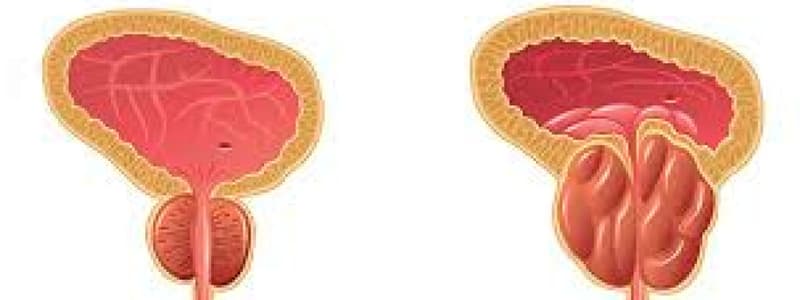
Male Reproductive (BPH)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is excessive prostate cell growth
- Primarily occurs in men aged 80 and older (80% prevalence)
- Prostate growth is testosterone-sensitive
- The enlarged prostate presses on the urethra, hindering urine flow
Symptoms (S/S)
- Frequent urination
- Small urine volume
- Difficulty emptying the bladder completely
Diagnosis
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test to rule out cancer
Treatments
- Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA): A needle ablation procedure
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): Most common surgical procedure, involves cutting/removing prostate tissue with a catheter and irrigation afterwards.
- Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP): Incision of the prostate using a catheter
- Three way catheter is used after TURP surgery. The catheter constantly irrigates the area.
Medications (Classification)
-
Peripherally Acting Alpha Adrenergic Blockers: These medications block receptors in the prostate, relaxing the prostate tissue
- Examples include Tamsulosin (Flomax).
- Side effects: headache, fatigue, dizziness, lethargy, tachycardia, hypotension, sexual dysfunction; should be held before surgery.
-
5-alpha-Reductase Inhibitors/Androgen Inhibitors: These medications inhibit the enzymes that convert testosterone into a form that enlarges the prostate. This reduces prostate size.
- Example: Finasteride (Proscar).
- Side effect: Cannot donate blood for 6 months after using this medication
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.