Podcast
Questions and Answers
The lumbosacral plexus is a network of nerves formed by which of the following?
The lumbosacral plexus is a network of nerves formed by which of the following?
- Dorsal rami of the sacral spinal nerves only
- Dorsal rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerves
- Ventral rami of the lumbar spinal nerves only
- Ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerves (correct)
What are the two main parts into which the lumbosacral plexus is typically divided for examination and study?
What are the two main parts into which the lumbosacral plexus is typically divided for examination and study?
- The superior and inferior gluteal plexuses
- The lumbar and sacral plexuses (correct)
- The femoral and obturator plexuses
- The iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal plexuses
Given its anatomical location, which of the following muscles is in close proximity to the sacral plexus?
Given its anatomical location, which of the following muscles is in close proximity to the sacral plexus?
- Iliacus muscle
- Quadratus lumborum muscle
- Psoas major muscle
- Piriformis muscle (correct)
Which spinal nerve segments primarily contribute to the formation of the lumbar plexus?
Which spinal nerve segments primarily contribute to the formation of the lumbar plexus?
Which of the following nerves that originate from the lumbar plexus innervates the skin of the suprapubic and inguinal regions?
Which of the following nerves that originate from the lumbar plexus innervates the skin of the suprapubic and inguinal regions?
A patient reports pain and altered sensation along the anterolateral surface of their thigh. Which nerve, originating from the lumbar plexus, is most likely affected?
A patient reports pain and altered sensation along the anterolateral surface of their thigh. Which nerve, originating from the lumbar plexus, is most likely affected?
Which of the following best describes the path of the genitofemoral nerve after it runs inferiorly along the psoas muscle?
Which of the following best describes the path of the genitofemoral nerve after it runs inferiorly along the psoas muscle?
The femoral nerve is known to innervate the anterior thigh muscles. In addition to motor function, which cutaneous region does it supply through its branches?
The femoral nerve is known to innervate the anterior thigh muscles. In addition to motor function, which cutaneous region does it supply through its branches?
A patient has difficulty adducting the thigh. Which nerve, originating from the lumbar plexus, is most likely affected?
A patient has difficulty adducting the thigh. Which nerve, originating from the lumbar plexus, is most likely affected?
The obturator nerve runs inferiorly on its lateral border and passes through which foramen to reach its target muscles?
The obturator nerve runs inferiorly on its lateral border and passes through which foramen to reach its target muscles?
Which nerve is formed by the union of part of the ventral ramus of L4 and the ventral ramus of L5?
Which nerve is formed by the union of part of the ventral ramus of L4 and the ventral ramus of L5?
Which of the following nerve roots contribute to the formation of the sacral plexus?
Which of the following nerve roots contribute to the formation of the sacral plexus?
Which of the following nerves that originates from the sacral plexus innervates the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae lata muscles?
Which of the following nerves that originates from the sacral plexus innervates the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae lata muscles?
A patient cannot abduct their thigh. Which of the following nerves may be damaged?
A patient cannot abduct their thigh. Which of the following nerves may be damaged?
Which of the following nerves stems from the sacral plexus and innervates the gluteus maximus muscle?
Which of the following nerves stems from the sacral plexus and innervates the gluteus maximus muscle?
Where does the sciatic nerve typically divide into its two major branches?
Where does the sciatic nerve typically divide into its two major branches?
Which two nerves arise from the sciatic nerve?
Which two nerves arise from the sciatic nerve?
What part of the lower limb is supplied by the tibial nerve?
What part of the lower limb is supplied by the tibial nerve?
Which of the following nerves, arising from the sacral plexus, innervates the external anal sphincter and provides sensory fibers to the skin of the anal region?
Which of the following nerves, arising from the sacral plexus, innervates the external anal sphincter and provides sensory fibers to the skin of the anal region?
After exiting the pelvis, the pudendal nerve re-enters through which foramen?
After exiting the pelvis, the pudendal nerve re-enters through which foramen?
The common peroneal (fibular) nerve divides into two branches around the lateral part of the knee joint. These are the superficial and deep peroneal nerves. What does the superficial peroneal nerve innervate?
The common peroneal (fibular) nerve divides into two branches around the lateral part of the knee joint. These are the superficial and deep peroneal nerves. What does the superficial peroneal nerve innervate?
A person has lost sensation on the medial aspect of their buttock. Which nerve has most like been damaged?
A person has lost sensation on the medial aspect of their buttock. Which nerve has most like been damaged?
A patient presents with an inability to plantarflex the foot and difficulty with toe flexion. Sensation is diminished on the plantar surface of the foot. Which nerve is MOST likely affected?
A patient presents with an inability to plantarflex the foot and difficulty with toe flexion. Sensation is diminished on the plantar surface of the foot. Which nerve is MOST likely affected?
Following a pelvic fracture, a patient experiences weakness in hip adduction and sensory loss on the medial thigh. What nerve is MOST likely injured?
Following a pelvic fracture, a patient experiences weakness in hip adduction and sensory loss on the medial thigh. What nerve is MOST likely injured?
A person experiences issues with dorsiflexion of the foot. This indicates which nerve may have damage?
A person experiences issues with dorsiflexion of the foot. This indicates which nerve may have damage?
A 60-year-old patient reports experiencing numbness and tingling in the lateral aspect of their leg and dorsum of their foot. Which nerve is MOST likely involved?
A 60-year-old patient reports experiencing numbness and tingling in the lateral aspect of their leg and dorsum of their foot. Which nerve is MOST likely involved?
Which of the following structures carries preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the hypogastric (pelvic) plexus?
Which of the following structures carries preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the hypogastric (pelvic) plexus?
Following a motor vehicle accident, a patient has lost all sensation in the skin covering the perineum. Function of the bowel and bladder are intact. Which nerve root or nerve is MOST likely damaged?
Following a motor vehicle accident, a patient has lost all sensation in the skin covering the perineum. Function of the bowel and bladder are intact. Which nerve root or nerve is MOST likely damaged?
What is the origin of the sural nerve?
What is the origin of the sural nerve?
What muscles are innervated by the obturator nerve?
What muscles are innervated by the obturator nerve?
Which of the following nerve roots contribute to the ventral rami of the coccygeal plexus?
Which of the following nerve roots contribute to the ventral rami of the coccygeal plexus?
The medial and lateral plantar nerves are terminal branches of what nerve?
The medial and lateral plantar nerves are terminal branches of what nerve?
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg are innervated by the deep peroneal nerve. What portion of the leg and foot does this nerve supply?
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg are innervated by the deep peroneal nerve. What portion of the leg and foot does this nerve supply?
Which nerve is responsible for supplying the skin on the posterior aspect of the thigh?
Which nerve is responsible for supplying the skin on the posterior aspect of the thigh?
Pelvic splanchnic nerves arising from which roots of the sacral plexus?
Pelvic splanchnic nerves arising from which roots of the sacral plexus?
A branch of the femoral nerve, the saphenous nerve, is responsible for supplying which part of the leg and foot?
A branch of the femoral nerve, the saphenous nerve, is responsible for supplying which part of the leg and foot?
The lumbosacral plexus is essential for motor and sensory innervation of the lower limb. Injury to which of the following nerve components would MOST likely result in both difficulty with hip flexion and impaired sensation of the anterior thigh?
The lumbosacral plexus is essential for motor and sensory innervation of the lower limb. Injury to which of the following nerve components would MOST likely result in both difficulty with hip flexion and impaired sensation of the anterior thigh?
What is the most accurate description of the lumbosacral trunk's formation?
What is the most accurate description of the lumbosacral trunk's formation?
Which of the following accurately describes the path of the superior gluteal nerve after it exits the pelvis?
Which of the following accurately describes the path of the superior gluteal nerve after it exits the pelvis?
A patient reports sensory deficits on the medial aspect of the leg and foot. Which nerve is MOST likely involved?
A patient reports sensory deficits on the medial aspect of the leg and foot. Which nerve is MOST likely involved?
If a patient is experiencing pain when flexing their hip, which nerve is MOST likely the cause of pain?
If a patient is experiencing pain when flexing their hip, which nerve is MOST likely the cause of pain?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the contribution of the ventral ramus of T12 to the lumbar plexus formation?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the contribution of the ventral ramus of T12 to the lumbar plexus formation?
A patient exhibits weakness in thigh adduction accompanied by sensory loss on the medial thigh. Considering these findings, where is the lesion MOST likely located?
A patient exhibits weakness in thigh adduction accompanied by sensory loss on the medial thigh. Considering these findings, where is the lesion MOST likely located?
If the common peroneal nerve is severed, what functional deficit would MOST likely be observed?
If the common peroneal nerve is severed, what functional deficit would MOST likely be observed?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg and supplies skin on the lower half of the anterolateral leg and most of the dorsum of the foot?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg and supplies skin on the lower half of the anterolateral leg and most of the dorsum of the foot?
If a lesion affects the nerve that passes through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis, which muscle's function would be MOST directly affected?
If a lesion affects the nerve that passes through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis, which muscle's function would be MOST directly affected?
Which of the following nerves, originating from the sacral plexus, provides primary innervation to the perineal muscles and sensory supply to the skin of the anal and genital regions?
Which of the following nerves, originating from the sacral plexus, provides primary innervation to the perineal muscles and sensory supply to the skin of the anal and genital regions?
A patient with difficulty in hip abduction MOST likely suffered damage to which nerve or muscle group?
A patient with difficulty in hip abduction MOST likely suffered damage to which nerve or muscle group?
After exiting the pelvis, the pudendal nerve traverses which of the following anatomical pathways?
After exiting the pelvis, the pudendal nerve traverses which of the following anatomical pathways?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin on the posterior aspect of the thigh?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin on the posterior aspect of the thigh?
Pelvic splanchnic nerves carry which type of fibers to the hypogastric plexus?
Pelvic splanchnic nerves carry which type of fibers to the hypogastric plexus?
The coccygeal plexus is formed by the union of which of the following?
The coccygeal plexus is formed by the union of which of the following?
Flashcards
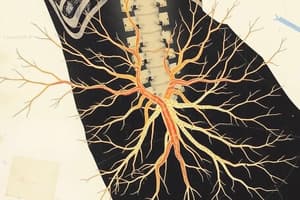
What is the lumbosacral plexus?
What is the lumbosacral plexus?
A network of nerves formed by the ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerves.
What forms the lumbar plexus?
What forms the lumbar plexus?
Formed by the union of ventral rami of L1, L2, L3, and a major part of L4 spinal nerves, with a small contribution from T12.
What are the branches of the lumbar plexus?
What are the branches of the lumbar plexus?
Iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, lateral femoral cutaneous, obturator, and femoral nerves.
What do iliohypogastric & ilioinguinal nerves do?
What do iliohypogastric & ilioinguinal nerves do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the path of the genitofemoral nerve?
What is the path of the genitofemoral nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What area does the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve supply?
What area does the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve supply?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the femoral nerve?
What is the role of the femoral nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the path and function of obturator nerve?
What is the path and function of obturator nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What forms the sacral plexus?
What forms the sacral plexus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the major branches of the sacral plexus?
What are the major branches of the sacral plexus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What direct muscular branches arise from sacral plexus?
What direct muscular branches arise from sacral plexus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the pelvic splanchnic nerves?
What is the function of the pelvic splanchnic nerves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the superior gluteal nerve innervate?
What does the superior gluteal nerve innervate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the inferior gluteal nerve innervate?
What does the inferior gluteal nerve innervate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the sciatic nerve?
What is the sciatic nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does the tibial nerve operate?
Where does the tibial nerve operate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the common peroneal nerve?
What is the common peroneal nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Give the functions of the Peroneal (fibular) nerve
Give the functions of the Peroneal (fibular) nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve function?
Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe Perforating cutaneous nerve
Describe Perforating cutaneous nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the path of the pudendal nerve.
Describe the path of the pudendal nerve.
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the coccygeal plexus formed?
How is the coccygeal plexus formed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Lumbosacral plexus is by the ventral rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal nerves.
- Usually examined in two parts; lumbar plexus and sacral plexus.
Lumbar Plexus
- Lies in the posterior abdominal wall, posterior to the psoas major muscle.
- Formed by the union of the ventral rami of the L1, L2, and L3 spinal nerves
- Also formed by a major part of ventral ramus of L4 spinal nerve.
- There is usually a small contribution to the L1 from the ventral ramus of T12.
Branches of the lumbar plexus are:
- Iliohypogastric nerve
- Ilioinguinal nerve
- Genitofemoral nerve
- Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- Obturator nerve
- Femoral nerve
Iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves:
- Innervate the muscles of the abdominal wall.
- Sensory fibers supply the skin of the suprapubic and inguinal regions.
Genitofemoral nerve:
- Runs inferiorly along the anterior part of the psoas muscle and terminates around the inguinal ligament.
- Gives two branches; genital and femoral
- Genital branch: Passes through the inguinal canal and supplies the scrotum in males and labium majus in females.
- Femoral branch: Passes under the inguinal ligament and supplies the skin area anterior to the inguinal ligament.
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve:
- Passes under the inguinal ligament and supplies the skin on the anterolateral surface of the thigh.
Femoral nerve:
- Innervates the anterior thigh muscles and supplies the skin of the anteriomedial part of the thigh.
- The saphenous nerve branch supplies the medial parts of the leg and the foot.
Obturator nerve:
- Enters the pelvis, runs inferiorly on its lateral border, and passes through the obturator foramen to reach the medial part of the thigh.
- Innervates the obturator externus and adductor group of muscles (medial thigh muscles) of the thigh.
- Supplies a small area of skin on the medial aspect of the thigh.
Sacral Plexus
- Lies in the posterior wall of the lesser pelvis, in close relation with the piriformis muscle.
- Formed by the union of the following:
- Lumbosacral trunk
- Ventral rami of the S1, S2, and S3 spinal nerves
- Part of ventral ramus of S4 spinal nerve
Branches of the sacral plexus
- Superior gluteal nerve
- Inferior gluteal nerve
- Sciatic nerve (formed of tibial and common peroneal nerves)
- Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- Pudendal nerve
- Perforating cutaneous nerve
- There are also direct muscular branches from this plexus.
Direct muscular branches of the sacral plexus:
- Nerve to priformis muscle
- Nerves to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- Nerves to obturator internus and superior gemellus muscles
- Nerves to levator ani and coccygeus muscles
- Pelvic splanchnic nerves arising from S2, S3, and S4 roots.
- Carry preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the hypogastric (pelvic) plexus.
Superior gluteal nerve:
- Passes posteriorly and leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen (through its suprapiriform part) to reach the gluteal region.
- Innervates the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae lata muscles.
Inferior gluteal nerve:
- Passes posteriorly and leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen (through its infrapiriform part) to reach the gluteal region.
- Innervates the gluteus maximus muscle.
Sciatic nerve:
- The largest nerve of the body.
- Passes posteriorly and leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen (through its infrapiriform part) to reach the gluteal region.
- Usually terminates in the posterior lower part of the thigh by dividing into the tibial nerve and common peroneal (fibular) nerve.
- Supplies the posterior thigh muscles, as well as all the muscles of the leg and foot.
- Sensory branches of the tibial and fibular nerves supply the whole of the skin of the leg and foot, except for their medial parts. The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve, supplies the medial parts.
Tibial nerve:
- Extends along the posterior compartment of the leg and innervates the muscles in this region
- Sural nerve is a branch of supplies the skin of the posteralateral parts of leg and foot
- Deep to the flexor retinaculum gives of its two terminal branches:
- Medial plantar nerve
- Lateral plantar nerve
Common peroneal (fibular) nerve:
- Divides into two branches around the lateral part of the knee joint.
Superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve:
- Innervates the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg and supplies a skin of the lower half of the anterolateral leg and most of the dorsum of the foot.
Deep peroneal (fibular) nerve:
- Innervates the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg and supplies a small skin area at the dorsum of the foot
Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve:
- Passes posteriorly and leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen (through its infrapiriform part).
- Supplies the skin on the posterior aspect of the thigh.
Perforating cutaneous nerve:
- Supplies the skin of the medial part of the buttock.
Pudendal nerve:
- Passes posteriorly and leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen (through its infrapiriform part)
- Reenters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen and passes through the pudendal canal (Alcock's canal) at the lateral wall of the ischiorectal fossa
- Innervates the external anal sphincter and the perineal muscles.
- Sensory fibers supply the skin of anal and genital regions
Coccygeal Plexus
- Is formed by the union of the following:
- Part of ventral ramus of S4 spinal nerve
- Ventral rami of S5 spinal nerve and coccygeal nerve(s)
- Anococcygeal nerves arising from this plexus supply a small area of skin of the coccygeal region.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.