Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role does gluconeogenesis play in the liver's function?
What role does gluconeogenesis play in the liver's function?
- It synthesizes triglycerides from glucose.
- It converts glucose to fatty acids.
- It stores excess glucose as glycogen.
- It creates glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. (correct)
Which substance is primarily used by the liver for glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
Which substance is primarily used by the liver for glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
- Starch
- Lactic acid
- Galactose and fructose (correct)
- Glucose
What is the main function of VLDL in the liver?
What is the main function of VLDL in the liver?
- Bile production
- Fatty acid distribution (correct)
- Cholesterol absorption
- Glycogen storage
Which of the following is NOT a storage function of the liver?
Which of the following is NOT a storage function of the liver?
Which of the following statements about bilirubin processing by the liver is true?
Which of the following statements about bilirubin processing by the liver is true?
What is the role of somatomedins synthesized by the liver?
What is the role of somatomedins synthesized by the liver?
Which plasma protein synthesized by the liver is crucial for blood clotting?
Which plasma protein synthesized by the liver is crucial for blood clotting?
What is the primary effect of the liver's detoxification function?
What is the primary effect of the liver's detoxification function?
Which statement regarding the role of hepatocytes in lipid metabolism is true?
Which statement regarding the role of hepatocytes in lipid metabolism is true?
What is the significance of ketones produced by hepatocytes?
What is the significance of ketones produced by hepatocytes?
Which function is NOT performed by hepatocytes?
Which function is NOT performed by hepatocytes?
During periods of low nutrient availability, hepatocytes primarily utilize which source to produce glucose?
During periods of low nutrient availability, hepatocytes primarily utilize which source to produce glucose?
What is a primary function of high density lipoproteins (HDLs) synthesized by hepatocytes?
What is a primary function of high density lipoproteins (HDLs) synthesized by hepatocytes?
What type of amino acids are primarily synthesized by hepatocytes?
What type of amino acids are primarily synthesized by hepatocytes?
Which statement accurately describes the storage of glycogen?
Which statement accurately describes the storage of glycogen?
What essential role do VLDLs play in lipid metabolism?
What essential role do VLDLs play in lipid metabolism?
What components do bile salts contain that contribute to their dual function?
What components do bile salts contain that contribute to their dual function?
Which process is involved in the conversion of heme to bilirubin?
Which process is involved in the conversion of heme to bilirubin?
What is the primary function of Phase I reactions in drug metabolism?
What is the primary function of Phase I reactions in drug metabolism?
What role does bile play in the digestion of dietary fats?
What role does bile play in the digestion of dietary fats?
Which of the following best describes the outcome of drug metabolism?
Which of the following best describes the outcome of drug metabolism?
In which cellular structure do Phase I reactions predominantly occur?
In which cellular structure do Phase I reactions predominantly occur?
What compounds can be involved in Phase II reactions for drug metabolism?
What compounds can be involved in Phase II reactions for drug metabolism?
How does bilirubin travel to the liver after its formation?
How does bilirubin travel to the liver after its formation?
What is the primary function of the liver in maintaining nutrient homeostasis during periods of fasting?
What is the primary function of the liver in maintaining nutrient homeostasis during periods of fasting?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the role of glucokinase in the liver?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the role of glucokinase in the liver?
What is the primary role of albumin in the body?
What is the primary role of albumin in the body?
Which of the following conditions could potentially lead to prolonged bleeding?
Which of the following conditions could potentially lead to prolonged bleeding?
What is the primary reason that the liver is the main organ responsible for urea production?
What is the primary reason that the liver is the main organ responsible for urea production?
Which of the following plasma proteins are NOT synthesized by hepatocytes?
Which of the following plasma proteins are NOT synthesized by hepatocytes?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of the liver in the synthesis and storage of lipids?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of the liver in the synthesis and storage of lipids?
How can liver dysfunction lead to edema formation throughout the body?
How can liver dysfunction lead to edema formation throughout the body?
What is the primary effect of frequent or regular drug administration on cytochrome P-450 activity?
What is the primary effect of frequent or regular drug administration on cytochrome P-450 activity?
What is the primary reason why many drugs undergo "first-pass metabolism"?
What is the primary reason why many drugs undergo "first-pass metabolism"?
Which of the following vitamins can be stored by the liver for the longest duration?
Which of the following vitamins can be stored by the liver for the longest duration?
What is the role of apoferritin in iron storage within the liver?
What is the role of apoferritin in iron storage within the liver?
What is the relationship between somatomedins and Human Growth Hormone (HGH)?
What is the relationship between somatomedins and Human Growth Hormone (HGH)?
What is the primary function of Kupffer cells in the liver?
What is the primary function of Kupffer cells in the liver?
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the relationship between drug administration and cytochrome P-450?
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the relationship between drug administration and cytochrome P-450?
How does the liver contribute to the regulation of iron levels in the body?
How does the liver contribute to the regulation of iron levels in the body?
Flashcards
Glycogen in Hepatocytes
Glycogen in Hepatocytes
Hepatocytes contain the highest glycogen concentrations in the body.
VLDL (Very Low Density Lipoproteins)
VLDL (Very Low Density Lipoproteins)
Lipoproteins made by hepatocytes to distribute triglycerides in the blood.
HDL (High Density Lipoproteins)
HDL (High Density Lipoproteins)
Lipoproteins that scavenge cholesterol and provide apoproteins for VLDLs.
Ketones
Ketones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-essential Amino Acids
Non-essential Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fatty Acid Metabolism
Fatty Acid Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal Muscle Proteolysis
Skeletal Muscle Proteolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Functions
Liver Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
VLDL
VLDL
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Synthesis
Bile Synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Detoxification
Detoxification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Storage
Vitamin Storage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bilirubin Excretion
Bilirubin Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urea
Urea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycogen
Glycogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucokinase
Glucokinase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clotting Factors
Clotting Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Albumin
Albumin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Dysfunction
Liver Dysfunction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triglycerides
Triglycerides
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Salts
Bile Salts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micelles
Micelles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bilirubin
Bilirubin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phase I Reactions
Phase I Reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytochrome P-450
Cytochrome P-450
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phase II Reactions
Phase II Reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucuronate Conjugation
Glucuronate Conjugation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Drug Metabolism
Drug Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
First-pass metabolism
First-pass metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ferritin
Ferritin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatomedins (IGFs)
Somatomedins (IGFs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kupffer Cells
Kupffer Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iron Storage
Iron Storage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
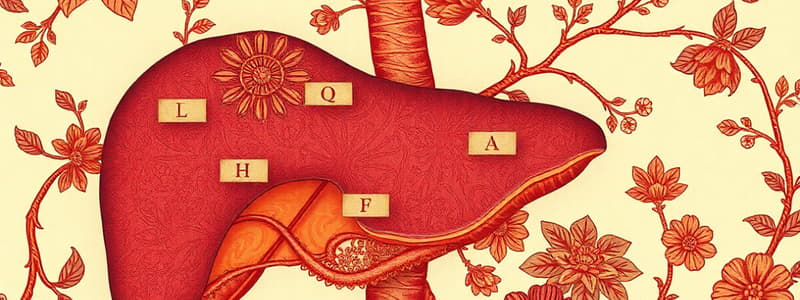
Liver Functions
- The liver plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and life by performing a broad range of functions.
- Maintaining nutrient homeostasis: The liver regulates blood nutrient levels. This includes glucose supply for neurons, and distributing fatty acids as ketones or triglycerides (VLDLs).
- Storing nutrients: Glycogen is stored in the liver to release glucose during times of need, and the liver stores lipids as well.
- Synthesizing and releasing plasma proteins: The liver creates many plasma proteins, including clotting factors and albumin.
- Synthesizing and releasing bile: Bile, containing bile salts and other components, helps digest fats.
- Processing and excreting bilirubin: The liver processes and eliminates bilirubin, a waste product.
- Detoxification and excretion: The liver removes toxins, drugs, and hormones, and prepares them for excretion.
- Storing vitamins: The liver stores vitamins A, D, and B12 for a period of time, preventing deficiencies.
- Iron storage: The liver stores iron in the form of ferritin, ensuring its availability for red blood cell production.
- Synthesizing somatomedins: The liver plays a crucial role in producing hormones related to growth.
- Blood cleansing: The liver filters blood, removing bacteria and other potential threats.
Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrate storage: The liver stores glucose as glycogen.
- Glycogenolysis: This is the breakdown of glycogen to release glucose when needed.
- Gluconeogenesis: The liver creates glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
- Dietary sugar processing: The liver processes galactose and fructose from the diet.
Lipids
- Lipid synthesis and release: The liver synthesizes and releases VLDLs (very-low-density lipoproteins), and HDLs (high-density lipoproteins).
- Ketone production: The liver creates ketones from fatty acids.
- Lipid Storage: The liver stores lipids as triglycerides but this is more prevalent in disease conditions.
Amino Acids
- Amino acid handling and glucose production: The liver processes amino acids from skeletal muscle protein breakdown, primarily creating glucose via gluconeogenesis.
- Non-essential amino acid synthesis: The liver plays a pivotal role in synthesizing many non-essential amino acids, rather than consuming them externally.
- Urea production: The liver plays a crucial role in removing nitrogenous groups from amino acids, producing urea (a major waste product).
Nutrient Storage
- Glycogen storage: The liver efficiently stores glycogen, ready for release during low glucose periods.
- Lipid storage: While not a primary function, the liver can store lipids, particularly triglycerides. This storage is more common in disease states.
Plasma protein synthesis
- Clotting factors: The liver produces several essential clotting factors, needing vitamin K for some.
- Albumin: Albumin, is the most abundant plasma protein, maintaining osmotic balance and binding various substances.
Bile synthesis and function
- Bile Composition: Bile contains bile salts, which emulsify fats, and components like cholesterol and bilirubin.
- Fat Emulsification: Bile salts break down large fat globules into smaller ones, aiding in digestion and absorption.
Detoxification
- Drug and hormone metabolism: The liver processes drugs and hormones, making them more excretable, or changing their activity.
- Phase I and II reactions: The liver uses biotransformations to make drugs and hormones more water-soluble for excretion.
Other Functions
- Vitamin storage: The liver significantly stores vitamins A, D, and B12.
- Iron storage: The liver stores iron as ferritin, making it available for red blood cell production.
- Somatomedin synthesis: The liver produces hormones that stimulate growth.
- Blood purification: The Kupffer cells within the liver remove bacteria and other foreign material from the bloodstream.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.