Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary focus of the learning outcomes regarding the liver and biliary system?
What is the primary focus of the learning outcomes regarding the liver and biliary system?
- Discuss the pharmacology of liver medications
- Describe the anatomy and clinical relevance of the liver and biliary system (correct)
- Conduct liver function tests
- Identify the liver on histological slides
Which of the following structures is NOT specifically mentioned as part of the biliary system anatomy?
Which of the following structures is NOT specifically mentioned as part of the biliary system anatomy?
- Hepatic artery (correct)
- Common bile duct
- Gallbladder
- Major duodenal papilla
What is a porto-systemic anastomosis primarily described as?
What is a porto-systemic anastomosis primarily described as?
- An obstruction in the bile duct leading to gallbladder disease
- A connection between the portal venous system and systemic veins (correct)
- The catheterization of the hepatic artery
- An increased pressure in the hepatic artery
What structures join to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Vater)?
What structures join to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Vater)?
Which book is recommended for anatomical reference regarding the liver?
Which book is recommended for anatomical reference regarding the liver?
What does the learning outcomes suggest is necessary to describe regarding the major duodenal papilla?
What does the learning outcomes suggest is necessary to describe regarding the major duodenal papilla?
Where does the common bile duct open into the duodenum?
Where does the common bile duct open into the duodenum?
In relation to the hepatic artery and portal vein, where does the common bile duct course?
In relation to the hepatic artery and portal vein, where does the common bile duct course?
What surrounds the major duodenal papilla where the common bile duct opens?
What surrounds the major duodenal papilla where the common bile duct opens?
Which duct is described as anterior to the hepatic portal vein?
Which duct is described as anterior to the hepatic portal vein?
Which veins are responsible for draining the neck of the gallbladder directly into the portal vein?
Which veins are responsible for draining the neck of the gallbladder directly into the portal vein?
What anatomical structure forms the hepatic portal vein?
What anatomical structure forms the hepatic portal vein?
What is the consequence of increased portal pressure?
What is the consequence of increased portal pressure?
What does the blood from the portal vein do after passing through the liver?
What does the blood from the portal vein do after passing through the liver?
Which veins play a role in porto-caval anastomosis?
Which veins play a role in porto-caval anastomosis?
Which of the following statements about the hepatic portal vein is true?
Which of the following statements about the hepatic portal vein is true?
What vein drains the gallbladder's fundus and body directly into the liver?
What vein drains the gallbladder's fundus and body directly into the liver?
Which veins are involved in the anastomosis that can result in caput medusae?
Which veins are involved in the anastomosis that can result in caput medusae?
Which nerves provide parasympathetic innervation to the gallbladder?
Which nerves provide parasympathetic innervation to the gallbladder?
What is a common symptom associated with cholecystitis?
What is a common symptom associated with cholecystitis?
Which of the following conditions is associated with portal hypertension?
Which of the following conditions is associated with portal hypertension?
What hormone stimulates the contraction of the gallbladder?
What hormone stimulates the contraction of the gallbladder?
Which imaging technique is used for assessing the biliary and pancreatic ducts?
Which imaging technique is used for assessing the biliary and pancreatic ducts?
Which nerve plexus is the source of sympathetic innervation to the hepatic area?
Which nerve plexus is the source of sympathetic innervation to the hepatic area?
Which clinical condition is characterized by abnormal dilation of blood vessels in the esophagus?
Which clinical condition is characterized by abnormal dilation of blood vessels in the esophagus?
What major structure does the cystic duct connect with the common bile duct?
What major structure does the cystic duct connect with the common bile duct?
What does the quadrate lobe lie between according to its anatomical position?
What does the quadrate lobe lie between according to its anatomical position?
Which lobes of the liver are categorized as functional lobes?
Which lobes of the liver are categorized as functional lobes?
Which structure is part of the portal triad entering the liver at the porta hepatis?
Which structure is part of the portal triad entering the liver at the porta hepatis?
Where does the fundus of the gallbladder project anatomically?
Where does the fundus of the gallbladder project anatomically?
What is the typical capacity of the gallbladder?
What is the typical capacity of the gallbladder?
What anatomical landmark is used to determine Murphy’s point?
What anatomical landmark is used to determine Murphy’s point?
What are the hepatic segments based on?
What are the hepatic segments based on?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the gallbladder's anatomy?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the gallbladder's anatomy?
Where does the gallbladder lie in relation to the quadrate lobe?
Where does the gallbladder lie in relation to the quadrate lobe?
What is Pringle’s Manoeuvre associated with?
What is Pringle’s Manoeuvre associated with?
Which structure is primarily responsible for draining blood into the liver from the digestive tract?
Which structure is primarily responsible for draining blood into the liver from the digestive tract?
What anatomical feature is commonly referred to as Hartman's pouch?
What anatomical feature is commonly referred to as Hartman's pouch?
Where does the common bile duct typically open into the duodenum?
Where does the common bile duct typically open into the duodenum?
Which artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver?
Which artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver?
What is the main substance drained by the hepatic portal vein?
What is the main substance drained by the hepatic portal vein?
What leads to the development of alternative blood pathways in liver cirrhosis?
What leads to the development of alternative blood pathways in liver cirrhosis?
Which anatomical site is NOT associated with venous enlargement in the context of liver cirrhosis?
Which anatomical site is NOT associated with venous enlargement in the context of liver cirrhosis?
Which pathway is a portal system related to the development of varices in liver cirrhosis?
Which pathway is a portal system related to the development of varices in liver cirrhosis?
Which condition is likely to cause anastomosis between systemic and portal veins?
Which condition is likely to cause anastomosis between systemic and portal veins?
What is the consequence of venous enlargement at the gastroesophageal junction?
What is the consequence of venous enlargement at the gastroesophageal junction?
What is the main pathway for drainage of lymph from the gallbladder?
What is the main pathway for drainage of lymph from the gallbladder?
Which lymph nodes do the superficial lymphatics from the posterior diaphragmatic surfaces ultimately drain into?
Which lymph nodes do the superficial lymphatics from the posterior diaphragmatic surfaces ultimately drain into?
Which structure accompanies the hepatic artery and portal vein within the hepatic nerve plexus?
Which structure accompanies the hepatic artery and portal vein within the hepatic nerve plexus?
Which statement accurately describes the innervation of the gallbladder?
Which statement accurately describes the innervation of the gallbladder?
What is the fate of lymph drained from hepatic lymph nodes?
What is the fate of lymph drained from hepatic lymph nodes?
From where do the superficial lymphatics of the anterior diaphragmatic surfaces primarily drain?
From where do the superficial lymphatics of the anterior diaphragmatic surfaces primarily drain?
Which nodes act as an intermediary between gallbladder lymphatics and the thoracic duct?
Which nodes act as an intermediary between gallbladder lymphatics and the thoracic duct?
What is a key characteristic of parasympathetic fibers to the gallbladder?
What is a key characteristic of parasympathetic fibers to the gallbladder?
What divides the functional lobes of the liver into eight segments?
What divides the functional lobes of the liver into eight segments?
Which anatomical feature is used to locate the fundus of the gallbladder?
Which anatomical feature is used to locate the fundus of the gallbladder?
Which duct connects the gallbladder with the common hepatic duct?
Which duct connects the gallbladder with the common hepatic duct?
What is the anatomical location of the quadrate lobe relative to the liver?
What is the anatomical location of the quadrate lobe relative to the liver?
What is the role of Pringle’s Manoeuvre during surgery?
What is the role of Pringle’s Manoeuvre during surgery?
Which lobe of the liver is categorized as an independent functional unit based on bile drainage?
Which lobe of the liver is categorized as an independent functional unit based on bile drainage?
How much bile can the gallbladder typically store?
How much bile can the gallbladder typically store?
Where is Murphy’s point located in relation to the ribcage?
Where is Murphy’s point located in relation to the ribcage?
What anatomical location does the gallbladder occupy?
What anatomical location does the gallbladder occupy?
Which ligament connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
Which ligament connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall?
What is the primary feature that divides the liver into right and left lobes?
What is the primary feature that divides the liver into right and left lobes?
Which ligament is located at the free margin of the liver?
Which ligament is located at the free margin of the liver?
Which structure forms the barrier between the caudate lobe and the fossa for the inferior vena cava (IVC)?
Which structure forms the barrier between the caudate lobe and the fossa for the inferior vena cava (IVC)?
Which of the following ligaments is associated with the diaphragm?
Which of the following ligaments is associated with the diaphragm?
What anatomical feature creates the right sagittal fissure on the liver's visceral surface?
What anatomical feature creates the right sagittal fissure on the liver's visceral surface?
Which ligament forms the left sagittal fissure on the liver?
Which ligament forms the left sagittal fissure on the liver?
Which two ligaments provide attachment of the liver to the superior diaphragm?
Which two ligaments provide attachment of the liver to the superior diaphragm?
What forms the caudate lobe of the liver?
What forms the caudate lobe of the liver?
Which ligament is specifically mentioned as connecting the liver to the duodenum?
Which ligament is specifically mentioned as connecting the liver to the duodenum?
Flashcards
Falciform Ligament
Falciform Ligament
Divides the liver into left and right lobes.
Porta Hepatis
Porta Hepatis
Entrance to the liver; where the portal triad, lymphatics, and nerves enter.
Portal Triad
Portal Triad
Hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, and common bile duct.
Gallbladder Function
Gallbladder Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pringle’s Manoeuvre
Pringle’s Manoeuvre
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cystic Duct
Cystic Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphincter of Oddi
Sphincter of Oddi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hepatic Veins
Hepatic Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Porto-Systemic Anastomoses
Porto-Systemic Anastomoses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
ERCP
ERCP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
anterior diaphragmatic lymphatics
anterior diaphragmatic lymphatics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Round Ligament of the Liver
Round Ligament of the Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Sagittal Fissure
Right Sagittal Fissure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fundus of the Gallbladder
Fundus of the Gallbladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surface landmark of Gallbladder
Surface landmark of Gallbladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Blood Supply
Liver Blood Supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
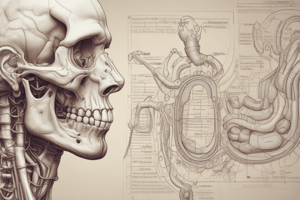
Liver Anatomy
- The liver is divided into anatomical lobes (left, right, caudate and quadrate) and functional lobes (left and right halves).
- Functional halves are further divided into 8 segments, each with its own biliary drainage and blood supply.
- The portal triad consists of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, and common bile duct.
- The porta hepatis is the entrance to the liver, where the portal triad, lymphatics, and nerves enter.
- Pringle’s Manoeuvre is a surgical technique that involves clamping the hepatoduodenal ligament to control blood flow to the liver.
Gallbladder
- The gallbladder is a pear-shaped structure with a fundus, body, and neck.
- It lies in the gallbladder fossa on the visceral surface of the right lobe of the liver.
- The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile secreted by the liver.
- The cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct.
- The common bile duct joins the main pancreatic duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Vater), which opens into the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla.
- The sphincter of the ampulla (of Oddi) controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Venous Drainage
- Blood from the hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery passes through the liver.
- Hepatic veins return blood to the inferior vena cava (IVC).
- The cystic veins drain the neck of the gallbladder directly into the portal vein, while the fundus and body drain directly to the liver (into the hepatic sinusoids).
Porto-Systemic Anastomoses
- These connections allow blood to bypass the liver when portal pressure is increased.
- The para-umbilical veins anastomose with the small epigastric veins, which can result in caput medusae.
- The oesophageal veins (draining into the azygos vein) anastomose with the left gastric vein, which can lead to oesophageal varices.
Nerves
- The hepatic nerve plexus is derived from the coeliac plexus and accompanies the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein.
- Nerves to the gallbladder pass along the cystic artery from the celiac nerve plexus.
- Cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulates contraction of the gallbladder and bile release.
Clinical Conditions
- Portal hypertension can lead to oesophageal varices and caput medusae.
- Hepatomegaly is an enlarged liver.
- Liver infections, such as abscesses, can be caused by various organisms.
- Liver cancer can be primary or metastatic.
- Trauma to the liver can be managed using Pringle’s Manoeuvre.
- Storage disorders and enzyme deficiencies can affect liver function.
- Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease with irreversible scarring.
Imaging
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatogram (ERCP) is an imaging technique used to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatogram (MRCP) is an imaging technique used to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts without using contrast fluid.
Case Study
- A 48-year-old female presents with abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice.
- Imaging reveals signs consistent with cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and cholelithiasis (gallstones).
- Gallstones can obstruct the biliary duct system, leading to complications like cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
Lymphatics
- Superficial lymphatics from anterior diaphragmatic and visceral surfaces drain into 3-4 nodes at the porta hepatis (hepatic lymph nodes).
- Hepatic lymph nodes drain into celiac lymph nodes.
- Coeliac lymph nodes drain into cisterna chyli, then to the thoracic duct.
- Superficial lymphatics from the posterior diaphragmatic and visceral surfaces drain to phrenic lymph nodes.
- Phrenic lymph nodes drain to posterior mediastinal lymph nodes, then to the right thoracic duct.
- Gallbladder lymphatics drain to hepatic nodes through a cystic node located at the neck of the gallbladder, finally reaching the coeliac nodes.
Nerves
- Hepatic nerve plexus originates from the coeliac plexus and accompanies the hepatic artery and portal vein.
- Parasympathetic innervation of the hepatic nerve plexus comes from the vagus nerve.
- Nerves to the gallbladder travel alongside the cystic artery from the coeliac nerve plexus.
- Parasympathetic innervation of the gallbladder is from the vagus nerve.
Associated Ligaments
- The liver is attached to the anterior abdominal wall by the falciform ligament.
- The round ligament of the liver (ligamentum teres), located at the free margin of the falciform ligament, is a remnant of the fetal umbilical vein.
- The liver is connected to the stomach by the hepatogastric ligament.
- The liver is attached to the duodenum via the hepatoduodenal ligament.
- The liver is connected to the diaphragm by the right and left triangular ligaments, as well as the anterior and posterior coronary ligaments.
Anatomical Lobes
- The liver is divided into right and left lobes by the falciform ligament.
- The visceral surface of the liver has an H-pattern.
- The right sagittal fissure is formed by the fossa for the gallbladder and the inferior vena cava (IVC).
- The left sagittal fissure is created by the fissure for the ligamentum venosum and the fissure for the round ligament (ligamentum teres).
- The caudate lobe is located between the fissure for the ligamentum venosum and the fossa for the IVC.
- The quadrate lobe is situated between the fissure for the ligamentum teres and the fossa for the gallbladder.
Functional Lobes
- The functional lobes divide the liver into left and right halves, further subdivided into eight segments each.
- The eight hepatic (or surgical) segments form independent functional units based on biliary drainage and blood supply.
Porta Hepatis
- The porta hepatis is the main entrance point to the liver and is where the portal triad enters.
- The portal triad consists of:
- Hepatic artery: Carries oxygenated blood from the systemic circulation.
- Hepatic portal vein: Carries deoxygenated blood rich in nutrients from the small intestine.
- Common bile duct: Transports bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum.
Gallbladder
- The fundus of the gallbladder projects onto the lower border of the liver and touches the parietal peritoneum of the anterior abdominal wall at the tip of the ninth costal cartilage.
- Surface landmark of the gallbladder coincides with the intersection of the lateral border of the right rectus abdominis and the costal margin.
- Murphy's point is located at the level of the transpyloric plane and the right ribcage.
- The gallbladder lies in the gallbladder fossa on the visceral surface of the right lobe of the liver, adjacent to the quadrate lobe.
- It functions in the storage and concentration of bile secreted by the liver, with a capacity of approximately 50mL.
Common Bile Duct
- The common bile duct is formed by the union of the cystic duct from the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct from the liver.
- The common bile duct connects the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum, where it merges with the main pancreatic duct, forming the hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Oddi).
- The hepatopancreatic ampulla is surrounded by the sphincter of Oddi (also called Glisson's sphincter) which controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
Liver Blood Supply
- The liver receives blood from two primary sources:
- Hepatic artery: Provides oxygenated blood from the systemic circulation.
- Hepatic portal vein: Delivers deoxygenated blood rich in nutrients from the digestive tract, specifically the small intestine, spleen, and pancreas.
- The hepatic artery branches into the right and left hepatic arteries, each supplying a corresponding hepatic lobe.
- The hepatic portal vein is formed by the union of the splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein, and inferior mesenteric vein.
- Portal hypertension, caused by liver cirrhosis or other conditions that obstruct blood flow to the liver, leads to:
- Increased pressure in the portal venous system
- Blood-taking alternative pathways, like the gastroesophageal junction, anus, and anterior abdominal wall to relieve the pressure.
- Venous enlargement in these areas (varices).
Pringle's Manoeuvre
- Pringle's Manoeuvre involves clamping the hepatoduodenal ligament to temporarily stop blood flow to the liver. This technique is used during surgery to control bleeding and allows for a bloodless field.
- The hepatoduodenal ligament is the free margin of the lesser omentum, which contains the portal triad (hepatic artery, portal vein, and common bile duct).
- The manoeuvre involves clamping the ligament at the epiploic foramen (of Winslow), the entrance to the omental bursa.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.