Podcast
Questions and Answers
What distinguishes a motif from a theme?
What distinguishes a motif from a theme?
- A motif is always a negative element in a story.
- A motif can be expressed as a complete sentence.
- A motif primarily relates to character development.
- A motif can be expressed as a single word or fragmentary phrase. (correct)
The protagonist of a story is always a morally good character.
The protagonist of a story is always a morally good character.
False (B)
Define the term 'point-of-view' in narrative structure.
Define the term 'point-of-view' in narrative structure.
Point-of-view is the identity of the narrative voice through which the reader experiences the story.
The ________ refers to the time and place in which a story takes place.
The ________ refers to the time and place in which a story takes place.
Match the following literary techniques with their definitions:
Match the following literary techniques with their definitions:
Which of the following best describes tone in a narrative?
Which of the following best describes tone in a narrative?
Literary techniques are present in every text.
Literary techniques are present in every text.
What is the primary purpose of a theme in a literary work?
What is the primary purpose of a theme in a literary work?
What is the term used for the character that opposes the protagonist?
What is the term used for the character that opposes the protagonist?
The climax of a story is typically where everything goes wrong and the outcome becomes inevitable.
The climax of a story is typically where everything goes wrong and the outcome becomes inevitable.
Define 'characterization'.
Define 'characterization'.
A recurring important idea or image in a literary work is known as a ______.
A recurring important idea or image in a literary work is known as a ______.
Match the literary element with its correct definition:
Match the literary element with its correct definition:
Which of the following is a component of narrative structure?
Which of the following is a component of narrative structure?
Context refers to the main characters and events in a story.
Context refers to the main characters and events in a story.
What is an example of literary conflict?
What is an example of literary conflict?
What literary device is used in Neil Armstrong’s statement when he says, 'That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind'?
What literary device is used in Neil Armstrong’s statement when he says, 'That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind'?
Repetition is always considered redundant in writing.
Repetition is always considered redundant in writing.
What is the primary purpose of using symbolism in literature?
What is the primary purpose of using symbolism in literature?
The phrase 'My love is like a red, red rose' exemplifies a __________.
The phrase 'My love is like a red, red rose' exemplifies a __________.
Match the literary technique to its definition:
Match the literary technique to its definition:
Which of the following phrases is a demonstration of personification?
Which of the following phrases is a demonstration of personification?
A symbol must be an abstract idea to be effective in literature.
A symbol must be an abstract idea to be effective in literature.
Identify the literary technique used in: 'Where there is smoke, there is fire.'
Identify the literary technique used in: 'Where there is smoke, there is fire.'
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
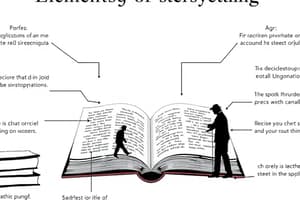
Literary Elements
- Antagonist: The character who opposes the protagonist in a significant way.
- Characterization: How an author reveals a character's personality, life, history, values, and physical attributes.
- Climax: The turning point in a story where the end results become inevitable, the dramatic high point where something goes wrong.
- Conflict: The problem or issue in a narrative that drives the storyline.
- Context: The surrounding information influencing a story, plot, character, author, or time period.
- Dialogue: The words spoken by characters within a narrative, used to communicate ideas and actions.
- Mood: The overarching atmosphere or emotional condition created by a narrative.
- Motif: A recurring important idea or image throughout a work.
- Narrator: The person or entity telling the story.
- Point of View: The perspective from which the story is told, indicating how the reader experiences the events.
- Plot: The logical sequence of events that unfold within a story.
- Protagonist: The main character of a story, often the one the reader identifies with.
- Setting: The time and place where a story takes place.
- Structure: The way the elements of a story are arranged.
- Theme: The central idea or message conveyed by a story, typically expressed as a complete sentence.
- Tone: The narrator's apparent emotional state conveyed through their language.
Literary Techniques
- Allegory: Abstract ideas given physical form through characters, actions, or events.
- Parallelism: Repetition of similar grammatical structures to emphasize a contrast.
- Personification (1): Attributing human-like awareness to inanimate objects or abstract ideas.
- Repetition: Deliberate use of words, phrases, or structures to emphasize an idea.
- Simile: Direct comparison between unlike things using "like" or "as."
- Symbolism/Symbol: Using specific objects or images to represent abstract ideas.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.