Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the basic unit of structure and function in living things?
What is the basic unit of structure and function in living things?
- Organ systems
- Cells (correct)
- Organs
- Tissues
Which type of tissue is responsible for protecting, absorbing, and excreting materials?
Which type of tissue is responsible for protecting, absorbing, and excreting materials?
- Nervous
- Muscle
- Connective
- Epithelial (correct)
What is the function of connective tissue?
What is the function of connective tissue?
- To bind epithelial to other structures (correct)
- To cause voluntary movements
- To excrete materials
- To transmit nerve impulses
Which tissue receives and transmits nerve impulses?
Which tissue receives and transmits nerve impulses?
What is the term for maintaining a stable internal environment in the body?
What is the term for maintaining a stable internal environment in the body?
Which system guards against infection and injury?
Which system guards against infection and injury?
Which system helps protect the body from disease?
Which system helps protect the body from disease?
What is the role of the respiratory system?
What is the role of the respiratory system?
What is the main function of the digestive system?
What is the main function of the digestive system?
Which system eliminates waste products from the body?
Which system eliminates waste products from the body?
Which system controls growth, development, and metabolism?
Which system controls growth, development, and metabolism?
What process involves a response that opposes the original stimulus?
What process involves a response that opposes the original stimulus?
What is the function of the respiratory system?
What is the function of the respiratory system?
What is the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration called?
What is the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration called?
What is the function of gills in aquatic animals?
What is the function of gills in aquatic animals?
What is the name of the openings on the body surface of some terrestrial animals that lead to tracheal tubes?
What is the name of the openings on the body surface of some terrestrial animals that lead to tracheal tubes?
What structures are the location of gas exchange in mammalian lungs?
What structures are the location of gas exchange in mammalian lungs?
What is the primary function of the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of the circulatory system?
What type of circulatory system has blood coming in direct contact with body tissues?
What type of circulatory system has blood coming in direct contact with body tissues?
Where does blood circulate in a closed circulatory system?
Where does blood circulate in a closed circulatory system?
What is the function of the atrium?
What is the function of the atrium?
What type of loop circulation do vertebrates with gills commonly have?
What type of loop circulation do vertebrates with gills commonly have?
What vessels carry blood away from the heart?
What vessels carry blood away from the heart?
What is transported by red blood cells?
What is transported by red blood cells?
What is the function of valves in veins?
What is the function of valves in veins?
Flashcards
Cells
Cells
Basic unit of structure and function in living things. In multi-cellular organisms individual cells are specialized towards a particular function
Tissues
Tissues
A group of cells that perform a single function.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Protect, absorb, and excrete materials. (Ex: skin, digestive tract)
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organs
Organs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organ System
Organ System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homeostasis
Homeostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feedback inhibition/negative feedback
Feedback inhibition/negative feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory system
Respiratory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion
Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gills
Gills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Birds
Birds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulatory system
Circulatory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart
Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open Circulatory System
Open Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed Circulatory System
Closed Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single loop circulatory system
Single loop circulatory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atrium
Atrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricle
Ventricle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double loop circulatory system
Double loop circulatory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Levels of Organization in the Body
- Cells act as the fundamental units of structure and function in living organisms
- In multicellular organisms, cells specialize to perform specific functions
- Tissues are groups of cells performing a unified function
- Epithelial tissue protects, absorbs, and excretes materials
- Connective tissue binds epithelial tissue to other structures and transports substances
- Nervous tissue is responsible for receiving and transmitting nerve impulses
- Muscle tissue enables both voluntary and involuntary movements
- Organs are composed of different tissues working together for a specific function
- Organ systems include groups of organs that work closely together
- Organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis
Homeostasis
- Homeostasis involves organisms maintaining constant internal conditions despite external environmental changes
- Feedback inhibition/negative feedback occurs when a stimulus triggers a response that counteracts the initial stimulus
- Activation of sweating is a response to rising body temperature
- Shivering is a response to a drop in body temperature
The Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is responsible for facilitating gas exchange
- Cellular respiration needs oxygen and produces carbon dioxide
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + H2O + energy (ATP) is the equation for cellular respiration
- Respiratory structures facilitate gas movement through passive diffusion
- Diffusion refers to the movement of substances from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
- Thinner membranes and larger surface areas increase permeability and speed up diffusion
- Respiratory surfaces provide a large surface area, a moist environment, a selectively permeable membrane, and maintained concentration differences of O2 and CO2 to promote diffusion
Respiratory Systems in Different Animals
- Aquatic animals like small invertebrates have thin-walled bodies with wet outer surfaces and rely on diffusion
- Larger, more active aquatic animals pump water over gills
- Gills consist of feathery structures that provide a large surface area of thin, selectively permeable membrane, enhancing gas exchange in water
- Land animals maintain moist respiratory membranes
- Multiple systems interact to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide back and forth across different surfaces
- Respiration can occur across the skin in moist environments
- Some invertebrates have a mantle cavity: a moist tissue-lined cavity with blood vessels for gas exchange
- Book lungs are parallel layers of thin tissues containing blood vessels
- Tracheal tubes allow air to enter and exit through spiracles
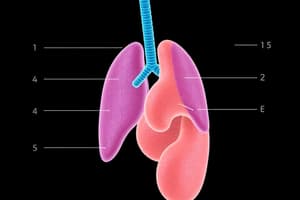
Lungs
- Lungs facilitate the exchange of O2 and CO2 between blood and air
- Oxygen-rich air is inhaled through the trachea
- Oxygen diffuses into the blood through lung capillaries
- Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillaries into the lungs
- Carbon dioxide and oxygen-poor air is exhaled
- The surface area of lungs increases from amphibians to reptiles to mammals
- Amphibians have simple sacs with ridges
- Reptiles have chambers that increase the surface area
- Mammals have extensively branched lungs that end in alveoli (bubble-like structures)
- Alveoli are surrounded by capillaries, where blood picks up O2, leading to the release of CO2 through diffusion
- Birds lungs allow air to flow mostly in one direction
- Birds air flow ensures no oxygen-poor air is trapped in the system
- Gas exchange surfaces are continuously exposed to fresh air, powering the flight muscles
The Circulatory System
- The circulatory system transports energy and nutrients that have been broken down from food
- The circulatory system transports oxygen inhaled from the lungs to other tissues
- It also carries carbon dioxide and waste materials away from tissues
- Blood serves as the medium for transporting materials throughout the body
- The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood
- There are two types of circulatory systems: open and closed
Circulatory Systems: Open vs Closed
- Open circulatory systems have hearts that pump blood through vessels emptying into sinuses, or spongy cavities
- Blood in open circulatory systems makes direct contact with body tissues within the sinuses
- Blood collects in another set of sinuses, eventually returning to the heart
- Arthropods and most mollusks have open circulatory systems
- Closed circulatory systems circulate blood within vessels throughout the body
- A heart pumps blood through vessels
- Oxygen and nutrients reach body tissues by diffusing across the thin capillary walls
- Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels
- Blood is contained within blood vessels, circulation is more efficient
- Annelids and all vertebrates have closed circulatory systems
Circulation Loops
- Single loop circulatory systems pushes blood around the body in only one direction
- Oxgen rich blood is red
- Oxygen poor blood is blue
- Vertebrates that use gills for respiration are found to have a single loop circulatory system
- The atrium is the chamber which receives blood from the body
- The ventricle is the chamber that pumps blood out of the heart
- Double loop circulatory systems involves blood moving through the heart twice separate
- Vertebrates that use lungs for respiration are found to have a double loop circulatory system
Chambered Hearts
- Terrestrial vertebrates evolved increasing capillary networks that became larger
- Using a single pump to force blood through a larger body is incresingly inefficient
- Amphibian hearts have two atria and one ventricle
- Amphibians right atria receive oxygen poor blood from the body
- The single ventricle distributes oxygen-poor blood to the lungs and oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body
- The left atria receives oxygen rich blood from the lungs
- Reptilian hearts also contain two atria, and one ventricle
- Reptiles have a partial partition in the single ventricle making the circulation of oxygen rich and poor blood more efficient
Mammalian Hearts
- Mammalian hearts are two separate pumps existing next to each other
- The two pumps are separated by partitions which stop or restrict passage of blood between the atria and ventricles
- Pulmonary circulation carries blood between the heart and lungs
- Systemic circulation carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body
Arteries, Capillaries, and Veins
- Arteries are large vessels that carry blood from the heart to the tissues of the body
- Except for the pulmonary artery, all other arteries carry oxygen-rich blood
- Thick, elastic walls help withstand powerful pressure produced from heart contractions
- Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels, which allow O2 to diffuse from the blood into the tissues, and CO2 to move from the tissue into the blood
- Veins return the blood from the body to the heart
- Valves ensure blood flows in one direction
Blood Functions
- Respiratory gas exchange between O2 and CO2
- Transports nutrients obtained from the digestive system
- Blood transports hormones and signals linking to the endocrine system
- Transports waste through the body
- Fights infections through the immune system
- Regulates body temperature
- Clots wounds and minimizes loses of vital fluid
- Human bodies contain 4 - 6 liters of blood, and 55% is plasma
- Red blood cells/erythrocytes transport oxygen and are produced by bone marrow
- Platelets and plasma proteins will cause blood to clot and seal wounds
Clots
- Thrombus - A blood clot that forms within the blood vessels and causes limitations on blood movement
- With thrombosis, tissue looses oxygen and dies
- Heart attack - a blockage of blood on the heart muscle
- Atherosclerosis - Built-up of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels
- Arteriosclerosis causes narrow blood vessels, or plaque
- Aneurysm - A bulge in the wall of the blood vessels, caused from high blood pressure
- Hypertensions cause the aneurysm to burst/rupture and lead to internal bleeding, and death.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.