Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following scenarios accurately describes a Fee Simple Defeasible estate?
Which of the following scenarios accurately describes a Fee Simple Defeasible estate?
- An individual owns a property as long as they maintain a specific profession, with the title reverting to the previous owner if they cease that profession. (correct)
- An individual is granted land for the duration of their lifetime.
- An individual is granted the right to use a property for a definite period, after which ownership transfers to another party.
- An individual owns a property with no restrictions and can transfer it to heirs without any conditions.
In a Conditional Ownership With Reverter Clause, legal action is required to revert the title back to the seller if a condition is broken.
In a Conditional Ownership With Reverter Clause, legal action is required to revert the title back to the seller if a condition is broken.
False (B)
Explain the key distinction between a 'Conventional' Life Estate and a 'Pur Autre Vie' Life Estate.
Explain the key distinction between a 'Conventional' Life Estate and a 'Pur Autre Vie' Life Estate.
A Conventional life estate is dependent on the life of the person receiving the estate, whereas a Pur Autre Vie life estate is dependent on the life of another person, not the life tenant.
Under the Uniform Probate Code (UPC), instead of dower and curtesy, a surviving spouse typically receives a portion of the estate, known as the __________ share rights.
Under the Uniform Probate Code (UPC), instead of dower and curtesy, a surviving spouse typically receives a portion of the estate, known as the __________ share rights.
Match the following terms related to wills with their correct descriptions:
Match the following terms related to wills with their correct descriptions:
Which type of will is entirely handwritten and, depending on the jurisdiction, may or may not require witnesses?
Which type of will is entirely handwritten and, depending on the jurisdiction, may or may not require witnesses?
A codicil is a completely new will that replaces any prior wills.
A codicil is a completely new will that replaces any prior wills.
What is the primary purpose of a Living Will?
What is the primary purpose of a Living Will?
Explain the term 'escheat' and under what circumstances does it occur?
Explain the term 'escheat' and under what circumstances does it occur?
A Homestead Estate provides protection against __________ and judgements, ensuring a piece of property remains available to the owner and their family.
A Homestead Estate provides protection against __________ and judgements, ensuring a piece of property remains available to the owner and their family.
What is the term for transferring real property through a will?
What is the term for transferring real property through a will?
In a Fee Simple Absolute estate, what level of ownership is conveyed?
In a Fee Simple Absolute estate, what level of ownership is conveyed?
What happens to a property in a Life Estate upon the death of the life tenant?
What happens to a property in a Life Estate upon the death of the life tenant?
Which term describes someone who dies without a will?
Which term describes someone who dies without a will?
What is a handwritten will called?
What is a handwritten will called?
Which of the following is a characteristic of an Estate for Years?
Which of the following is a characteristic of an Estate for Years?
What is the main purpose of a will?
What is the main purpose of a will?
Which of the following describes a 'Pur Autre Vie' life estate?
Which of the following describes a 'Pur Autre Vie' life estate?
What is the role of an executor?
What is the role of an executor?
A change to an existing will is known as what?
A change to an existing will is known as what?
Flashcards
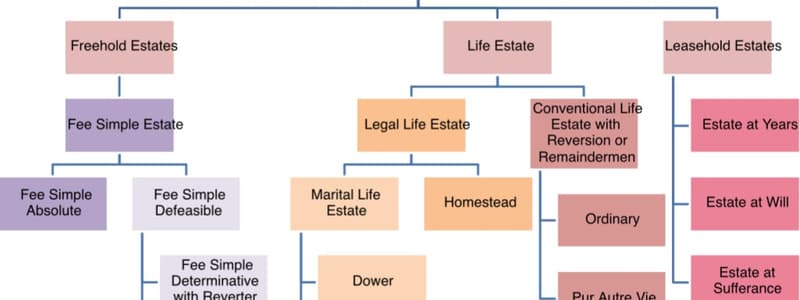
Freehold Estates
Freehold Estates
Ownership/property that can be transferred to heirs forever.
Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute
Complete & highest ownership with full bundle of rights; ownership has no conditions.
Fee Simple Defeasible
Fee Simple Defeasible
Highest degree ownership but with conditions/exclusions; has almost all bundle of rights.
Life Estate
Life Estate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pur Autre Vie
Pur Autre Vie
Signup and view all the flashcards
Will
Will
Signup and view all the flashcards
Devise
Devise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testate
Testate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intestate
Intestate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Codicil
Codicil
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estate in Land
Estate in Land
Signup and view all the flashcards
Condition Subsequent
Condition Subsequent
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reverter Clause
Reverter Clause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Life Tenant
Life Tenant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conventional Life Estate
Conventional Life Estate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Legal Life Estate
Legal Life Estate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dower & Curtesy
Dower & Curtesy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homestead Estate
Homestead Estate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testator/Testatrix
Testator/Testatrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuncupative Will
Nuncupative Will
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Transfer of Ownership
- Estates involve the ability to transfer ownership/property to heirs indefinitely.
- An Estate in Land grants ownership rights to real property.
- These rights are determined by the property's immobility, as an interest derived from the land that can’t be moved.
- These rights are also determined by the potential for indeterminate duration of ownership, property able to be passed on forever if requirements met & follow law such as paying taxes & mortgage on time.
- Freehold and Non-freehold estates are two types of estates.
- An Estate for Years has a definite time period.
Fee Simple Estate
- Fee Simple Absolute/Title/Estate is the most complete form of ownership with a full bundle of rights, not subject to conditions or accidents.
- Fee Simple Defeasible/Determinable/Qualified provides a high degree of ownership but with conditions or exclusions that impact the bundle of rights.
- Condition Subsequent With Right of Re-Entry means the title/interest isn't transferred until a condition is met and lasts only as long as the condition is satisfied.
- Conditional Ownership With Reverter Clause results in the title reverting to the seller if a condition is broken due to reversion rights, without needing legal action.
Life Estate
- A Life Estate is governed by statutory law.
- Life Estate defines property title/freehold estate based on the length of someone's life and ends at death.
- Life Estates involve a grantor of life estate and either a remainderman or reversion arrangement to avoid probate.
- A Life Tenant holds and has the right to sell, mortgage, or lease their ownership or interest in the property, but the estate is not inheritable.
- Conventional life estates depend on the life of the person receiving the estate. once the person dies, the property goes to the remainderman.
- Pur Autre Vie life estates depend on the life of another person, not the life tenants.
- Granted title can be used to take care of a special needs child, having title as long as the child lives.
- Once the the child dies, the title reverts or remainderman.
- Legal Life Estates are established by law and end at death, with ownership reverting to a remainderman.
Dower, Curtesy, & Homestead
- Dower & Curtesy are old common law concepts replaced by the Uniform Probate Code, which gives a surviving spouse a portion of the estate but restricts property conveyance and is subject to statutory share rights, like in Utah.
- Dower refers to a wife’s rights to her deceased husband’s property.
- Curtesy refers to a husband’s rights to his deceased wife’s property.
- Historically, 1/3 dower rights went to the widow for herself and family.
- Homestead Estates protect a piece of property from creditors and judgments (except mortgages and taxes) in states that permit them, with varying filing requirements.
- An individual can only have one homestead at a time, even with multiple homes.
Wills
- A Will is a document listing assets (real or personal property) and their intended recipients.
- Wills may be subject to probate.
- Devise refers to transfer of real property via a will, while bequest/legacy refers to transfer of personal property; this distinction may be legally blurred to honor the testator's intent.
- Devisor is the person who makes the will.
- Devisee is the person who receives real property by will.
- Devises refer to real property in a will.
- Descent refers to acquiring ownership of an estate through inheritance.
- Testate/Testator/Testatrix refers to someone who died with a will.
- Intestate refers to someone who died without a will, potentially leading to Escheat.
- Executor/Executrix is the person who carries out the will's instructions.
- A Formal/Written Will is drafted by an attorney and is most common.
- A Nuncupative Will is an oral or deathbed will, allowed in some states with witness requirements by at least 2 people.
- A Holographic Will is a handwritten will that needs to be witnessed.
- A Living Will outlines wishes regarding life support, organ donation, etc., in case of incapacitation, with a grantor managing assets while alive.
- When the grantor dies, assets are transferred to trustee of choice.
- A Codicil Will represents a change or amendment to an existing will.
- Probate is a court process for handling asset distribution, in which the person’s intentions are considered.
- Not all wills need to be probated.
- Probate can be lengthy and a huge financial burden.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.