Podcast
Questions and Answers
What condition is indicated by osteophytes around the distal patella and other knee joint areas?
What condition is indicated by osteophytes around the distal patella and other knee joint areas?
- Cruciate ligament injury
- Fat pad syndrome
- Patellar luxation
- Joint degeneration (correct)
Which treatment option is recommended for small dogs with knee injuries?
Which treatment option is recommended for small dogs with knee injuries?
- Strict rest for 6-8 weeks (correct)
- Arthroscopy
- Tibial plateau levelling osteotomy (TPLO)
- Tibial tuberosity advancement (TTA)
What complication can arise in 40% of patients with a cruciate ligament injury?
What complication can arise in 40% of patients with a cruciate ligament injury?
- Contralateral cruciate ligament injury (correct)
- Patella luxation
- Infection
- Meniscal damage
Which breed type is most commonly associated with medial patellar luxation?
Which breed type is most commonly associated with medial patellar luxation?
What radiographic finding corresponds to the fat pad sign?
What radiographic finding corresponds to the fat pad sign?
What does the severity of lameness correlate with?
What does the severity of lameness correlate with?
What is a characteristic behavior of a patient with intermittent weight bearing lameness?
What is a characteristic behavior of a patient with intermittent weight bearing lameness?
What sensation is associated with stifle luxation during a clinical examination?
What sensation is associated with stifle luxation during a clinical examination?
Which technique is appropriate for luxating the patella manually?
Which technique is appropriate for luxating the patella manually?
How are standard orthogonal radiographs utilized in evaluating patella position?
How are standard orthogonal radiographs utilized in evaluating patella position?
What indicates a substantial change on radiographs concerning patella luxation?
What indicates a substantial change on radiographs concerning patella luxation?
What grades of luxation may allow the patella to temporarily be located in the trochlear groove?
What grades of luxation may allow the patella to temporarily be located in the trochlear groove?
What finding on radiographs cannot be used to completely rule out?
What finding on radiographs cannot be used to completely rule out?
What lameness is typically associated with chronic osteoarthritis (OA)?
What lameness is typically associated with chronic osteoarthritis (OA)?
What treatment option is indicated for dogs with Grade 1 and 2 bone tumours?
What treatment option is indicated for dogs with Grade 1 and 2 bone tumours?
Which test is used to assess the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL)?
Which test is used to assess the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL)?
Which type of bone neoplasm is most common in dogs?
Which type of bone neoplasm is most common in dogs?
Which of the following is NOT a sign of stifle joint effusion during palpation?
Which of the following is NOT a sign of stifle joint effusion during palpation?
During the cranial tibial thrust test, what indicates a loss of integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament?
During the cranial tibial thrust test, what indicates a loss of integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament?
What is a key characteristic of bone tumours in dogs that may indicate malignancy?
What is a key characteristic of bone tumours in dogs that may indicate malignancy?
What imaging result is commonly associated with panosteitis in dogs?
What imaging result is commonly associated with panosteitis in dogs?
What is indicated by a positive 'sit-test' in a physical examination?
What is indicated by a positive 'sit-test' in a physical examination?
What is the prognosis for dogs with Grade 4 bone tumours?
What is the prognosis for dogs with Grade 4 bone tumours?
Which condition can you infer when observing pain on flexion of the stifle joint?
Which condition can you infer when observing pain on flexion of the stifle joint?
What symptom is typically NOT associated with osteoarthritis as it worsens over time?
What symptom is typically NOT associated with osteoarthritis as it worsens over time?
In what age group are bone tumours most commonly found in cats?
In what age group are bone tumours most commonly found in cats?
What does a positive cranial drawer test suggest?
What does a positive cranial drawer test suggest?
What are common signs of bone tumours in dogs?
What are common signs of bone tumours in dogs?
What is a characteristic sign of emotional distress related to panosteitis in young dogs?
What is a characteristic sign of emotional distress related to panosteitis in young dogs?
What observable sign indicates fore limb lameness?
What observable sign indicates fore limb lameness?
Which of the following is NOT a sign of hind limb lameness?
Which of the following is NOT a sign of hind limb lameness?
What is the recommended approach for examining a lame limb?
What is the recommended approach for examining a lame limb?
Which of the following conditions is classified as a disorder of growth in dogs under 1 year?
Which of the following conditions is classified as a disorder of growth in dogs under 1 year?
What is a common presentation of acute cranial cruciate ligament disease (CCLD)?
What is a common presentation of acute cranial cruciate ligament disease (CCLD)?
Which breed types can be affected by cranial cruciate disease (CCLD)?
Which breed types can be affected by cranial cruciate disease (CCLD)?
Which of these is NOT a component of an orthopedic examination?
Which of these is NOT a component of an orthopedic examination?
What is a common issue for large breeds that is listed as a differential diagnosis?
What is a common issue for large breeds that is listed as a differential diagnosis?
What is a common sign of joint issues in cats related to lameness or stiffness?
What is a common sign of joint issues in cats related to lameness or stiffness?
Which of the following is NOT considered an investigation method for diagnosing joint issues?
Which of the following is NOT considered an investigation method for diagnosing joint issues?
What is a notable behavioral change observed in pets with joint problems?
What is a notable behavioral change observed in pets with joint problems?
Which treatment option is suitable for managing degenerative joint disease in pets?
Which treatment option is suitable for managing degenerative joint disease in pets?
What is a common physical examination finding in animals with joint problems?
What is a common physical examination finding in animals with joint problems?
What type of medication should be avoided for pain management in cats?
What type of medication should be avoided for pain management in cats?
Which sign is commonly associated with chronic joint problems in dogs or cats?
Which sign is commonly associated with chronic joint problems in dogs or cats?
Which aspect is crucial for managing client expectations in pets with joint issues?
Which aspect is crucial for managing client expectations in pets with joint issues?
Flashcards
Radiographic signs of CCL rupture
Radiographic signs of CCL rupture
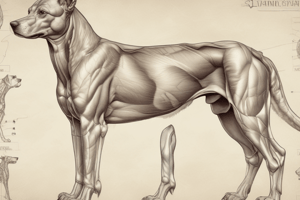
Osteophytes forming around the kneecap (patella), the groove in the femur (supratrochlear region), the top of the shinbone (tibial margins) and the femur (femoral margins), and small bones behind the knee (fabellae).
Fat pad sign in CCL rupture
Fat pad sign in CCL rupture
The area in front of the femur appears lighter on x-rays due to fluid accumulation, indicating inflammation and swelling.
Tibial Plateau Levelling Osteotomy (TPLO)
Tibial Plateau Levelling Osteotomy (TPLO)
A surgical procedure that levels the top surface of the shinbone (tibial plateau) to reduce stress on the CCL.
Patellar Luxation
Patellar Luxation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA)
Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head Nodding (Downward)
Head Nodding (Downward)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Head Nodding (Upward)
Head Nodding (Upward)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dorsal Pelvic Displacement
Dorsal Pelvic Displacement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shortened Stride
Shortened Stride
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lameness Grading
Lameness Grading
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthopaedic Examination
Orthopaedic Examination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differential Diagnosis List
Differential Diagnosis List
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Cruciate Disease (CCLD)
Cranial Cruciate Disease (CCLD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progressive Lameness
Progressive Lameness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Drawer Test
Cranial Drawer Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Tibial Thrust Test
Cranial Tibial Thrust Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain on Hyperextension
Pain on Hyperextension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loss of Range of Motion (ROM)
Loss of Range of Motion (ROM)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stifle Joint Effusion
Stifle Joint Effusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Buttress
Medial Buttress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermittent Weight Bearing Lameness
Intermittent Weight Bearing Lameness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Cruciate Ligament Deficiency (CCLD)
Cranial Cruciate Ligament Deficiency (CCLD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lameness Severity and Luxation Grade
Lameness Severity and Luxation Grade
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skipping Lameness
Skipping Lameness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Manually Luxating the Patella
Manually Luxating the Patella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Standard Orthogonal Radiographs
Standard Orthogonal Radiographs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral, Flexed Radiograph
Lateral, Flexed Radiograph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemangiosarcoma
Hemangiosarcoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrosarcoma
Fibrosarcoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Panosteitis
Panosteitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Biopsy
Bone Biopsy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jamshidi Bone Biopsy Needle
Jamshidi Bone Biopsy Needle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary DJD
Secondary DJD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morning Stiffness and Lameness
Morning Stiffness and Lameness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonspecific Radiographic Findings
Nonspecific Radiographic Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Managing DJD
Managing DJD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weight Control for DJD
Weight Control for DJD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exercise Control for DJD
Exercise Control for DJD
Signup and view all the flashcards
NSAID Use in DJD
NSAID Use in DJD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Lameness in Companion Animals
- Lameness is a disruption of normal locomotion
- Understanding how various presentations of lameness relate to different injuries is crucial
- Constructing a differential diagnosis list based on clinical presentations, selecting appropriate diagnoses, and identifying suitable medical/surgical interventions are essential
- Determining an appropriate prognosis for the common causes of lameness is also vital.
Learning Objectives
- Understand how various presentations of lameness in companion animals relate to different injuries
- Construct a differential diagnosis list based on clinical presentations related to common causes of lameness
- Determine appropriate diagnostics
- Determine appropriate medical and surgical interventions for the management and treatment of common causes of lameness
- Determine appropriate prognosis for common causes of lameness
Lameness: Disruption of Normal Locomotion
- Categories include: orthopaedic, oncological, and neurological
- Images of each category are included.
Clinical Approach
- History and signalment
- Distant observation
- Gait observation
- General physical examination
- Orthopaedic/neurological assessment
- Systemic issue or not?
- Affected limb(s)
- Affected structure(s)
- List of differential diagnosis
History
- Owner's complaint (affected limb(s), severity, onset)
- Acute or insidious onset?
- Traumatic episode associated?
- Is the lameness intermittent or continuous?
- Does the lameness improve, worsen, or remain static during the day/after rest/exercise?
- Does the severity change with the ground surface?
- Is the animal comfortable lying, sitting, and standing?
- How much exercise does the animal receive currently?
- General well-being
- Travel history/imported from abroad?
Distant Observation
- Off-loading of affected limb during standing
- Weakness
- Plantigrade stance
- Difficulty in rising/sitting
- Does the animal sit square?
Gait Analysis
- Observe animal's gait at walk and trot
- Bilateral lameness may be difficult to observe.
- Forelimb lameness: head nods downward as the sound limb is placed, head nods upward when the lame limb is placed.
- Hindlimb lameness: dorsal displacement of the pelvis, shortened stride
Lameness Grading
- Scoring system for assessing lameness
- Includes descriptions of the lameness associated with each grade
- Grade 0-5
- Scoring for lameness should use various clinical tools
Orthopaedic Examination
- Examine the lame limb last (pain elicited)
- Large/giant breed dogs are most easily examined on the floor.
- Small breed dogs/cats examined on the clinical examination table.
- Assistance may be required
- Purpose: to identify anatomical deformities/displacement, pain/crepitus, range of movement of joints, integrity of supporting structures of each joint
List of Differential Diagnosis
- Lists potential diagnoses by age group (dogs <1 vs >1 year) and breed (large vs. small vs. chondrodystrophic)
- Specific diagnoses include: cranial cruciate disease, patella luxation, panosteitis, osteosarcoma, degenerative joint disease, and avascular necrosis.
Cranial Cruciate Disease (CCLD)
- Signalment: small and large breeds, young and old, males and females, cats
- History: sudden onset of non-weight-bearing or partial weight-bearing lameness (acute CCLD), or mild weight-bearing lameness associated with exercise, improves with rest (partial tear)
- Chronic: weight bearing lameness associated with osteoarthritis
Physical Examination
- Postural changes (lameness, off-loading affected limb during stance, "sit-test")
- Palpation (effusion, pain on hyperextension, pain on flexion, loss of ROM, atrophy of muscles, medial buttress, cranial drawer/tibial compression test, meniscal click)
Cranial Drawer Test
- Patient in lateral recumbency
- Hold the patella/caudal aspect of lateral femoral condyle
- Locate tibial tuberosity/fibular head
- The tibia is moved forward/relative to the femur
- Painful-difficult to perform
Cranial Tibial Thrust
- Patient’s stifle in near full extension
- Use one hand on patellar ligament / tibial tuberosity
- Flex the hock with the other hand
- Observe for movement of the tibial crest in relation to femur
Radiology
- Osteophytes (around distal patella, supratrochlear region, tibial and femoral margins)
- Fat pad sign (area cranial to the femur whiter than normal stifle)
Treatment Options
- Conservative treatment (rest, 6-8 weeks), more effective in small dogs (<15kg) if ineffective meniscal damage
- Surgical treatment (medium/large dogs >15kg), arthrotomy/arthroscopy, tibial plateau leveling osteotomy, tibial wedge osteotomy, TTA
Patella Luxation
- Signalment: younger dogs (small breeds >> large breeds), MPL more frequent in small than large breeds, cats
- History: intermittent, weight-bearing lameness related to grade of luxations
- Leg in flexed position, few steps, skipping
- Concurrent CCLD 25%
Grading of Patella Luxation
- Grade 1, 2, 3, 4
- Clinical symptoms and deformities are considered for proper grading
Clinical Examination
- Identify the patella
- Move the stifle through its ROM
- A popping sensation when luxating is often associated with the sign
Investigations: Radiology
- Standard orthogonal radiographs of the stifle should be obtained (craniocaudal, lateral)
- Evaluate patella position
- Assess for joint effusion and degenerative changes
- Substantial changes indicate CCLD
Treatment Plan
- Conservative treatment (Grade 1 and 2): physiotherapy, hydrotherapy
- Surgical treatment (Grade 3 and 4); also Grade 2 if the dog is lame/painful
Bone Tumours in Dogs
- Signalment: middle-aged/older patients, large breeds
- History: severe lameness, poor response to analgesia, bony swelling, pathological fracture
- Most common: osteosarcoma
- Other diagnoses: chondrosarcoma, hemangiosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, secondary metastasis (urogenital, mammary)
- Common sites: 75% appendicular, forelimbs > hindlimbs
Investigations
- Imaging findings (cortical bone thinning, bone lysis, bone proliferation, elevation of periosteum mottled appearance, thoracic imaging, high metastasic rate required 3 chest views (radiography or CT))
- Tissue biopsy (Jamshidi bone biopsy needle)
Bone Neoplasia in Dogs: Treatment and Prognosis
- Tumor-specific information on incidence, metastasis, treatment, and prognosis
Bone Tumours in Cats
- Rare in comparison to dogs
- Osteosarcoma most common.
- Signalment: mature cats
- Presentation: lameness, limb deformities, pathological fractures
- Diagnosis; local radiographs and thoracic radiographs
- Treatment: amputation
- Prognosis: reasonable with amputation, 10% risk of metastasis
Panositis
- Signalment: Young dogs (<2-year-old), male > female, large breeds
- History: shifting lameness, pain on palpation, chronic intermittent lameness
- Investiation: patchy areas of increased opacity within medullary canal (thumb print sign)
Treatment and Prognosis (Panositis)
- Conservative treatment: pain relief, exercise restrictions
- Self-limiting: resolves within 2 years
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
- Signalment: middle-aged/older patients, small and large breeds (cats affected as well)
- History: lameness/stiffness, chronic presentation, insidious onset, worsens morning/rest, improves with exercise/warming up
- Difficulty raising/jumping/stairs, altered behaviour(aggression, lethargy), urination and defecation outside the litter tray (cats)
Clinical Examination (DJD)
- Stiffness, lameness, muscular atrophy, reduction in ROM, crepitus, altered gait (reduce stride length, altered swing phase), unkept appearance (cat), pain on examination, swollen joints
Investigations (DJD)
- Radiography (signs nonspecific, osteophytes, enthesophytes, intra-articular mineralisation, subchondral sclerosis, soft tissue enlargement)
- Synovial fluid analysis, arthroscopy
Conservative Treatment (DJD)
- Client education, expectations, weight control(ideal body condition score), exercise control, environmental changes for cats (access to feeding bowl, favourite sleeping spot, litter box)
- Physiotherapy/Hydrotherapy
- Medical management (NSAIDs, paracetamol, gabapentin, amantadine, monoclonal antibody therapy)
- Nutritional supplementation
Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head (Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease)
- Signalment: small breed dogs (miniature poodles, WHWT), young 4-11 months, cats affected by similar issue
- History: variable lameness, potentially non-weight bearing
- Clinical findings: pain, crepitus on hip examination
- Investigations: radiography
- Treatment: femoral head and neck osteotomy, total hip arthroplasty
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.