Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the kidneys?
What is the main function of the kidneys?
- Production of hormones related to digestion
- Removal of metabolic waste from the bloodstream (correct)
- Storage of nutrients and energy
- Regulation of body temperature
Which anatomical structure is NOT a part of the nephron?
Which anatomical structure is NOT a part of the nephron?
- Glomerulus
- Collecting duct
- Renal pelvis (correct)
- Loop of Henle
Which statement accurately describes the filtration apparatus of the kidney?
Which statement accurately describes the filtration apparatus of the kidney?
- It filters blood through porous capillaries in the glomerulus. (correct)
- It is primarily involved in hormonal secretion.
- It absorbs nutrients from the urine.
- It regulates urine color and concentration.
Which option correctly identifies the pathway of blood flow in the kidney?
Which option correctly identifies the pathway of blood flow in the kidney?
What do the terms positive balance and negative balance refer to in renal function?
What do the terms positive balance and negative balance refer to in renal function?
Study Notes
Kidney Function
- Main function: Filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
- Other functions: Regulate blood volume, electrolyte balance, and blood pressure.
- Contribute: To the production of red blood cells.
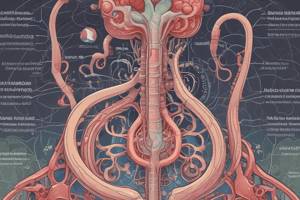
Functional Anatomy of the Kidney
- Two kidneys: Located on either side of the vertebral column, behind the peritoneum.
- External structure: Bean-shaped organ with a concave medial border, a renal hilum, and a renal pelvis.
- Internal structure: Composed of an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
- Functional unit: Nephron, responsible for urine production.
Components of the Nephron
- Renal corpuscle: Filtration unit, consisting of the glomerulus (capillary network) and Bowman's capsule (surrounding the glomerulus).
- Proximal convoluted tubule: Reabsorbs most of the filtered water, glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes.
- Loop of Henle: Descending limb is permeable to water, ascending limb is impermeable to water, and reabsorbs salts.
- Distal convoluted tubule: Reabsorbs water and electrolytes under hormonal control.
- Collecting duct: Receives fluid from several nephrons, reabsorbs water, and contributes to urine concentration.
Filtration Apparatus of the Kidney
- Glomerular filtration: The process by which the kidney filters blood to produce ultrafiltrate.
- Filtration barrier: Composed of three layers: the glomerular capillary endothelium, the basement membrane, and the podocytes.
- Filtrate: Contains water, small solutes like glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes, but excludes large proteins and blood cells.
Blood Flow in the Kidney
- Arterial blood: Enters the kidney through the renal artery.
- Blood flow to the nephron: Renal artery branches into afferent arterioles supplying the glomerulus, then efferent arterioles leaving the glomerulus.
- Peritubular capillaries: Surrounding the renal tubules, reabsorb reabsorbed substances.
- Venous blood: Exits the kidney through the renal vein.
Components of Renal Function
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR): The volume of filtrate produced per unit time, reflecting kidney function.
- Tubular reabsorption: Process of recovering useful substances from the filtrate back into the blood.
- Tubular secretion: Process of removing waste products and excess substances from the blood into the filtrate.
- Urine formation: Resulting from filtration, reabsorption, and secretion processes.
Balance, Steady State, Positive and Negative Balance
- Balance: The difference between intake and output of a substance.
- Steady state: A condition where the intake and output of a substance are equal.
- Positive balance: Intake exceeds output, leading to an increase in the body's stores.
- Negative balance: Output exceeds intake, leading to a depletion of the body's stores.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the essential functions and anatomy of the kidneys. This quiz covers the main functions of kidneys, the structure of the nephron, and the key components involved in urine production. Perfect for students learning about human physiology!