Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a component considered when describing the kidney?
Which of the following is NOT a component considered when describing the kidney?
- Layers
- Ligaments
- Types
- Color (correct)
The ligamentum hepatorenalis, which connects the right kidney to the liver, is notably absent in which species?
The ligamentum hepatorenalis, which connects the right kidney to the liver, is notably absent in which species?
- Pigs (correct)
- Horses
- Dogs
- Cattle
Which type of kidney is characterized by a smooth, unilobar structure?
Which type of kidney is characterized by a smooth, unilobar structure?
- Kidney of a cow
- Kidney with lobated-multilobar structure
- Kidney of a pig
- Kidney of a dog (correct)
Which of the following structures is NOT a layer of the ureter?
Which of the following structures is NOT a layer of the ureter?
What is the topographical relation of the right kidney to the left kidney in most species?
What is the topographical relation of the right kidney to the left kidney in most species?
Which anatomical feature is present in the urinary bladder of most species but absent in bovines?
Which anatomical feature is present in the urinary bladder of most species but absent in bovines?
Which ligament attaches the urinary bladder's ventral surface to the symphysis pelvina?
Which ligament attaches the urinary bladder's ventral surface to the symphysis pelvina?
What is the primary functional difference between the female urethra and the male urethra?
What is the primary functional difference between the female urethra and the male urethra?
Which of the following is the correct term for the hair root?
Which of the following is the correct term for the hair root?
What is the primary component of the cortex of a hair?
What is the primary component of the cortex of a hair?
Which structures are unique to certain breeds/species and serve functional and protective roles?
Which structures are unique to certain breeds/species and serve functional and protective roles?
What is the anatomical term that refers to the bony structure found within a horn?
What is the anatomical term that refers to the bony structure found within a horn?
Which anatomical structure is vascularized in poultry and functions in thermoregulation?
Which anatomical structure is vascularized in poultry and functions in thermoregulation?
Sebum is secreted by which type of gland?
Sebum is secreted by which type of gland?
What type of nephrons are crucial for concentrating urine and maintaining water balance?
What type of nephrons are crucial for concentrating urine and maintaining water balance?
Which term describes the active removal of hydrogen and potassium ions from the blood into the tubules?
Which term describes the active removal of hydrogen and potassium ions from the blood into the tubules?
What role does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) play in tubular function?
What role does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) play in tubular function?
Avian kidneys contain which two types of nephrons?
Avian kidneys contain which two types of nephrons?
The process of transforming mammary epithelial cells into secretory cells is known as:
The process of transforming mammary epithelial cells into secretory cells is known as:
What is the key hormone for milk-synthesis initiation and maintenance?
What is the key hormone for milk-synthesis initiation and maintenance?
What is galactopoiesis?
What is galactopoiesis?
What is the function of oxytocin in milk secretion?
What is the function of oxytocin in milk secretion?
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system in the udder?
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system in the udder?
Which component of the kidney's anatomical structure is NOT typically found in cows?
Which component of the kidney's anatomical structure is NOT typically found in cows?
The renal corpuscle consists of the glomerulus and what other structure?
The renal corpuscle consists of the glomerulus and what other structure?
Which part of the hair follicle contains epidermal stem cells?
Which part of the hair follicle contains epidermal stem cells?
What is the function of Merocrine Sweat Glands?
What is the function of Merocrine Sweat Glands?
What is the process where FIL (Feedback Inhibitor of Lactation) builds up?
What is the process where FIL (Feedback Inhibitor of Lactation) builds up?
Which action does Oxytocin trigger to allow for milk ejection?
Which action does Oxytocin trigger to allow for milk ejection?
The balance between what two factors is crucial for homoeostasis?
The balance between what two factors is crucial for homoeostasis?
Where is ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) produced?
Where is ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) produced?
What is the process of structural regression of mammary tissue?
What is the process of structural regression of mammary tissue?
What process is directly involved with removing substances like glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes and moving them back into the blood?
What process is directly involved with removing substances like glucose, amino acids, and electrolytes and moving them back into the blood?
Mammary glands grow at the same rate as the body during which life stage?
Mammary glands grow at the same rate as the body during which life stage?
What is the function of the Cuticle (cuticula) related to internal structure?
What is the function of the Cuticle (cuticula) related to internal structure?
What is the name of the primary defense that is closed by a sphincter muscle and sealed by keratin associated with udders?
What is the name of the primary defense that is closed by a sphincter muscle and sealed by keratin associated with udders?
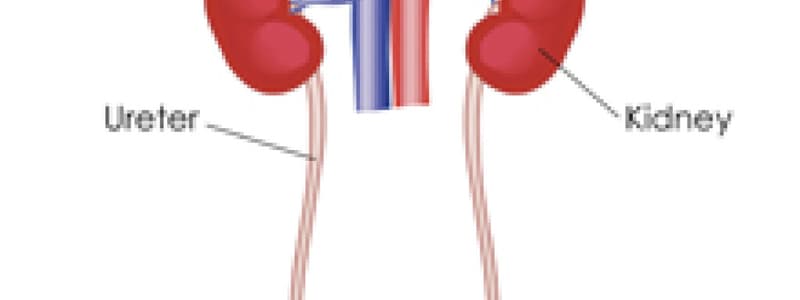
What is the location of kidney?
What is the location of kidney?
What does the Kidney include?
What does the Kidney include?
Flashcards
Anatomical Terms
Anatomical Terms
Anatomical terms are mandatory in English and Latin.
Kidney (Ren)
Kidney (Ren)
Organ type, anatomical structure, layers, mesenterium, ligaments, types, topography, and features of species.
Anatomical Structure of the Kidney
Anatomical Structure of the Kidney
Lobus renalis, Papilla renalis, Columnae renalis, Pyramides renalis, Calices renales, Pelvis renalis, Sinus renalis.
Layers of the Kidney
Layers of the Kidney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lig. Hepatorenalis
Lig. Hepatorenalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Topography of the Kidneys
Topography of the Kidneys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter Topography
Ureter Topography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pars Abdominalis
Pars Abdominalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pars Pelvina
Pars Pelvina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apex Vesicae
Apex Vesicae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Vesicae
Corpus Vesicae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervix Vesicae
Cervix Vesicae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigonum Vesicae
Trigonum Vesicae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lig. Vesicae Laterale
Lig. Vesicae Laterale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra Topography
Urethra Topography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Female Urethra (Urethra Feminina)
Female Urethra (Urethra Feminina)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hair Structure (Pili)
Hair Structure (Pili)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cuticle (Cuticula)
Cuticle (Cuticula)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortex (Hair)
Cortex (Hair)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Hairs
Types of Hairs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin Folds
Skin Folds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horns (Cornu)
Horns (Cornu)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Skin Glands
Common Skin Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammary Glands
Mammary Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Pads: Species Features
Foot Pads: Species Features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Equine Hoof
Equine Hoof
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bovine and Pig Hooves
Bovine and Pig Hooves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Comb and Wattles
Comb and Wattles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney stroma.
Kidney stroma.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parts of nephron
Parts of nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structure of Renal Corpuscle
Structure of Renal Corpuscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Renal Corpuscle
Function of Renal Corpuscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle
Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epidermis
Epidermis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dermis
Dermis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypodermis
Hypodermis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hair Follicles
Hair Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hair Matrix Cells
Hair Matrix Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Kidney (Ren)
- Encompasses organ type, anatomical structure, layers, mesenterium, ligaments, types, topography, and species-specific features
- Anatomical structures include:
- Lobus renalis
- Papilla renalis
- Columnae renalis
- Pyramides renalis
- Calices renales (major and minor)
- Pelvis renalis
- Sinus renalis
- Hilus
Kidney Layers
- Cortex renis
- Medulla renis
- Capsule renalis
Mesenterium & Ligaments
- Lig. hepatorenalis connects the right kidney to the liver, but is absent in pigs
Kidney Topography
- Kidneys are located in the abdominal cavity, lumbar region, and are retroperitoneal
- Right kidney is usually cranial to the left, except in pigs
Kidney Types
- Smooth-unilobar (unipyramidal) kidneys are found in dogs, cats, horses, sheep, and goats
- Smooth-multilobar (multipyramidal) kidneys are found in pigs
- Lobated-multilobar (multipyramidal) kidneys are found in bovine
Ureter
- Features anatomical structure, topography, parts, and species differences
- Anatomical Structure: Fibromuscular tube (0~1 cm) with three layers:
- Tunica adventitia (outer fibrous layer)
- Tunica muscularis (middle functional layer for peristalsis)
- Tunica mucosa (+ ureteric glands in horses - Gll. uretericae)
- Topography: Extends from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder
- Parts:
- Pars abdominalis: From the renal pelvis to the hilus renalis
- Pars pelvina: From the pelvic cavity to the urinary bladder
Urinary Bladder (Vesica Urinaria)
- Involves anatomical structure, topography, ligaments, and species-specific features
- Three regions:
- Apex vesicae: Cranial blind end
- Corpus vesicae: Middle region
- Cervix vesicae: Caudal funnel-shaped part leading to the urethra
- Internal features:
- Ureteric ostium
- Trigonum vesicae: Triangular smooth mucosal area, absent in bovines
- Crista urethralis
Bladder Ligaments
- Lig. vesicae laterale attaches to the dorsolateral pelvic wall
- Lig. teres vesicae is a remnant of the umbilical artery
- Lig. vesicae medianum attaches the ventral surface to the symphysis pelvina
- Topography: Located in the pelvic cavity
Urethra
- Covers anatomical structure, topography, features of males and females, and species variations
- Anatomical features include:
- Ostium urethrae internum
- Ostium urethrae externum
- Topography
- Connects the urinary bladder to the exterior
Male Urethra (Urethra masculina)
- Two parts:
- Pars pelvina
- Pars penina
Female Urethra (Urethra feminina)
- Shorter in length and serves only for urine excretion
Hair (Pili)
- Involves anatomical structure, types, place, features of species, and skin folds
- Hair is a keratinized structure that originates from hair follicles embedded in the dermis
- Structure:
- Apex pili
- Scapus pili
- Radix pili
- Bulbus pili
- Folliculus pili
- Papilla pili
- Arrector muscles of the hair
Hair Internal Structure
- Cuticle (cuticula): Protective function from outside factors
- Cortex (cortex): Contains keratin and pigments
- Medulla/core (medulla)
Hair Types
- Primary (guard) hairs
- Secondary (wool) hairs
- Tactile (sinus) hairs
Where Hair Is Found
- Hair covers most of the body except for areas such as the nose and footpads in certain species
Variations in Hair
- Guard hairs are prominent in dogs, while wool hairs dominate in sheep
Skin Folds
- Common in certain breeds/species (e.g., the facial folds in bulldogs) and serve functional and protective roles
Guard Hairs (Capilli)
- Anatomical structure, parts, and topography
Horn (Cornu)
- Focuses on anatomical structure, parts, and topography
- Horns are permanent keratinized structures arising from the corneal process of the frontal bone
- Parts:
- Horn core (bony structure)
- Keratinized horn sheath
- Base where growth occurs
- Topography: Found in species like cattle, goats, and some sheep
- Processus cornualis
- Dermis cornus
- Epidermis cornus
- Three anatomical parts:
- Apex cornus
- Corpus cornus
- Basis cornus
Skin Glands
- Includes common, specialized, and mammary glands, anatomical structure, types, topography, parts and features of species
- Common glands: Sebaceous (oil) glands and sweat glands
- Specialized glands: Scent glands (e.g., anal glands in dogs, infraorbital glands in sheep
- Topography: Distributed throughout the body, with specialized glands located in specific regions (e.g., tail glands in dogs, carpal glands in pigs)
- Mammary glands: Modified sweat glands responsible for milk production, varying in number and arrangement among species
Foot Pads (Tori)
- Topography is located on the underside of feet, varying by species
- Anatomical structure
- Thickened, keratinized epidermis with underlying connective tissue and fat for shock absorption
- Species features
- Carnivores have distinct digital, metacarpal, and carpal pads, while ruminants have digital cushions
Hooves and Claws
- Equine hoof, bovine/pig hooves, and carnivore claws, including anatomical structure, parts, and species differences
- Equine hoof includes the wall, sole, frog, and digital cushion, with weight-bearing functions
- Bovine and pig hooves have a cloven structure with two primary digits
- Carnivore claws are curved, keratinized extensions of the distal phalanx, used for grasping and defense
Skin Structures of Poultry
- Includes feathers, comb, wattles, beak, and claws
- Feathers are specialized keratinized structures providing insulation and aerodynamics
- Comb and wattles are vascularized skin structures for thermoregulation
- Beak: Keratinized structure used for feeding
Histology of Renal Stroma and Parenchyma
- Stroma (interstitial tissue) surrounds nephrons, ducts, blood, and lymphatic vessels
- Cortex: Contains fibroblasts and macrophages
- Medulla: Contains myofibroblast-like interstitial cells
- Parenchyma
- Cortex: Contains renal corpuscles, convoluted tubules, and medullary rays
- Medulla: Organized into pyramids containing straight tubules and collecting ducts
Structural Parts of Nephron
- Renal corpuscle (glomerulus + Bowman's capsule)
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle (descending and ascending limbs)
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting tubule/duct
Renal Corpuscle
- Structure: Contains a glomerulus surrounded by Bowman’s capsule
- Function: Filtration of blood to form primary urine
Filtration Barrier of Glomerulus
- Glomerular endothelium (fenestrated capillaries)
- Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) (negatively charged, acts as an ion-selective filter)
- Podocytes (with foot processes forming filtration slits covered by diaphragms)
Renal Tubules
- Proximal convoluted tubule: Simple cuboidal epithelium with microvilli, major site for reabsorption
- Loop of Henle: Descending limb (squamous epithelium, permeable to water), Ascending limb (impermeable to water, permeable to Na+ and Cl-)
Ureter and Urethra
- Ureter features include:
- Mucosa: Folded, lined by transitional epithelium
- No submucosa
- Muscularis: Two layers (upper part), three layers (lower third)
- Outer layer: Serosa/adventitia
Urinary Bladder
- Mucosa
- Transitional epithelium, flattens when bladder is full
- Muscularis
- Three layers (inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal)
- Serosa
- Covers the body and apex, while adventitia is found at the neck
Epidermis, Dermis, and Hypodermis
- Epidermis
- Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
- Dermis
- Dense connective tissue, containing blood vessels and nerves
- Hypodermis
- Loose connective tissue, contains fat for insulation
Hair Histology
- Medulla consists of loosely connected keratinized cells with soft keratin (only present in thick hairs)
- Cortex is the largest layer, made up of cortical cells filled with hard keratin
- Cuticle is the outermost layer composed of overlapping, semitransparent keratinized squamous cells that protect the hair
Hair Follicle
- Epidermal invaginations that produce hair
- Four regions:
- Infundibulum extends from the surface opening to the sebaceous gland duct
- Isthmus reaches from the sebaceous gland opening to the arrector pili muscle insertion
- Follicular Bulge, near the arrector pili muscle, contains epidermal stem cells
- Inferior Segment ends at the bulb which contains the dermal papilla (stimulates hair growth)
- Hair Matrix Cells: Located around the dermal papilla, they divide and proliferate to form new hair
Tactile Hair Histology
- Tactile hairs (whiskers) are larger and deeply rooted in the dermis and hypodermis and connected to specialized nerve endings that allow for sensory perception
Skin Glands
- Sebaceous Glands are associated with hair follicles and secrete sebum
- Apocrine Sweat Glands sweat glands active in horses
- Merocrine Sweat Glands are found in carnivore footpads, horse frogs, and nasolabial areas of ruminants and swine which lubricate, moisturize, and cool the skin
Mammary Gland
- Compound tubuloalveolar gland
- Secretory alveoli lined by simple cuboidal epithelium surrounded by myoepithelial cells
- Duct system: Alveolus → Intralobular duct → Lobular duct → Lactiferous (lobar) duct, Lactiferous sinus → Teat sinus → Papillary duct (teat canal)
- Epithelial transition: Transformation from simple cuboidal in ducts to stratified squamous in the papillary duct
Milk Secretion
- Merocrine for proteins
- Apocrine for lipids
Active and Inactive Mammary Glands
- Active glands exhibit open alveoli, and parenchyma dominates
- Inactive glands exhibit Parenchyma that is mostly replaced by stroma
Kidney Physiology
- Function of Excretion
Kidney Nephrons
- Cortical nephrons are located primarily in the outer cortex, have shorter loops of Henle, and filter blood and reabsorb substances
- Juxtamedullary nephrons possess longer loops of Henle extending deep into the medulla, crucial for concentrating urine and maintaining water balance
Renal Blood Flow
- Critical for maintaining filtration pressure and kidney function: The hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus encourages filtration, while pressure in the Bowman's capsule and osmotic pressure in the capillaries counteract it
Glomerular Filtration Rate
- Blood filtration rate in the glomerulus, usually 125 mL/min in healthy adults
- Blood pressure, membrane permeability, and oncotic pressure affect filtration
- GFR regulation is controlled by intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms
Tubular Function
- Clearance is the kidneys' ability to remove substances from the blood
- Tubular reabsorption involves the movement of substances back into the blood
- Secretion involves the active removal of substances from the blood into the tubules
- Glucose is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule, while excess leads to glucosuria
- Protein is usually not filtered, but its presence in urine indicates damage
- Ions are actively regulated to maintain homeostasis
- Reabsorption of water is controlled by Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Body Fluid Regulation
- Body fluid volume and osmolarity are managed through hormonal control
- Kidney adjusts urine concentration and sodium to maintain homeostasis
Urinary Tract
- Comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
- Urine travels from kidney to bladder through the ureters and is stored until excretion
Water Balance
- Balance between water intake and loss is important and the kidneys are responsible for adjusting urine output
Urination
- Controlled by the micturition reflex, involving the bladder, sphincters, and nervous system
Kidney Function in Newborns
- Immature at birth, leading to reduced ability to concentrate urine
- Newbowns have a higher risk of dehydration due to immature regulatory mechanisms
Avian Kidney Function
- Possess both reptilian and mammalian-type nephrons
- Excrete uric acid, conserving water
Lactation Physiology
- Process includes Mammary Gland Development and Growth
Mammogenesis
- Fetal life: Mammary glands grow at the same rate as the body
- Puberty: Growth becomes allometric, with fat development and duct formation
- Pregnancy to Parturition: Development of lobuli and alveoli: Prolactin secretion increases during late pregnancy
Lactation Phases
- Known as Lactogenesis, transformation of epithelial cells to secretory ones, occurs near parturition
- Progesterone drops, prolactin receptors are synthesized
- Prolactin initiates production of α-lactalbumin which starts milk secretion
Milk Production Maintenance
- Known as Galactopoiesis
- Metabolic hormone regulation (prolactin, GH, insulin, glucagon, glucocorticoids) is required with continued suckling/milking
Hormonal Control
- Prolactin, key hormone for milk synthesis
- Progesterone promotes udder development and inhibits lactation before parturition
- Cortisol triggers lactogenesis
- Estrogen supports duct growth and can induce lactation with progesterone
- Oxytocin causes milk ejection
- Growth Hormone (GH) maintains milk production
Involution
- Occurs when milking stops
- FIL (Feedback Inhibitor of Lactation) builds up if milk isn't removed, suppressing further milk synthesis
Milk Ejection
- Neuroendocrine reflex: Stimuli triggers hypothalmus to release oxytocin
- Oxytocin triggers myoepithelial cell contraction causing milk ejection
Milk Types
- Colostrum is produced for first few days post-parturition, rich in immunoglobulins, proteins, minerals, and fat which is vital for neonates
- Regular milk consists of fat, protein, lactose, vitamins, and minerals synthesized in mammary epithelial cells which varies by species and lactation stage
Lactation Curve
- Milk yield rises, then gradually declines
- Fat and protein content increase near end of lactation, while lactose decreases slightly later and mineral content rises
Udder Defense Against Infection
- Streak canal is a primary defense which is closed by and sealed by keratin
- Fürstenburg’s Rosette smooths with milk accumulation and contributes to immune defense by detecting pathogens
Blood System of the Udder
- Utilizes a large amount of blood to produce milk
- Blood enters via arteries and exits through veins
- Also requires a crucial lymphatic system
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.