Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following describes the correct order of structures encountered by urine as it exits the kidney?
Which of the following describes the correct order of structures encountered by urine as it exits the kidney?
- Major calyx, minor calyx, papilla, ureter
- Minor calyx, papilla, major calyx, ureter
- Papilla, major calyx, minor calyx, ureter
- Papilla, minor calyx, major calyx, ureter (correct)
A histological sample of kidney tissue shows a glomerulus located in the outer region. Based solely on this information, which type of nephron is it most likely to be?
A histological sample of kidney tissue shows a glomerulus located in the outer region. Based solely on this information, which type of nephron is it most likely to be?
- A superficial cortical nephron with a long loop of Henle.
- A juxtamedullary nephron with a long loop of Henle.
- A juxtamedullary nephron with a short loop of Henle.
- A superficial cortical nephron with a short loop of Henle. (correct)
Damage to the epithelial cells lining the proximal convoluted tubule would most likely directly impair which renal function?
Damage to the epithelial cells lining the proximal convoluted tubule would most likely directly impair which renal function?
- Ultrafiltration
- Reabsorption (correct)
- Secretion
- Filtration
In a kidney undergoing sagittal section, which of the following is the outermost layer observed?
In a kidney undergoing sagittal section, which of the following is the outermost layer observed?
Which statement correctly compares superficial cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons?
Which statement correctly compares superficial cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons?
If the afferent arteriole leading to the glomerulus is constricted, what immediate effect would this have on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
If the afferent arteriole leading to the glomerulus is constricted, what immediate effect would this have on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
Which of the following structures is directly involved in the ultrafiltration of blood?
Which of the following structures is directly involved in the ultrafiltration of blood?
Which feature is characteristic of the cells lining the proximal convoluted tubule and directly contributes to its primary function?
Which feature is characteristic of the cells lining the proximal convoluted tubule and directly contributes to its primary function?
A drug that inhibits the function of the loop of Henle would primarily affect?
A drug that inhibits the function of the loop of Henle would primarily affect?
The kidney's medulla is further segmented into two distinct zones. What are these called?
The kidney's medulla is further segmented into two distinct zones. What are these called?
Flashcards
Kidney Cortex
Kidney Cortex
Outer layer of the kidney, just beneath the capsule.
Kidney Medulla
Kidney Medulla
Centrally located area of the kidney, divided into outer and inner regions.
Kidney Papilla
Kidney Papilla
The apex of the inner medulla, leading into minor and major calyces.
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle
Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superficial cortical nephrons
Superficial cortical nephrons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
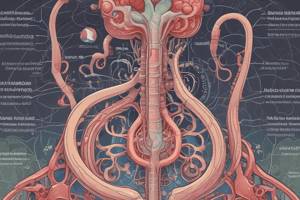
Gross Anatomic Features of the Kidney
- Kidneys are bean-shaped organs in the retroperitoneal space.
- In a sagittal section, kidneys have three main areas:
- Cortex: the outer layer beneath the capsule.
- Medulla: centrally located, divided into outer (with outer and inner stripes) and inner regions.
- Papilla: the apex of the inner medulla, leading to minor and major calyces (continuations of the ureter).
- Urine flows from the kidneys into the ureters and then to the bladder for storage.
The Nephron
- Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney, with ~1 million per kidney
- A nephron consists of a glomerulus and a renal tubule.
- The glomerulus is a network of glomerular capillaries from an afferent arteriole, encased by Bowman's capsule
- Blood ultrafiltration occurs across glomerular capillaries into Bowman's space, beginning urine formation.
- Nephron sections are tubular structures lined with epithelial cells, responsible for reabsorption and secretion.
- Segments of the nephron:
- Bowman's space
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Proximal straight tubule
- Loop of Henle (thin descending limb, thin ascending limb, thick ascending limb)
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting ducts
Cell Structure
- Epithelial cells lining each nephron part have unique ultrastructural characteristics matched to their segment
- Proximal convoluted tubule cells have a brush border of microvilli on their luminal side.
- This increases surface area for reabsorption.
Types of Nephrons
- Two primary nephron types exist:
- Superficial cortical nephrons
- Juxtamedullary nephrons
- They are differentiated by glomeruli location,
- Superficial cortical nephrons: glomeruli are in the outer cortex
- Juxtamedullary nephrons: glomeruli are near the corticomedullary border
- Superficial cortical nephrons feature shorter loops of Henle
- Juxtamedullary nephrons are equipped with longer loops of Henle extending deep into the inner medulla and papilla, crucial for urine concentration due to their larger glomeruli and higher glomerular filtration rates (GFRs).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.