Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary reason the right kidney is positioned lower than the left kidney?
What is the primary reason the right kidney is positioned lower than the left kidney?
- It is affected by the presence of the liver. (correct)
- It has a different blood supply.
- It has a thicker fibrous capsule.
- It is larger in size.
Which structure is most anterior in the hilum of the kidney?
Which structure is most anterior in the hilum of the kidney?
- Ureter
- Renal artery
- Renal vein (correct)
- Renal pelvis
What covering of the kidney acts as a cushion and helps to hold the kidney in a fixed position?
What covering of the kidney acts as a cushion and helps to hold the kidney in a fixed position?
- Renal fascia
- Paranephric fat
- Perirenal fat (correct)
- Fibrous capsule
Which measurement is NOT correct regarding the dimensions of the kidney?
Which measurement is NOT correct regarding the dimensions of the kidney?
Which structure primarily drains blood directly into the inferior vena cava?
Which structure primarily drains blood directly into the inferior vena cava?
What is the anatomical position of the hilum of the kidney in relation to the transpyloric plane?
What is the anatomical position of the hilum of the kidney in relation to the transpyloric plane?
What factor does NOT affect kidney fixation?
What factor does NOT affect kidney fixation?
Which of the following statements about Morris' Parallelogram is true?
Which of the following statements about Morris' Parallelogram is true?
What is NOT included in the coverings of the kidneys?
What is NOT included in the coverings of the kidneys?
Which descriptor is accurate regarding the borders of the kidney?
Which descriptor is accurate regarding the borders of the kidney?
What is the clinical significance of a tumor invading the left renal vein?
What is the clinical significance of a tumor invading the left renal vein?
What separates the kidneys from the abdominal cavity?
What separates the kidneys from the abdominal cavity?
Where do the afferent fibers of the renal sympathetic plexus enter the spinal cord?
Where do the afferent fibers of the renal sympathetic plexus enter the spinal cord?
How many segmental arteries does the renal artery divide into?
How many segmental arteries does the renal artery divide into?
Which statement about the left renal vein's drainage is accurate?
Which statement about the left renal vein's drainage is accurate?
In which anatomical location is the renal angle found?
In which anatomical location is the renal angle found?
Which kidney surface is NOT associated with the left kidney?
Which kidney surface is NOT associated with the left kidney?
How far above the hilum does the upper pole of the kidney lie?
How far above the hilum does the upper pole of the kidney lie?
What contributes to the parasympathetic nerve supply to the kidneys?
What contributes to the parasympathetic nerve supply to the kidneys?
Flashcards
Kidney
Kidney
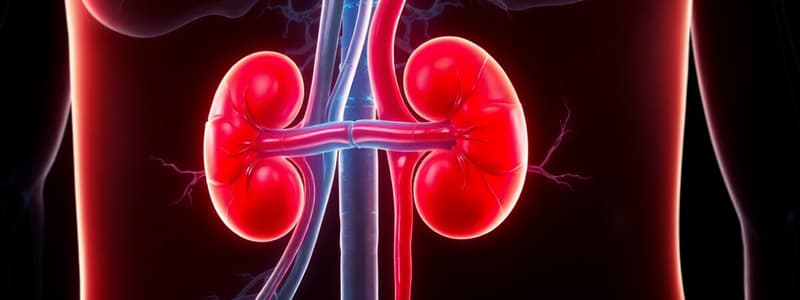
The kidney is a bean-shaped organ responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. It's vital for maintaining fluid balance and electrolyte levels.
Kidney Borders
Kidney Borders
The lateral border of the kidney is convex, curving outwards, while the medial border is concave, curving inwards, and contains the hilum.
Hilum
Hilum
The hilum is a notch on the medial border of the kidney where blood vessels, nerves, and the ureter enter and exit.
Kidney Position
Kidney Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Position - Right vs Left
Kidney Position - Right vs Left
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Coverings
Kidney Coverings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Capsule
Fibrous Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Fascia
Renal Fascia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Artery
Renal Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Vein
Renal Vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Renal Vein Tributaries
Left Renal Vein Tributaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Lymph Drainage
Kidney Lymph Drainage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Cell Carcinoma & Varicocele
Renal Cell Carcinoma & Varicocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Plexus
Renal Plexus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Sympathetic Nerves
Renal Sympathetic Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Parasympathetic Nerves
Renal Parasympathetic Nerves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Hilum Location
Renal Hilum Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper Pole Location
Upper Pole Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower Pole Location
Lower Pole Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Kidney Anatomy
- The kidney is bean-shaped
- The kidney is located retroperitoneally, in the upper part of the posterior abdominal region, on both sides of the vertebral column
- The kidneys extend from T12 superiorly to L3 inferiorly
- The right kidney is 1/2 inch (approx) lower than the left due to the liver's relationship.
- Kidneys weigh approximately 150 grams
- Kidney length is 4.5 inches, breadth 2.5 inches, and thickness is 1.5 inches
- The hilum lies on the transpyloric plane, 5 cm from the middle line.
- The upper pole lies 2.5 cm away from the mid-line and 5 cm above the hilum.
- The lower pole is 5 cm below the hilum and 7.5 cm from the mid-line.
- The renal angle is the area between the lateral borders of the erector spinae muscles and inferior borders of the 12th rib.
- Kidney is covered by the fibrous capsule, perirenal fat, renal fascia, and paranephric fat.
Kidney Blood Supply
- The renal artery arises from the abdominal aorta at the level of L2.
- The renal artery usually divides into 5 segmental arteries.
- The renal vein emerges from the hilum in front of the renal artery and drains into the inferior vena cava.
- The left renal vein receives the left adrenal vein, a branch of the inferior phrenic vein, and the left gonadal vein.
Kidney Innervation
- Renal sympathetic plexus: Afferent fibers travel through the renal plexus and enter the spinal cord at the 10th, 11th, and 12th thoracic nerves.
- Parasympathetic fibers: from the vagus nerve reach the kidney through the renal plexus.
Renal Hilum Differentiation
- The medial border of the kidney is concave, containing the hilum.
- The lateral border of the kidney is convex.
- In the hilum, the renal vein is the most anterior structure.
- The renal pelvis is posterior, and the renal artery is between them.
- The ureter passes downward along the lower part of the medial border.
Kidney Position and Stabilization
- Intra-abdominal pressure and the arrangement of adjacent organs stabilize the kidneys.
- The extensions of the covering fascia and fat also stabilize the kidneys.
- The renal vessels that connect the kidneys to the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava contribute to stability.
Renal Ptosis
- Rapid loss of pre-renal fat tissue may cause kidney ptosis (dropping of the kidney into the pelvis).
- This condition can lead to ureter kinking and severe pain.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.