Podcast
Questions and Answers
What primary concern does the study of economics address?
What primary concern does the study of economics address?
- Studying political systems
- How to maximize profits for businesses
- Exploring human psychology
- Analyzing the allocation of limited resources (correct)
What does the term 'scarcity' refer to in economics?
What does the term 'scarcity' refer to in economics?
- The ability to produce goods efficiently
- The effective distribution of income
- An abundance of resources
- A situation where demand exceeds supply (correct)
Which of the following best defines 'opportunity cost'?
Which of the following best defines 'opportunity cost'?
- The total cost of producing a good
- The monetary value of a good in a market
- The cost of all resources spent on a product
- The loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen (correct)
What does the etymology of the word 'economics' suggest about its meaning?
What does the etymology of the word 'economics' suggest about its meaning?
How are resources typically allocated in most societies?
How are resources typically allocated in most societies?
Which factor of production does not include human effort?
Which factor of production does not include human effort?
What is the essential concept behind trade-offs in economics?
What is the essential concept behind trade-offs in economics?
What evidence indicates that economics intersects with other fields?
What evidence indicates that economics intersects with other fields?
How does a concentrated buyer structure influence the market?
How does a concentrated buyer structure influence the market?
What does high customer turnover indicate about a market?
What does high customer turnover indicate about a market?
How does product differentiation affect firm competition?
How does product differentiation affect firm competition?
In what way do input costs impact market dynamics?
In what way do input costs impact market dynamics?
What is the likely effect of having a large number of players in a market?
What is the likely effect of having a large number of players in a market?
Which scenario describes low product differentiation?
Which scenario describes low product differentiation?
What does the extent of product differentiation primarily affect?
What does the extent of product differentiation primarily affect?
Why might markets with low input costs experience more entrants?
Why might markets with low input costs experience more entrants?
What aspect does microeconomics primarily focus on?
What aspect does microeconomics primarily focus on?
Which of the following represents the highest level in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
Which of the following represents the highest level in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
According to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, when do individuals primarily pursue love and belongingness?
According to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, when do individuals primarily pursue love and belongingness?
What key concept does the study of economics fundamentally address?
What key concept does the study of economics fundamentally address?
Which term is associated with the motivation for personal growth and creativity in Maslow's theory?
Which term is associated with the motivation for personal growth and creativity in Maslow's theory?
What did Hesiod emphasize in his views on economics?
What did Hesiod emphasize in his views on economics?
What is the potential impact of a market with few players?
What is the potential impact of a market with few players?
What is a critical observation of the Hierarchy of Needs in terms of individual progression?
What is a critical observation of the Hierarchy of Needs in terms of individual progression?
How does high vertical integration affect competition in a market?
How does high vertical integration affect competition in a market?
What encompasses safety needs according to Maslow's Hierarchy?
What encompasses safety needs according to Maslow's Hierarchy?
What does a high market share of the largest firm indicate?
What does a high market share of the largest firm indicate?
What characterizes a natural monopoly?
What characterizes a natural monopoly?
What type of monopoly is created and owned by the government?
What type of monopoly is created and owned by the government?
Which of the following statements about monopolies is true?
Which of the following statements about monopolies is true?
What is a potential consequence of low vertical integration in a market?
What is a potential consequence of low vertical integration in a market?
What does a market structured as a monopoly often lead to?
What does a market structured as a monopoly often lead to?
What defines a Technological Monopoly?
What defines a Technological Monopoly?
Which of the following best describes Vertical Integration?
Which of the following best describes Vertical Integration?
What characterizes an Oligopoly?
What characterizes an Oligopoly?
What is a disadvantage of Oligopolies?
What is a disadvantage of Oligopolies?
How do Horizontal and Vertical Integration differ?
How do Horizontal and Vertical Integration differ?
What role do governments often play concerning Oligopolies?
What role do governments often play concerning Oligopolies?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a Geographic Monopoly?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a Geographic Monopoly?
What is a primary advantage of an Oligopoly?
What is a primary advantage of an Oligopoly?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Introduction to Economics
- Economics studies how to allocate limited resources to satisfy unlimited human wants, focusing on production, distribution, and consumption.
- Microeconomics analyzes individual and business choices, while macroeconomics evaluates overall economic behavior.
- Early economist Hesiod emphasized the importance of efficient allocation of labor, materials, and time to combat scarcity.
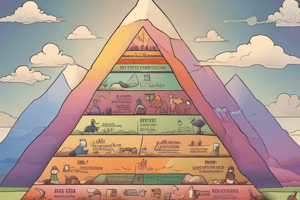
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Proposed by Abraham Maslow in 1943, this theory describes five tiers of human needs, depicted as a pyramid.
- Physiological Needs: Fundamental requirements like food, water, and rest; these must be met first.
- Safety Needs: Seek safety and security after physiological needs, encompassing health and financial stability.
- Love and Belongingness Needs: Focus on relationships, friendships, and community connections once safety is secured.
- Esteem Needs: Pursue self-esteem, confidence, and recognition following social belonging.
- Self-Actualization Needs: Highest level, focusing on personal growth and realizing one's potential, achieved after lower levels are satisfied.
Scarcity and Resource Management
- Scarcity occurs when demand exceeds supply, affecting the monetary value placed on goods and services.
- Economics examines decision-making of individuals, firms, and governments regarding resource allocation.
- "Oikonomia," the Greek origin of "economics," translates to household management, highlighting resource earnings and spending.
Trade-Offs and Opportunity Costs
- Trade-offs involve sacrificing one choice for another; understanding this is critical for optimal decision-making.
- Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when a decision is made.
Factors of Production
- Land: Encompasses all natural resources utilized for production, including real estate and raw materials.
- Labor: Represents human effort in producing goods and services, influenced by market structure.
- Customer Turnover: Indicates how often customers switch suppliers, reflecting competition and brand loyalty.
- Product Differentiation: Distinction between products impacts competition and pricing strategies.
- Costs of Inputs: Input prices influence production costs and market competition.
- Market Players: The number of firms affects competitive dynamics, categorizing markets into types like monopoly and perfect competition.
- Vertical Integration: Firms controlling multiple stages of production can achieve efficiencies or reduce competition.
- Largest Player's Market Share: High market share indicates concentration and often implies reduced competition.
Monopoly
- A monopoly is where a single seller dominates a market, restricting competition and consumer choice.
- Types of monopolies include:
- Natural Monopoly: One firm can supply at a lower cost due to high start-up costs, unfeasible for competition.
- Government Monopoly: Controlled by the government for essential services.
- Technological Monopoly: A company holds a patent for a method or process.
- Geographic Monopoly: Exists in specific areas with limited access to goods or services.
Integration Strategies
- Vertical Integration: Companies own various production stages, enhancing operations but requiring significant investment.
- Horizontal Integration: Firms acquire similar businesses at the same production level.
Oligopoly
- An oligopoly consists of a few firms controlling significant market share, allowing manipulation of production and pricing.
- Governments regulate oligopolies to prevent collusion and price-fixing; cartels may circumvent these laws.
- Advantages include limited competition, leading to higher profits for firms.
- Disadvantages include high barriers to entry, making it difficult for new companies to enter the market.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.