Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is cartilage?
What is cartilage?
- A firm, avascular, non-calcified connective tissue (correct)
- A type of nerve tissue
- A type of muscle tissue
- A fluid-filled sac
Where is cartilage found in the body?
Where is cartilage found in the body?
- On articular surfaces of free-moving joints (correct)
- Only in the brain
- In the heart
- In the stomach
What is the function of cartilage in the embryo/fetus?
What is the function of cartilage in the embryo/fetus?
- To filter waste
- To produce blood cells
- To form much of the temporary skeleton (correct)
- To digest food
What is the importance of the TMJ cartilage?
What is the importance of the TMJ cartilage?
What is the perichondrium?
What is the perichondrium?
What are the cells called that produce cartilage matrix?
What are the cells called that produce cartilage matrix?
What are mature cartilage cells called?
What are mature cartilage cells called?
What is the main component of the cartilage matrix?
What is the main component of the cartilage matrix?
What type of substance is the matrix?
What type of substance is the matrix?
Which of the following is a component of the cartilage matrix?
Which of the following is a component of the cartilage matrix?
How many main types of cartilage are there?
How many main types of cartilage are there?
Which of the following is a type of cartilage?
Which of the following is a type of cartilage?
What type of cartilage do all cartilages start as?
What type of cartilage do all cartilages start as?
Which type of cartilage is the principal type in the foetus?
Which type of cartilage is the principal type in the foetus?
Where is hyaline cartilage located?
Where is hyaline cartilage located?
Where are costal cartilages located?
Where are costal cartilages located?
What is a characteristic of fibrous cartilage?
What is a characteristic of fibrous cartilage?
Which of the following locations contains fibrous cartilage?
Which of the following locations contains fibrous cartilage?
What is special about elastic cartilage?
What is special about elastic cartilage?
Which of the following is made of elastic cartilage?
Which of the following is made of elastic cartilage?
Flashcards
What is cartilage?
What is cartilage?
A firm, avascular, non-calcified connective tissue that serves as a model for bones and allows joint flexibility.
Types of cartilage?
Types of cartilage?
Hyaline, fibrous, and elastic cartilage.
What is perichondrium?
What is perichondrium?
Provides cellular nutrition for cartilage.
What are chondroblasts?
What are chondroblasts?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are chondrocytes?
What are chondrocytes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hyaline cartilage?
What is hyaline cartilage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is fibrous cartilage?
What is fibrous cartilage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is elastic cartilage?
What is elastic cartilage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are costal cartilages?
What are costal cartilages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of airway cartilage?
What is the purpose of airway cartilage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Cartilage is being presented by Julie Watson
- The GDC learning outcomes include 1.1.5, 1.1.6 and 1.17
Learning Outcomes
- Describe composition and development of cartilage.
- Identify differences types of cartilage and where they are found.
- General function of cartilage types in the body.
- Prior human biology learning is expected.
General Info on Cartilage
- A firm, avascular, non-calcified connective tissue.
- Forms much of the temporary skeleton in the embryo / fetus.
- Frequently serves as a model or template for the bones of the skeleton.
- Present on articular surfaces of free-moving joints allowing for flexibility.
- The most important cartilage in the head and neck is the TMJ.
- Issues with the TMJ may have a significant impact, with patients presenting with limited opening and discomfort.
- Cartilage depends on surrounding connective tissue for cellular nutrition, called the perichondrium and described as a fibrous connective tissue sheath.
- Cartilage is made up of cells and a matrix which includes fibers / collagen/ intracellular substances
Matrix
- Ground substance.
- Highly hydrogenated gel composed of proteoglycan, chondronectin and water.
Fibres
- The type and number of fibers depends on the type of cartilage.
- Fibers can be up to 40% of the dry weight of cartilage, giving it strength.
Perichondrium
- Capsular sheath that surrounds cartilage.
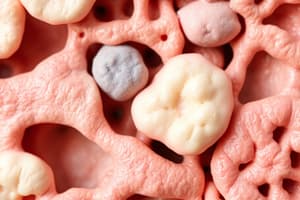
Chrondroblasts and Chondrocytes
- Immature cells, chondroblasts, produce cartilage matrix.
- Mature chondroblasts, chondrocytes, maintain the cartilage matrix.
Types of Cartilage
- Hyaline
- Fibrous
- Elastic
- All cartilage starts as Hyaline but then modifies according to need.
Hyaline Cartilage
- The principle type of cartilage, particularly in the fetus and infants.
- Characterized by small groups of chondrocyte cells
- The matrix is smooth and solid.
- Appears as a smooth bluish white, glassy tissue.
- It is not easily repaired following injury.
- Locations include articulating surfaces of bone, Costal cartilages attaching the ribs to the sternum and cartilages of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
Fibrous Cartilage
- Dense, tough, and slightly flexible tissue.
- Characterized by groups of chondrocytes separated from each other by thick bundles of collagen fibers.
- Collagen fibers are arranged predominantly in tight parallel bundles.
- Locations include: intervertebral discs, knee and jaw joints, surrounding the rim of the bony sockets of the hip and shoulder joints, and the pubic symphysis.
Elastic Cartilage
- Elastic fibers feature in the intracellular matrix.
- The least common type of cartilage tissue.
- Location: pinna of the ear, epiglottis and forming part of the tunica media of blood vessel walls.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.