Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following muscles does NOT directly contribute to the movement of the ribs during breathing?
Which of the following muscles does NOT directly contribute to the movement of the ribs during breathing?
- Internal Intercostal Muscles
- External Intercostal Muscles
- Innermost Intercostal Muscles
- Scalene Muscles (correct)
The innermost intercostal muscles run in the same direction as the external intercostal muscles.
The innermost intercostal muscles run in the same direction as the external intercostal muscles.
False (B)
What is the primary function of the intercostal muscles?
What is the primary function of the intercostal muscles?
To form a pressure barrel, resisting pressure changes in the thorax.
The ______ movement of the thoracic cage refers to the ribs being lifted laterally, increasing the lateral dimension of the thorax.
The ______ movement of the thoracic cage refers to the ribs being lifted laterally, increasing the lateral dimension of the thorax.
Match the following terms with their corresponding descriptions:
Match the following terms with their corresponding descriptions:
Study Notes
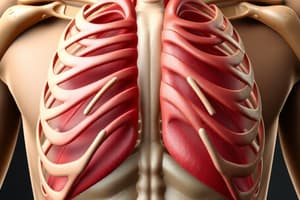
Intercostal Muscles
- Intercostal muscles are located between the ribs.
- Three layers exist: external, internal, and innermost intercostal muscles.
- These layers correspond to the three layers of muscles in the abdominal wall.
- External intercostal muscles run antero-inferiorly between the ribs, aiding in rib elevation (inspiration).
- Internal intercostal muscles run postero-inferiorly, aiding in rib depression (expiration).
- Innermost intercostal muscles are deep to the internal intercostals and run in the same direction.
- Often considered part of the internal intercostal layer.
Movements of the Thoracic Cage
- Pump handle movement: The sternum elevates superiorly and anteriorly, increasing the anteroposterior dimension of the thorax.
- Bucket handle movement: The ribs are lifted laterally, increasing the lateral dimension of the thorax.
- These movements combine to increase thoracic volume, facilitating inhalation.
- Intercostal muscles assist the diaphragm in breathing.
Function of Intercostal Muscles
- The primary function of intercostal muscles is to form a pressure barrel, resisting shifts in thoracic pressure.
- This allows for efficient and effective changes in thoracic volume during breathing.
- Intercostal muscles are innervated by intercostal nerves originating from the spinal cord.
- Intercostal nerve injury can cause intercostal muscle paralysis, impairing breathing.
Accessory Muscles of Inspiration
- Accessory muscles of inspiration attach to the ribs, but typically don't directly move them.
- They are recruited during strenuous breathing to assist in rib movement.
- Examples include the scalene muscles, sternocleidomastoid, and pectoralis minor.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.