Podcast
Questions and Answers
Explain the difference between direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IDIFA) in terms of the steps involved in the assay.
Explain the difference between direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IDIFA) in terms of the steps involved in the assay.
DIF involves a single step where a labeled primary antibody directly binds to the antigen in the sample. IDIFA, on the other hand, involves two steps: first, the unlabeled primary antibody binds to the antigen, and then a labeled secondary antibody binds to the primary antibody.
What is the primary purpose of using DIF in a diagnostic setting?
What is the primary purpose of using DIF in a diagnostic setting?
DIF is used to directly identify antigens present in a sample, such as tissue or cells.
Explain one advantage of using IDIFA over DIF regarding sensitivity and provide a reason for this advantage.
Explain one advantage of using IDIFA over DIF regarding sensitivity and provide a reason for this advantage.
IDIFA is generally more sensitive than DIF due to signal amplification. This is because multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody, resulting in a stronger fluorescent signal.
Describe a practical application of IDIFA in a diagnostic setting.
Describe a practical application of IDIFA in a diagnostic setting.
Compare DIF and IDIFA in terms of their time requirements and cost effectiveness.
Compare DIF and IDIFA in terms of their time requirements and cost effectiveness.
What is the basic principle behind Immunofluorescence (IF) and how does it work in detecting specific antigens or antibodies?
What is the basic principle behind Immunofluorescence (IF) and how does it work in detecting specific antigens or antibodies?
Explain the difference between Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) and Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IDIFA).
Explain the difference between Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) and Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IDIFA).
Why are Viral Plaques sometimes visualized using Immunofluorescence?
Why are Viral Plaques sometimes visualized using Immunofluorescence?
Describe the steps involved in performing a Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) assay.
Describe the steps involved in performing a Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) assay.
In the context of Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IDIFA), what does a 'positive reaction' indicate?
In the context of Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IDIFA), what does a 'positive reaction' indicate?
What type of light source is typically used to excite the fluorescent dyes in immunofluorescence techniques?
What type of light source is typically used to excite the fluorescent dyes in immunofluorescence techniques?
List two common fluorescent dyes used in Immunofluorescence and the color of light they emit.
List two common fluorescent dyes used in Immunofluorescence and the color of light they emit.
Explain why Immunofluorescence techniques are considered beneficial for visualizing specific antigens or antibodies.
Explain why Immunofluorescence techniques are considered beneficial for visualizing specific antigens or antibodies.
Flashcards
Immunofluorescence (IF)
Immunofluorescence (IF)
A technique that visualizes antigens using fluorescently labeled antibodies.
Fluorescent Dyes
Fluorescent Dyes
Substances that absorb UV light and emit visible fluorescence.
Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF)
Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF)
A technique that detects specific antigens using a single fluorescently labeled antibody.
Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IDIFA)
Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IDIFA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sample Preparation in DIF
Sample Preparation in DIF
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antigen Coating in IDIFA
Antigen Coating in IDIFA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluorescence Detection
Fluorescence Detection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Viral Plaque Visualization
Viral Plaque Visualization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specificity in DIF
Specificity in DIF
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensitivity in IDIFA
Sensitivity in IDIFA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Applications of DIF and IDIFA
Applications of DIF and IDIFA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Immunofluorescence
- Immunofluorescence is a technique visualizing specific antigens using antibodies chemically linked to fluorescent dyes.
- Fluorochromes are dyes absorbing short UV wavelengths and emitting longer wavelengths (e.g., visible green).
- Examples include fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) emitting green light and tetramethylrhodamine emitting red light.
- This helps visualize viral plaques for better observation.
Principle of Immunofluorescence (IF)
- IF is based on the specific antigen-antibody interaction.
- A labeled antibody binds to the specific antigen.
- Exposure to UV light causes the fluorescent dye to emit visible light, allowing visualization of the complex.
Requirements for Immunofluorescence
- A microscope with the capability to detect fluorescence
- A slide
- Fluorescently labeled antibodies
- Specimens
Methods of IF Assays
-
Direct IF Assay (DIFA):
- One step where a primary antibody labeled with a fluorochrome directly binds to the target antigen.
- A simple method to detect specific antigens.
- Requires a primary antibody with a built-in fluorochrome.
-
Indirect IF Assay (IDIFA):
- Two-step procedure.
- A primary Antibody first binds to the antigen.
- A secondary antibody (also fluorochrome-labelled) binds to the primary antibody, amplifying the signal.
- More versatile as different primary antibodies can match with the same fluorochrome-labelled secondary antibody.
- Provides higher sensitivity due to signal amplification.
Results of Immunofluorescence
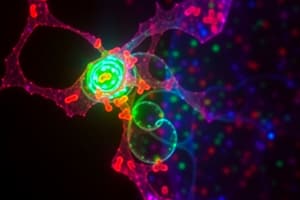
- A confocal image showing phosphorylated AKT (green) in adenovirus infected cardiomyocytes is one result.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.