Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where does the oxygen molecule enter the liquid phase?
Where does the oxygen molecule enter the liquid phase?
- In the epithelial cells
- In the connective tissue
- In the thin layer of fluid that coats the inside of the alveolus (correct)
- In the capillary
What is the purpose of the base membrane?
What is the purpose of the base membrane?
- To filter out oxygen molecules
- To separate the alveolus from the capillary
- To offer structural support to the lungs (correct)
- To prevent gas exchange
What is the shape of the epithelial cells?
What is the shape of the epithelial cells?
- Pancake-shaped (correct)
- Cubical
- Cylindrical
- Spherical
Where is the cardiac notch located?
Where is the cardiac notch located?
What is the function of the alveolus?
What is the function of the alveolus?
How many layers does the oxygen molecule need to pass through to reach the capillary?
How many layers does the oxygen molecule need to pass through to reach the capillary?
What is the term for the passage of oxygen from the alveolus to the capillary?
What is the term for the passage of oxygen from the alveolus to the capillary?
Where does the oxygen molecule finally enter?
Where does the oxygen molecule finally enter?
What is the shape of the cells that make up the walls of the capillary?
What is the shape of the cells that make up the walls of the capillary?
What carries oxygen molecules in the red blood cells?
What carries oxygen molecules in the red blood cells?
What is the function of the basement membrane and connective tissue?
What is the function of the basement membrane and connective tissue?
What is the primary component of the liquid layers in the rectangular cube model?
What is the primary component of the liquid layers in the rectangular cube model?
What does the first part of the alveolar gas equation represent?
What does the first part of the alveolar gas equation represent?
How many oxygen molecules can bind to one hemoglobin protein?
How many oxygen molecules can bind to one hemoglobin protein?
What is the purpose of the second equation discussed in the content?
What is the purpose of the second equation discussed in the content?
What is P1 in the context of the two equations?
What is P1 in the context of the two equations?
What is the term for the equation that relates to the gas exchange in the alveolus?
What is the term for the equation that relates to the gas exchange in the alveolus?
What might cause an increase in the amount of oxygen diffusing from the alveolus to the red blood cells?
What might cause an increase in the amount of oxygen diffusing from the alveolus to the red blood cells?
What is the function of the epithelial cells in the rectangular cube model?
What is the function of the epithelial cells in the rectangular cube model?
Why might a person at a higher altitude have an abnormal amount of oxygen diffusing over time?
Why might a person at a higher altitude have an abnormal amount of oxygen diffusing over time?
What is the term for the liquid layer that lines the inside of the alveolus?
What is the term for the liquid layer that lines the inside of the alveolus?
What is a possible reason for a decrease in the surface area available for gas exchange?
What is a possible reason for a decrease in the surface area available for gas exchange?
What is the primary function of the oxygen molecule in the rectangular cube model?
What is the primary function of the oxygen molecule in the rectangular cube model?
What is the shape of the rectangular cube model?
What is the shape of the rectangular cube model?
What is the term for the process of oxygen moving from the alveolus to the red blood cells?
What is the term for the process of oxygen moving from the alveolus to the red blood cells?
What is the unit of measurement for P1?
What is the unit of measurement for P1?
What is the term for the amount of oxygen that is delivered to the red blood cells?
What is the term for the amount of oxygen that is delivered to the red blood cells?
Why is thickness an important factor to consider in gas exchange?
Why is thickness an important factor to consider in gas exchange?
What may increase the thickness of the layer where oxygen diffusion takes place?
What may increase the thickness of the layer where oxygen diffusion takes place?
Why is the diffusion coefficient of oxygen in water at a certain body temperature relatively stable?
Why is the diffusion coefficient of oxygen in water at a certain body temperature relatively stable?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen that was returning from the body referred to as?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen that was returning from the body referred to as?
If an abnormal amount of oxygen is diffusing over time, what should you do?
If an abnormal amount of oxygen is diffusing over time, what should you do?
Why is it unlikely that the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood is the cause of an abnormal amount of oxygen diffusing over time?
Why is it unlikely that the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood is the cause of an abnormal amount of oxygen diffusing over time?
What is the purpose of considering the formulas that affect oxygen diffusion?
What is the purpose of considering the formulas that affect oxygen diffusion?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Respiratory System
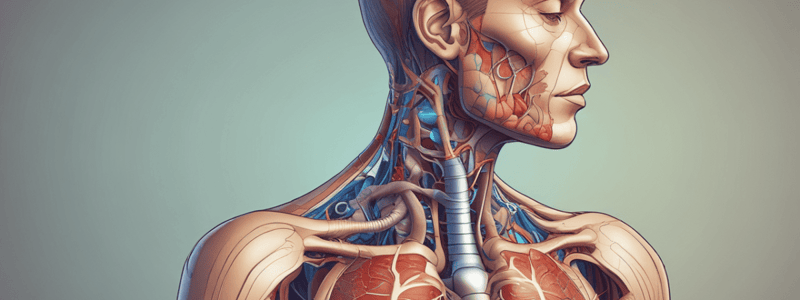
- Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose and passes through the trachea, which splits into two bronchi, one for each lung.
- The left lung has a cardiac notch, a depression that allows space for the heart, whereas the right lung does not have this notch.
Alveoli and Gas Exchange
- Alveoli are the smallest functional units of the lung, responsible for gas exchange.
- There are millions of alveoli in the lungs.
- Oxygen molecules diffuse from the alveolus into the blood through several layers: liquid lining the alveolus, epithelial cells, basement membrane, connective tissue, endothelial cells, and plasma.
Layers of the Alveolus
- Liquid lining the alveolus: a thin layer of fluid that coats the inside of the alveolus.
- Epithelial cells: flat, pancake-shaped cells that make up the walls of the alveolus.
- Basement membrane: a layer that offers structural support to the lungs.
- Connective tissue: a layer that provides additional structural support and contains proteins.
- Endothelial cells: flat, pancake-shaped cells that make up the walls of the capillary.
- Plasma: a liquid layer that carries oxygen molecules into the red blood cell.
Oxygen Binding to Hemoglobin
- Oxygen molecules bind to hemoglobin in the red blood cell.
- Hemoglobin has four binding sites for oxygen molecules.
- Once oxygen binds to hemoglobin, the red blood cell carries oxygen to the rest of the body.
Visualizing the Journey of Oxygen
- Imagine a rectangular cube with different layers, starting from the alveolus (gas phase) and ending at the red blood cell (liquid phase).
- The oxygen molecule must pass through several layers of liquid to reach the red blood cell.
- This process can be divided into two categories: gas and liquid.
Equations and Oxygen Diffusion
- The alveolar gas equation calculates the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveolus.
- Fick's law of diffusion calculates the amount of oxygen diffusing over time.
- Factors affecting oxygen diffusion include:
- Gradient of partial pressures (P1 - P2)
- Surface area (e.g., number of functional alveoli)
- Thickness of the layers (e.g., increased fluid in connective tissue)
- Diffusion coefficient (stable in oxygen within water at body temperature)
Troubleshooting Abnormal Oxygen Diffusion
- If the amount of oxygen diffusing over time is abnormal, consider the following factors:
- Partial pressure of oxygen in the alveolus (P1)
- Surface area (e.g., number of functional alveoli)
- Thickness of the layers (e.g., increased fluid in connective tissue)
- Other factors affecting oxygen diffusion (e.g., Fi O2, altitude, respiratory quotient)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.