Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the urinary bladder?
What is the primary function of the urinary bladder?
- Transmits urine from the kidney
- Stores urine (correct)
- Filters waste from blood
- Carries urine to the urethra
Which of the following correctly describes the male urethra?
Which of the following correctly describes the male urethra?
- Short and wide (correct)
- Long and wide
- Thin and lengthy
- Short and narrow
What is the primary function of the testis in the male genital system?
What is the primary function of the testis in the male genital system?
- Secretion of seminal fluid
- Storage of sperms
- Production of testosterone only
- Formation of sperms and hormone secretion (correct)
What is the role of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
Which structure in the male genital system is directly responsible for carrying sperm to the urethra?
Which structure in the male genital system is directly responsible for carrying sperm to the urethra?
What is the primary function of the prostate gland?
What is the primary function of the prostate gland?
Where does fertilization of an ovum by a spermatozoon occur?
Where does fertilization of an ovum by a spermatozoon occur?
What is the length of the uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes)?
What is the length of the uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes)?
Which gland produces a nutritive substance rich in protein, fructose, and vitamin C for sperm?
Which gland produces a nutritive substance rich in protein, fructose, and vitamin C for sperm?
What is the main function of the bulbourethral gland?
What is the main function of the bulbourethral gland?
What is the primary function of ovaries in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary function of ovaries in the female reproductive system?
In which structure is the urine stored in the body?
In which structure is the urine stored in the body?
What is the primary function of the pituitary gland?
What is the primary function of the pituitary gland?
Which hormone is secreted by the thyroid gland?
Which hormone is secreted by the thyroid gland?
Which gland secretes parathyroid hormone?
Which gland secretes parathyroid hormone?
What substances do the adrenal cortex produce?
What substances do the adrenal cortex produce?
What is the main function of insulin?
What is the main function of insulin?
What hormone is secreted by the ovaries?
What hormone is secreted by the ovaries?
Which cranial nerve is classified as a sensory nerve?
Which cranial nerve is classified as a sensory nerve?
Where is Broca’s motor area for speech located?
Where is Broca’s motor area for speech located?
Which of the following correctly matches the hypoglossal nerve?
Which of the following correctly matches the hypoglossal nerve?
Which gland is often referred to as the master gland of the endocrine system?
Which gland is often referred to as the master gland of the endocrine system?
What are the two main components of the digestive system?
What are the two main components of the digestive system?
Which part of the digestive system is involved in the mixing of food with saliva?
Which part of the digestive system is involved in the mixing of food with saliva?
Which area of the pharynx is located behind the nasal cavity?
Which area of the pharynx is located behind the nasal cavity?
What are the two sets of teeth called?
What are the two sets of teeth called?
Which of the following parts is not a component of the digestive tract?
Which of the following parts is not a component of the digestive tract?
What organ is primarily involved in bile production?
What organ is primarily involved in bile production?
What is the function of the laryngopharynx?
What is the function of the laryngopharynx?
Which structure is located behind the larynx?
Which structure is located behind the larynx?
Flashcards
Ureter
Ureter
Tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
Urinary bladder
Urinary bladder
A hollow muscular organ located in the pelvis that stores urine before it is excreted.
Urethra
Urethra
A tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Testis
Testis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicle
Seminal Vesicle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Gland
Bulbourethral Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovary
Ovary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian Tube (Uterine Tube)
Fallopian Tube (Uterine Tube)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus
Uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagina
Vagina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Pituitary Gland?
What is the Pituitary Gland?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Thyroid Gland?
What is the Thyroid Gland?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the Parathyroid Glands?
What are the Parathyroid Glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the Adrenal Glands?
What are the Adrenal Glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Pancreas's endocrine function?
What is the Pancreas's endocrine function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the endocrine function of Gonads?
What is the endocrine function of Gonads?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the parts of the Brain Stem?
What are the parts of the Brain Stem?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is Broca's area located?
Where is Broca's area located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which cranial nerve is associated with the sense of smell?
Which cranial nerve is associated with the sense of smell?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the pharynx?
What is the pharynx?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the tongue?
What is the tongue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the digestive system?
What is the digestive system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the digestive tract?
What is the digestive tract?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are digestive glands?
What are digestive glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is digestion?
What is digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the biliary system?
What is the biliary system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the pancreas?
What is the pancreas?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Urogenital System - BMS 101
- Students should be able to describe parts and functions of the urinary system, components of the male genital system, and components of the female genital system by the end of the lecture.
Urinary System
- Composed of kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra.
- The kidney is bean-shaped and located in the upper posterior abdominal wall.
- It has anterior and posterior surfaces, lateral and medial borders, and upper and lower poles.
- The hilum of the kidney is a part of the medial border containing the renal vein, renal artery, and the pelvis of the ureter.
- The ureter is a 25 cm muscular tube.
- It transports urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
- It has abdominal and pelvic parts.
- The urinary bladder is located within the pelvis.
- It receives the ureters and stores urine.
- Urine exits through the urethra.
- The urethra carries urine outside the body.
- The female urethra is short and wide (4 cm long).
- The male urethra is longer (20 cm long) and has 3 parts: prostatic, membranous, and penile/spongy.
Male Genital System
- Composed of testes, genital ducts, accessory sex glands, and penis.
- Testes are the primary male sex organs, located within the scrotum.
- They produce sperm formation and male sex hormones.
- Genital ducts: epididymis, vas deferens, and urethra
- Epididymis: stores and matures sperm, and secretes a nutritive substance for sperm.
- Vas deferens: transports sperm to the urethra.
- Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands
- Produce substances that nourish sperm.
- Penis: carries urine and semen outside the body.
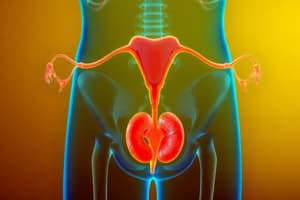
Female Genital System
- The female genital system consists of ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina
- Ovaries are primary reproductive organs; located in the lateral wall of the pelvis.
- Produce ova (egg cells) and female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
- Uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes): 10 cm long
- Receive the ovum, provide a passage for sperm, and fertilization occurs within them.
- Uterus: hollow, pear-shaped muscular organ
- Receives the fertilized ovum, provides nutrition, and is the site of the menstrual cycle.
- Vagina: muscular tube
- Passage for menstrual blood and childbirth.
Nervous System - Endocrine Glands
- The nervous system is divided into central and peripheral systems.
- The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
- The peripheral nervous system includes spinal nerves and cranial nerves (12 pairs)
- The endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Brain
- The brain lies inside the skull.
- The brain has three main parts: cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum.
Cerebrum
- Formed of two cerebral hemispheres
- Each cerebral hemisphere is formed of 4 lobes, frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
Brain Stem
- Formed of three parts: midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; Located beneath the brain
- Involved in basic bodily functions.
Cerebellum
- Two cerebellar hemispheres separated by the vermis
- Plays a role in motor control and balance.
Spinal Cord
- About 45cm long, located within the vertebral canal.
- 31 segments; 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal.
Spinal Nerves
- 31 pairs in the peripheral nervous system
- Formed of 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal nerves.
Cranial Nerves
- 12 pairs connected to the brain.
Endocrine Glands
- Ductless glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Examples include pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, suprarenal, and pancreas, and gonads.
Digestive System
- The digestive system comprises digestive tract and digestive glands. The tract includes mouth cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The glands include salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
Digestive Glands
- Salivary Glands (pairs): Parotid, Sublingual, Submandibular. -Produce saliva to aid in food digestion
- Liver: Largest organ in the body in the abdominal cavity’s upper right quadrant.
- Produces bile (aids in fat digestion).
- Pancreas: Located behind the stomach, part of the digestive tract.
- Produces pancreatic juice containing enzymes for complete food digestion.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.