Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is reproduction?
What is reproduction?
Reproduction is a biological process in which an organism produces offspring that are genetically similar to itself.
What are the two types of reproduction?
What are the two types of reproduction?
- Asexual Reproduction (correct)
- Binary Fission
- Fragmentation
- Sexual Reproduction (correct)
What is asexual reproduction?
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a process in which a single parent generates offspring without the need for gametes.
What is binary fission?
What is binary fission?
Give an example of an organism that reproduces by binary fission.
Give an example of an organism that reproduces by binary fission.
What is budding?
What is budding?
What is fragmentation?
What is fragmentation?
What is reproduction?
What is reproduction?
What are the two types of reproduction?
What are the two types of reproduction?
What is asexual reproduction?
What is asexual reproduction?
What is binary fission?
What is binary fission?
Give an example of an organism that reproduces by binary fission.
Give an example of an organism that reproduces by binary fission.
What is budding?
What is budding?
Which of the following methods is NOT a type of asexual reproduction?
Which of the following methods is NOT a type of asexual reproduction?
What is the main benefit of asexual reproduction?
What is the main benefit of asexual reproduction?
What can be a drawback of asexual reproduction?
What can be a drawback of asexual reproduction?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
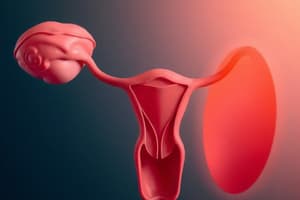
Overview of Human Reproduction
- Human reproduction begins with fertilization, forming a zygote from the union of male and female reproductive cells.
- The zygote undergoes cell division and differentiation, progressing through developmental stages to become an embryo and ultimately a fetus.
- The process is regulated by intricate reproductive systems and hormones in both genders.
- Social, ethical, and cultural factors also influence reproduction, including family planning and access to reproductive healthcare.
- Advances such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and genetic screening have reshaped reproductive choices, creating new opportunities and challenges.
- A comprehensive understanding of human reproduction is essential for enhancing reproductive health and addressing ethical dilemmas.
Definition of Reproduction
- Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce genetically similar offspring, ensuring the survival of species across generations.
Types of Reproduction
- Two primary types of reproduction exist: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
- Involves a single parent producing offspring without gametes, leading to genetically identical offspring.
- Common in plants, fungi, bacteria, and certain invertebrates, it allows rapid population growth without needing a mate.
- The lack of genetic diversity in offspring can increase susceptibility to diseases and resource limitations.
Methods of Asexual Reproduction
-
Binary Fission:
- A prevalent method in bacteria and single-celled organisms.
- Involves a single cell splitting into two genetically identical daughter cells.
- Example: Escherichia coli bacteria divide into two identical cells, each containing the original genetic material.
-
Budding:
- Observed in yeast and specific invertebrates, where a new organism forms as an outgrowth from the parent and detaches to function independently.
-
Fragmentation:
- A process seen in starfish and certain plants where the parent organism breaks into fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual.
Overview of Human Reproduction
- Human reproduction begins with fertilization, forming a zygote from the union of male and female reproductive cells.
- The zygote undergoes cell division and differentiation, progressing through developmental stages to become an embryo and ultimately a fetus.
- The process is regulated by intricate reproductive systems and hormones in both genders.
- Social, ethical, and cultural factors also influence reproduction, including family planning and access to reproductive healthcare.
- Advances such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and genetic screening have reshaped reproductive choices, creating new opportunities and challenges.
- A comprehensive understanding of human reproduction is essential for enhancing reproductive health and addressing ethical dilemmas.
Definition of Reproduction
- Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce genetically similar offspring, ensuring the survival of species across generations.
Types of Reproduction
- Two primary types of reproduction exist: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
- Involves a single parent producing offspring without gametes, leading to genetically identical offspring.
- Common in plants, fungi, bacteria, and certain invertebrates, it allows rapid population growth without needing a mate.
- The lack of genetic diversity in offspring can increase susceptibility to diseases and resource limitations.
Methods of Asexual Reproduction
-
Binary Fission:
- A prevalent method in bacteria and single-celled organisms.
- Involves a single cell splitting into two genetically identical daughter cells.
- Example: Escherichia coli bacteria divide into two identical cells, each containing the original genetic material.
-
Budding:
- Observed in yeast and specific invertebrates, where a new organism forms as an outgrowth from the parent and detaches to function independently.
-
Fragmentation:
- A process seen in starfish and certain plants where the parent organism breaks into fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.