Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the kidney?
What is the primary function of the kidney?
- To maintain the correct level of water and electrolytes in the blood (correct)
- To regulate body temperature
- To produce hormones and other essential biomolecules
- To store food and nutrients
Where are the kidneys located in the human body?
Where are the kidneys located in the human body?
- In the abdominal cavity
- Behind the liver and closer to the back (correct)
- On either side of the heart
- In the pelvic region
What is the outer part of the kidney called?
What is the outer part of the kidney called?
- Renal cortex (correct)
- Nephron
- Kidney capsule
- Renal medulla
What is the term for the functional units within the kidney?
What is the term for the functional units within the kidney?
What is the middle part of the kidney called?
What is the middle part of the kidney called?
How many kidneys do most humans have?
How many kidneys do most humans have?
What is another important function of the kidney besides excreting waste?
What is another important function of the kidney besides excreting waste?
What is the prefix 'renal' related to?
What is the prefix 'renal' related to?
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
What is the main function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
What is the main function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
What is the term for the direction of blood flow in the afferent arteriole?
What is the term for the direction of blood flow in the afferent arteriole?
What is the name of the space where the filtered fluid collects in the nephron?
What is the name of the space where the filtered fluid collects in the nephron?
What is the approximate number of nephrons in a typical kidney?
What is the approximate number of nephrons in a typical kidney?
What is the percentage of fluid that gets squeezed out as filtrate?
What is the percentage of fluid that gets squeezed out as filtrate?
What type of blood is present in the afferent arteriole?
What type of blood is present in the afferent arteriole?
What is the function of the podocytes in the glomerulus?
What is the function of the podocytes in the glomerulus?
What type of molecules get filtered into the Bowman's capsule?
What type of molecules get filtered into the Bowman's capsule?
What is the name of the structure where the filtrate is formed?
What is the name of the structure where the filtrate is formed?
What is the name of the structure that surrounds the glomerulus?
What is the name of the structure that surrounds the glomerulus?
What happens to the fluid that is filtered out of the blood in the glomerulus?
What happens to the fluid that is filtered out of the blood in the glomerulus?
What is the purpose of the proximal tubule?
What is the purpose of the proximal tubule?
What is the name of the type of tube that the filtrate passes through after the Bowman's capsule?
What is the name of the type of tube that the filtrate passes through after the Bowman's capsule?
Why is the glomerulus able to filter out waste and excess fluids from the blood?
Why is the glomerulus able to filter out waste and excess fluids from the blood?
What is the term for the process of reabsorbing substances back into the blood?
What is the term for the process of reabsorbing substances back into the blood?
What type of energy is used to pump out sodium in the proximal tubule?
What type of energy is used to pump out sodium in the proximal tubule?
What is the name of the cell type that lines the inside of the Bowman's capsule?
What is the name of the cell type that lines the inside of the Bowman's capsule?
What is the term for the fluid that forms in the Bowman's capsule?
What is the term for the fluid that forms in the Bowman's capsule?
What is the location of the Bowman's capsule in the nephron?
What is the location of the Bowman's capsule in the nephron?
What is the primary function of the proximal tubule?
What is the primary function of the proximal tubule?
What is the function of the capillary system located near the proximal tubule?
What is the function of the capillary system located near the proximal tubule?
What is the main reason for reabsorbing sodium and glucose in the proximal tubule?
What is the main reason for reabsorbing sodium and glucose in the proximal tubule?
What is the function of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
What is the function of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
Why does the ascending part of the loop of Henle pump out salts?
Why does the ascending part of the loop of Henle pump out salts?
What happens to water as it flows down the descending part of the loop of Henle?
What happens to water as it flows down the descending part of the loop of Henle?
Why can't biological systems use ATP to actively pump out water?
Why can't biological systems use ATP to actively pump out water?
What is the result of the loop of Henle making the renal medulla salty?
What is the result of the loop of Henle making the renal medulla salty?
What is the significance of the loop of Henle in water reabsorption?
What is the significance of the loop of Henle in water reabsorption?
What is the location of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
What is the location of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
What is the main purpose of the loop of Henle?
What is the main purpose of the loop of Henle?
What happens to the filtrate in the distal convoluted tubule?
What happens to the filtrate in the distal convoluted tubule?
What is the function of the collecting duct?
What is the function of the collecting duct?
What happens when the collecting duct passes through the medulla?
What happens when the collecting duct passes through the medulla?
What hormone regulates the permeability of the collecting duct?
What hormone regulates the permeability of the collecting duct?
What is the final product of the nephron?
What is the final product of the nephron?
What is the term for the process of reabsorbing essential nutrients back into the bloodstream?
What is the term for the process of reabsorbing essential nutrients back into the bloodstream?
Why does the filtrate become more concentrated in the collecting duct?
Why does the filtrate become more concentrated in the collecting duct?
What is the name of the part of the nephron where the filtrate first enters?
What is the name of the part of the nephron where the filtrate first enters?
What is the significance of the distal convoluted tubule's proximity to the Bowman's capsule?
What is the significance of the distal convoluted tubule's proximity to the Bowman's capsule?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
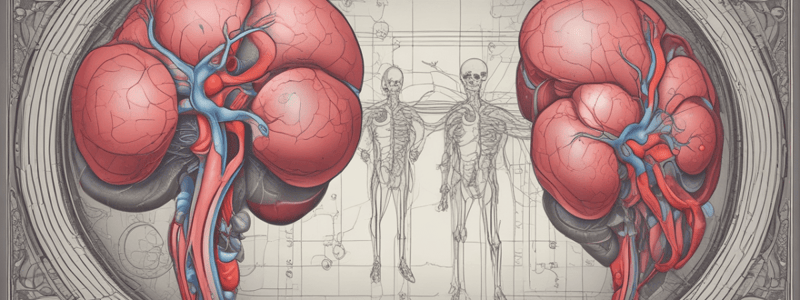
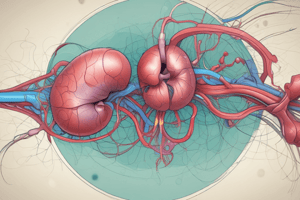
Kidney Overview
- The kidney is an organ that helps excrete waste, maintain water levels, and regulate electrolytes and blood pressure.
- It also produces hormones and maintains overall bodily functions.
- Each person has two kidneys, located near the spine, behind the liver.
Kidney Structure
- The kidney has two main parts: the renal cortex (outer layer) and the renal medulla (middle layer).
- The renal cortex is the outer layer, and the renal medulla is the middle layer.
Nephron Function
- The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron.
- Each kidney has approximately one million nephrons.
- The nephron filters blood and regulates water levels in the body.
Blood Flow in the Nephron
- Blood enters the nephron through an afferent arteriole.
- It then flows into the glomerulus, a porous structure that filters fluid and small molecules from the blood.
- The filtered fluid, called filtrate, enters the Bowman's space.
- The remaining blood leaves the glomerulus through an efferent arteriole.
Filtrate Formation
- The filtrate is formed when fluid and small molecules are filtered out of the blood in the glomerulus.
- This process is aided by podocytes, specialized cells that line the Bowman's capsule.
- The filtrate contains small ions, glucose, and amino acids.
Proximal Tubule
- The filtrate enters the proximal tubule, a winding tube that reabsorbs necessary substances back into the blood.
- The proximal tubule has a convoluted part and a straight part.
- Cells lining the proximal tubule actively reabsorb substances like glucose, sodium, and amino acids using ATP.
Loop of Henle
- The filtrate then enters the loop of Henle, a U-shaped tube that dips into the renal medulla.
- The loop of Henle is responsible for reabsorbing water and making the medulla salty.
- The ascending part of the loop of Henle actively pumps out salts, making the medulla hypertonic.
- The descending part of the loop of Henle is permeable only to water, which leaves the filtrate due to osmosis.
Distal Convoluted Tubule
- The filtrate then enters the distal convoluted tubule, where more reabsorption occurs.
- Calcium and sodium are reabsorbed, and more water is removed from the filtrate.
Collecting Duct
- The processed filtrate enters the collecting duct, where it becomes concentrated urine.
- The collecting duct passes through the renal medulla again, where anti-diuretic hormone can control water reabsorption, making the urine even more concentrated.
- The urine then leaves the kidney and enters the ureters, eventually reaching the urinary bladder.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.