Podcast
Questions and Answers
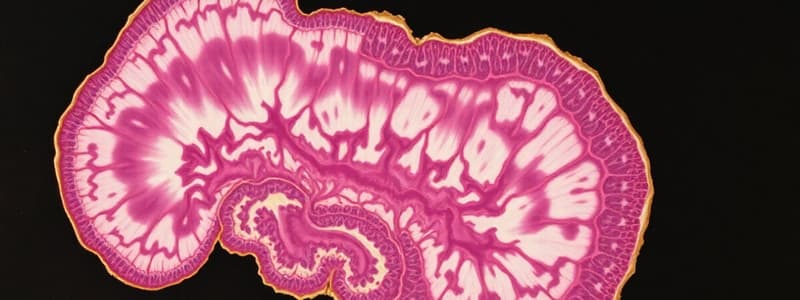
What is histology?
What is histology?
The study of the microscopic structure of tissues.
Which of the following are types of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following are types of epithelial tissue?
- Simple
- Stratified
- Pseudostratified
- All of the above (correct)
Connective tissue provides ______, stores energy, and transports materials.
Connective tissue provides ______, stores energy, and transports materials.
support
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Pathological histology examines healthy tissue.
Pathological histology examines healthy tissue.
What are the components of nervous tissue?
What are the components of nervous tissue?
The function of dendrites is to receive ______ from other neurons.
The function of dendrites is to receive ______ from other neurons.
What is the primary function of neurons?
What is the primary function of neurons?
Neuroglia transmit electrical impulses.
Neuroglia transmit electrical impulses.
What is the role of oligodendrocytes?
What is the role of oligodendrocytes?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Introduction to Histology
- Histology is the study of microscopic tissue structure, providing insights into cell and tissue functions and pathology.
- Crucial for diagnosing diseases by identifying normal tissue architecture and abnormalities, such as inflammation or cancer.
Types of Tissues
-
Epithelial Tissue:
- Types include Simple, Stratified, Pseudostratified, and Transitional.
- Functions: Protection, Secretion, Absorption, and Filtration.
-
Connective Tissue:
- Types include Loose, Dense, Cartilage, Bone, and Blood.
- Functions: Provides support, stores energy, and transports materials (e.g., vitamins and minerals).
-
Muscle Tissue:
- Types include Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth.
- Functions: Responsible for Movement, Posture, and Heat production.
-
Nervous Tissue:
- Composed of Neurons and Neuroglia; coordinates and controls body activities.
Branches of Histology
- General Histology: Study of the structure and function of tissues.
- Special Histology: Focuses on microscopic structures of organs (e.g., heart, digestive system).
- Pathological Histology: Examines diseased tissues.
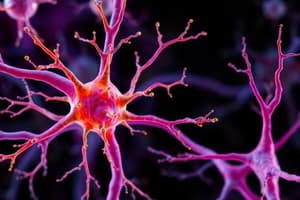
Nervous Tissue Components
- Neurons: Primary functional units that transmit electrical signals and process information.
- Neuroglia (Glial Cells): Supportive cells that maintain the neuronal environment, providing protection and nutrients.
Neuron Structures and Functions
- Dendrites: Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon: Long projection that transmits impulses away from the neuron to other neurons or effector cells.
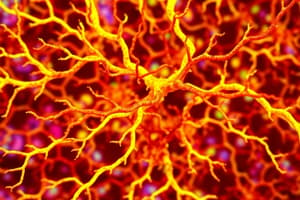
Types of Neuroglia and Their Functions
-
Astrocytes:
- Provide structural support, regulate blood flow, maintain the blood-brain barrier, and support the chemical environment for neurons.
-
Oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwann Cells (PNS):
- Produce myelin sheath, insulating axons and enhancing signal transmission speed.
-
Microglia:
- Act as the immune cells of the central nervous system, protecting against pathogens and debris.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.