Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the primary excretory role of the lungs?
Which of the following is the primary excretory role of the lungs?
- Excreting excess mineral salts
- Producing bile pigments
- Removing carbon dioxide and water vapor (correct)
- Removing urea from the blood
What substances are excreted by the skin?
What substances are excreted by the skin?
- Carbon dioxide and water vapor
- Urea and bile pigments
- Mineral salts and water (correct)
- Excess amino acids
Which organ is responsible for forming urea through the deamination of excess amino acids?
Which organ is responsible for forming urea through the deamination of excess amino acids?
- Liver (correct)
- Lungs
- Kidneys
- Skin
What role does the alimentary canal play in excretion?
What role does the alimentary canal play in excretion?
Which of the following are the kidneys responsible for excreting?
Which of the following are the kidneys responsible for excreting?
What is the main function of the bladder in the excretory system?
What is the main function of the bladder in the excretory system?
Which of the following mechanisms is vital for maintaining blood pH and preventing acidosis?
Which of the following mechanisms is vital for maintaining blood pH and preventing acidosis?
Which process does the liver perform to prepare waste products for safer elimination?
Which process does the liver perform to prepare waste products for safer elimination?
What are the primary functions of the urinary system?
What are the primary functions of the urinary system?
Which sequence correctly represents the organs of the urinary system involved in urine flow?
Which sequence correctly represents the organs of the urinary system involved in urine flow?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the kidneys?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of the kidneys?
What is the functional unit of the kidney called?
What is the functional unit of the kidney called?
In which part of the nephron does ultrafiltration occur?
In which part of the nephron does ultrafiltration occur?
Where does the majority of reabsorption take place in the nephron?
Where does the majority of reabsorption take place in the nephron?
The distal convoluted tubule is primarily responsible for which process?
The distal convoluted tubule is primarily responsible for which process?
What is the primary function of the collecting duct?
What is the primary function of the collecting duct?
Which hormone primarily helps the body retain water by increasing the permeability of the kidney's collecting ducts?
Which hormone primarily helps the body retain water by increasing the permeability of the kidney's collecting ducts?
Where is ADH synthesized?
Where is ADH synthesized?
How does aldosterone regulate blood pressure?
How does aldosterone regulate blood pressure?
What stimulates the secretion of aldosterone?
What stimulates the secretion of aldosterone?
Which statement explains how ADH responds to overhydration?
Which statement explains how ADH responds to overhydration?
What is a common symptom of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
What is a common symptom of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
What is a potential cause of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)?
What is a potential cause of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)?
Which of the following is a symptom of kidney stones?
Which of the following is a symptom of kidney stones?
What is glomerulonephritis characterized by?
What is glomerulonephritis characterized by?
How can kidney diseases impact the body over time?
How can kidney diseases impact the body over time?
Which of the following lifestyle changes can help prevent kidney diseases?
Which of the following lifestyle changes can help prevent kidney diseases?
A patient presents with a decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and proteinuria. Further tests reveal elevated levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine. Which condition is MOST likely causing these findings?
A patient presents with a decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and proteinuria. Further tests reveal elevated levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine. Which condition is MOST likely causing these findings?
A patient with a history of hypertension is diagnosed with nephrosclerosis. Which of the following pathological changes is MOST likely observed in the kidneys of this patient?
A patient with a history of hypertension is diagnosed with nephrosclerosis. Which of the following pathological changes is MOST likely observed in the kidneys of this patient?
A researcher is investigating the effects of a novel drug on kidney function. They observe that the drug significantly reduces the reabsorption of sodium ions (Na+) in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). Which of the following is the MOST likely consequence of this drug effect?
A researcher is investigating the effects of a novel drug on kidney function. They observe that the drug significantly reduces the reabsorption of sodium ions (Na+) in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). Which of the following is the MOST likely consequence of this drug effect?
A patient with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is undergoing hemodialysis. During the dialysis session, a technician accidentally sets the dialysate sodium concentration significantly lower than the patient's serum sodium concentration. Which of the following complications is MOST likely to occur due to this error?
A patient with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is undergoing hemodialysis. During the dialysis session, a technician accidentally sets the dialysate sodium concentration significantly lower than the patient's serum sodium concentration. Which of the following complications is MOST likely to occur due to this error?
Which condition would promote the body's ability to produce more concentrated urine?
Which condition would promote the body's ability to produce more concentrated urine?
The kidneys are located:
The kidneys are located:
Which hormone would DECREASE sodium reabsorption?
Which hormone would DECREASE sodium reabsorption?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of excretion?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of excretion?
Carbon dioxide and water vapor, which are excreted by the lungs, are primarily byproducts of what metabolic process?
Carbon dioxide and water vapor, which are excreted by the lungs, are primarily byproducts of what metabolic process?
Sweat, excreted by the skin, is composed of water, mineral salts, and small amounts of which other waste product?
Sweat, excreted by the skin, is composed of water, mineral salts, and small amounts of which other waste product?
Urea formation in the liver is a direct result of the metabolic breakdown of which type of biomolecule?
Urea formation in the liver is a direct result of the metabolic breakdown of which type of biomolecule?
Bile pigments, excreted via the alimentary canal, are derived from the breakdown of:
Bile pigments, excreted via the alimentary canal, are derived from the breakdown of:
Which of the following organs plays a crucial role in filtering blood and regulating electrolyte balance?
Which of the following organs plays a crucial role in filtering blood and regulating electrolyte balance?
The bladder's primary role in excretion is best described as:
The bladder's primary role in excretion is best described as:
Exhaling carbon dioxide by the lungs is critical for preventing which condition?
Exhaling carbon dioxide by the lungs is critical for preventing which condition?
Which of the following best describes the liver's role in preparing waste for excretion?
Which of the following best describes the liver's role in preparing waste for excretion?
The colon's role in excretion mainly involves removing:
The colon's role in excretion mainly involves removing:
What is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion?
What is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion?
In which part of the nephron does ultrafiltration of blood primarily take place?
In which part of the nephron does ultrafiltration of blood primarily take place?
The majority of reabsorption of water, ions, and organic nutrients occurs in which segment of the nephron?
The majority of reabsorption of water, ions, and organic nutrients occurs in which segment of the nephron?
Which part of the nephron is mainly responsible for the concentration of urine by creating a salt gradient in the medulla?
Which part of the nephron is mainly responsible for the concentration of urine by creating a salt gradient in the medulla?
In the nephron, tubular secretion primarily occurs in the:
In the nephron, tubular secretion primarily occurs in the:
The collecting duct's permeability to water is directly influenced by which hormone?
The collecting duct's permeability to water is directly influenced by which hormone?
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) is synthesized in which part of the brain?
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) is synthesized in which part of the brain?
Aldosterone primarily regulates blood pressure by increasing the reabsorption of:
Aldosterone primarily regulates blood pressure by increasing the reabsorption of:
Which of the following conditions would stimulate the secretion of aldosterone?
Which of the following conditions would stimulate the secretion of aldosterone?
How does ADH secretion change in response to overhydration?
How does ADH secretion change in response to overhydration?
A patient with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is likely to experience which of the following symptoms?
A patient with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is likely to experience which of the following symptoms?
Severe dehydration is a potential cause of which type of kidney disease?
Severe dehydration is a potential cause of which type of kidney disease?
Intense pain in the back or side, often radiating to the groin, is a characteristic symptom of:
Intense pain in the back or side, often radiating to the groin, is a characteristic symptom of:
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by:
Glomerulonephritis is characterized by:
Over time, kidney diseases can increase the risk of which cardiovascular complication?
Over time, kidney diseases can increase the risk of which cardiovascular complication?
Which lifestyle change is most beneficial in preventing kidney diseases?
Which lifestyle change is most beneficial in preventing kidney diseases?
In a healthy nephron, which of the following substances is LEAST likely to be found in the glomerular filtrate?
In a healthy nephron, which of the following substances is LEAST likely to be found in the glomerular filtrate?
If the afferent arteriole constricts, leading to reduced blood flow into the glomerulus, what immediate effect would this have on glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
If the afferent arteriole constricts, leading to reduced blood flow into the glomerulus, what immediate effect would this have on glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
A patient is experiencing metabolic acidosis. Which of the following renal responses would be expected to help restore blood pH?
A patient is experiencing metabolic acidosis. Which of the following renal responses would be expected to help restore blood pH?
In a scenario where the body is experiencing a severe salt deficit, which hormonal response would be the MOST immediate and effective in restoring sodium balance?
In a scenario where the body is experiencing a severe salt deficit, which hormonal response would be the MOST immediate and effective in restoring sodium balance?
Consider a patient who has a tumor in the adrenal cortex that causes excessive secretion of aldosterone. Which of the following electrolyte imbalances is MOST likely to be observed in this patient?
Consider a patient who has a tumor in the adrenal cortex that causes excessive secretion of aldosterone. Which of the following electrolyte imbalances is MOST likely to be observed in this patient?
Which of the following transport mechanisms is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of glucose in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Which of the following transport mechanisms is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of glucose in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
If a substance is freely filtered at the glomerulus, completely reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule, and not secreted, its clearance rate would be:
If a substance is freely filtered at the glomerulus, completely reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule, and not secreted, its clearance rate would be:
In the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle, which of the following processes is crucial for establishing the medullary osmotic gradient?
In the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle, which of the following processes is crucial for establishing the medullary osmotic gradient?
A patient presents with polyuria (excessive urination) and polydipsia (excessive thirst), and lab results show dilute urine despite elevated blood glucose levels. Which hormone deficiency or insensitivity is MOST likely contributing to these symptoms?
A patient presents with polyuria (excessive urination) and polydipsia (excessive thirst), and lab results show dilute urine despite elevated blood glucose levels. Which hormone deficiency or insensitivity is MOST likely contributing to these symptoms?
Which of the following is the primary waste product excreted by the lungs?
Which of the following is the primary waste product excreted by the lungs?
Through which structure in the skin is sweat primarily excreted?
Through which structure in the skin is sweat primarily excreted?
What metabolic process in the liver leads to the formation of urea?
What metabolic process in the liver leads to the formation of urea?
Which component of bile, excreted via the alimentary canal, is derived from the breakdown of hemoglobin?
Which component of bile, excreted via the alimentary canal, is derived from the breakdown of hemoglobin?
What is the main role of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis?
What is the main role of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis?
Which part of the urinary system directly stores urine before it is eliminated from the body?
Which part of the urinary system directly stores urine before it is eliminated from the body?
Exhaling carbon dioxide is crucial for preventing which condition related to blood pH?
Exhaling carbon dioxide is crucial for preventing which condition related to blood pH?
The liver prepares waste products for safer elimination by primarily performing what type of process?
The liver prepares waste products for safer elimination by primarily performing what type of process?
Which sequence accurately describes the flow of urine after it leaves the kidneys?
Which sequence accurately describes the flow of urine after it leaves the kidneys?
What is the microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney?
What is the microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney?
In which specific part of the nephron does ultrafiltration initially occur?
In which specific part of the nephron does ultrafiltration initially occur?
Where in the nephron is the majority of water, glucose, and amino acids reabsorbed back into the bloodstream?
Where in the nephron is the majority of water, glucose, and amino acids reabsorbed back into the bloodstream?
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is MOST responsible for which of the following processes in urine formation?
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is MOST responsible for which of the following processes in urine formation?
What is the primary function of the collecting duct in the nephron?
What is the primary function of the collecting duct in the nephron?
Which hormone primarily increases water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys?
Which hormone primarily increases water reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidneys?
Where is Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) synthesized in the body?
Where is Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) synthesized in the body?
How does aldosterone primarily contribute to the regulation of blood pressure?
How does aldosterone primarily contribute to the regulation of blood pressure?
Which of the following conditions would MOST directly stimulate the secretion of aldosterone?
Which of the following conditions would MOST directly stimulate the secretion of aldosterone?
How does ADH secretion typically respond to a state of overhydration in the body?
How does ADH secretion typically respond to a state of overhydration in the body?
Which of the following is a common symptom associated with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Which of the following is a common symptom associated with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Severe dehydration is a potential cause of which type of kidney condition?
Severe dehydration is a potential cause of which type of kidney condition?
Intense pain in the back or side, often radiating to the groin, is most characteristic of which kidney-related condition?
Intense pain in the back or side, often radiating to the groin, is most characteristic of which kidney-related condition?
Glomerulonephritis is primarily characterized by:
Glomerulonephritis is primarily characterized by:
Over time, kidney diseases can significantly increase the risk of developing which systemic health complication?
Over time, kidney diseases can significantly increase the risk of developing which systemic health complication?
Which of the following lifestyle changes is MOST beneficial in preventing kidney diseases?
Which of the following lifestyle changes is MOST beneficial in preventing kidney diseases?
In a healthy nephron, which substance is LEAST likely to be found in significant amounts in the glomerular filtrate?
In a healthy nephron, which substance is LEAST likely to be found in significant amounts in the glomerular filtrate?
If the afferent arteriole constricts, reducing blood flow to the glomerulus, what immediate effect would this have on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
If the afferent arteriole constricts, reducing blood flow to the glomerulus, what immediate effect would this have on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
A patient is experiencing metabolic acidosis. Which renal response would be expected to help restore blood pH balance?
A patient is experiencing metabolic acidosis. Which renal response would be expected to help restore blood pH balance?
During severe salt deficit, which hormonal response is MOST immediate and effective in restoring sodium balance?
During severe salt deficit, which hormonal response is MOST immediate and effective in restoring sodium balance?
A patient has a tumor in the adrenal cortex causing excessive aldosterone secretion. Which electrolyte imbalance is MOST likely to be observed?
A patient has a tumor in the adrenal cortex causing excessive aldosterone secretion. Which electrolyte imbalance is MOST likely to be observed?
Which transport mechanism is primarily responsible for glucose reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Which transport mechanism is primarily responsible for glucose reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
If a substance is freely filtered, completely reabsorbed in the PCT, and not secreted, its renal clearance rate would be approximately:
If a substance is freely filtered, completely reabsorbed in the PCT, and not secreted, its renal clearance rate would be approximately:
In the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle, which process is crucial for establishing the medullary osmotic gradient necessary for urine concentration?
In the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle, which process is crucial for establishing the medullary osmotic gradient necessary for urine concentration?
A patient presents with polyuria and polydipsia; lab results show dilute urine despite elevated blood glucose. Which hormone deficiency is MOST likely contributing to these symptoms?
A patient presents with polyuria and polydipsia; lab results show dilute urine despite elevated blood glucose. Which hormone deficiency is MOST likely contributing to these symptoms?
Flashcards
Excretion
Excretion
The biological process of eliminating metabolic waste products from an organism.
Lungs' Role in Excretion
Lungs' Role in Excretion
Removes carbon dioxide and water vapor from the body.
Skin's Role in Excretion
Skin's Role in Excretion
Excretes water, mineral salts, and small amounts of urea through sweat.
Liver's Role in Excretion
Liver's Role in Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alimentary Canal's Role
Alimentary Canal's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys' Role in Excretion
Kidneys' Role in Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder's Role in Excretion
Bladder's Role in Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Function
Urinary System Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Components of the Urinary System
Components of the Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney's Filtration Function
Kidney's Filtration Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney's Reabsorption Function
Kidney's Reabsorption Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney's Secretion Function
Kidney's Secretion Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney's Excretion Function
Kidney's Excretion Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle Function
Loop of Henle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reabsorption in PCT
Reabsorption in PCT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion in DCT
Tubular Secretion in DCT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Formation in Collecting Duct
Urine Formation in Collecting Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
pH Control in Urinary System
pH Control in Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH and Aldosterone
ADH and Aldosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone)
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aldosterone
Aldosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response to Dehydration
Response to Dehydration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response to High Salt Levels
Response to High Salt Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homeostasis
Homeostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Stones
Kidney Stones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lifestyle Changes for Kidney Health
Lifestyle Changes for Kidney Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regular Monitoring for Kidney Health
Regular Monitoring for Kidney Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lungs' Excretory Function
Lungs' Excretory Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin's Temperature Regulation
Skin's Temperature Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver's Role in Detoxification
Liver's Role in Detoxification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Colon's Excretory Role
Colon's Excretory Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys' Filtration and Regulation
Kidneys' Filtration and Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder's Storage Function
Bladder's Storage Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Location and Protection
Kidney Location and Protection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrafiltration in Bowman's Capsule
Ultrafiltration in Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Detection of Imbalance
Detection of Imbalance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Low Water Levels
Low Water Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
High Salt Levels
High Salt Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Disease
Kidney Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excretory Organs
Excretory Organs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deamination
Deamination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urea
Urea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Pigments
Bile Pigments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acidosis
Acidosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retroperitoneal
Retroperitoneal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Cortex
Kidney Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Medulla
Kidney Medulla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Pelvis
Renal Pelvis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmoreceptors
Osmoreceptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Edema
Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dialysis
Dialysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
kidney failure
kidney failure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Excretion refers to the biological process of eliminating metabolic waste to maintain internal stability and prevent harm from toxic accumulation.
Excretory Organs
- The lungs, skin, liver, alimentary canal (gut), kidneys, and bladder are the key organs involved in excretion in humans.
- Each organ plays a specialized role contributing to the body's overall homeostasis.
Lungs
- The lungs primarily excrete carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor.
- Carbon dioxide and water vapor originate from cellular respiration.
- Exhaling carbon dioxide is crucial for maintaining blood pH and preventing acidosis.
Skin
- The skin excretes water, mineral salts, and small amounts of urea through sweat glands.
- Mineral salts and urea are derived from the blood.
- Sweat evaporation regulates body temperature while excreting excess salts and small waste molecules.
Liver
- The liver excretes urea and bile pigments.
- Urea is produced through the deamination of excess amino acids.
- Bile pigments arise from the breakdown of hemoglobin.
- The liver processes toxins and waste products, preparing them for safer elimination.
Alimentary Canal (Gut)
- The colon, a part of the alimentary canal, excretes bile pigments and excess mineral salts.
- Bile, produced in the liver, delivers these components to the colon.
- The alimentary canal removes indigestible substances and waste products from the liver through feces.
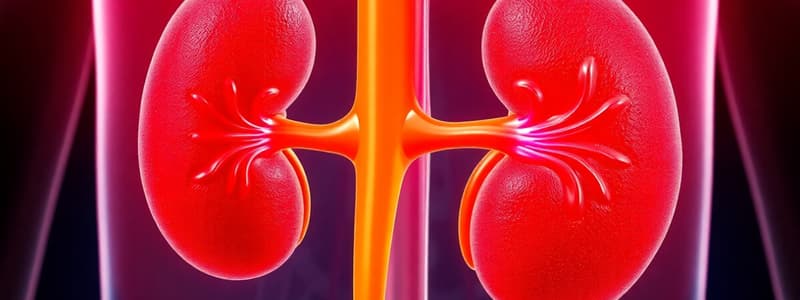
Kidneys
- The kidneys excrete urea, mineral salts, and water.
- Urea originates from the liver, where amino acids are deaminated.
- The kidneys regulate mineral salts and water based on dietary intake and physiological needs.
- They filter blood to remove excess ions, water, and nitrogenous wastes, crucial for balancing blood pressure, electrolytes, and acid-base levels.
Bladder
- The bladder stores urine excreted by the kidneys until it is expelled.
- The bladder's primary role is the storage and periodic removal of urine, which contains metabolic wastes.
- The bladder acts as a reservoir for urine, allowing controlled and convenient elimination of liquid waste.
Organ Roles
- Lungs: Crucial for maintaining blood pH and preventing acidosis by exhaling carbon dioxide.
- Skin: Regulates body temperature through sweat evaporation and excretes excess salts and small waste molecules.
- Liver: Processes toxins and waste products, preparing them for elimination.
- Alimentary Canal: Eliminates indigestible substances and waste products from the liver through feces.
- Kidneys: Filter blood to remove excess ions, water, and nitrogenous wastes, balancing blood pressure, electrolytes, and acid-base levels.
- Bladder: Serves as a reservoir for urine, providing controlled elimination of liquid waste.
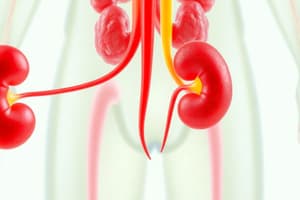
Urinary System Overview
- The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Osmoregulation, excretion of nitrogenous wastes, pH regulation, and the regulation of salt concentration in body fluids are the key functions.
Components of the Urinary System
- Kidneys: Filter blood.
- Ureters: Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Stores urine until expulsion.
- Urethra: Allows urine to exit the body.
- The kidneys are positioned retroperitoneally on either side of the spine, protected by adipose tissue and a renal capsule.
- The kidneys receive oxygen-rich and waste-laden blood via the renal arteries.
- Filtered, deoxygenated blood returns to the heart through the renal veins.
Kidney Structure and Function
- Cortex, medulla, and renal pelvis form the kidney.
- Blood is received via renal arteries, and filtered blood is returned to the heart through the renal veins.
- The kidneys filter blood, remove waste, reabsorb nutrients, secrete additional wastes, and excrete processed filtrate as urine.
- A renal capsule encloses each kidney, protecting its structure and function.
Nephron
- The nephron, about 1 million per kidney, is the kidney's functional unit.
- Each nephron contains a glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), Loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule (DCT), and collecting duct.
- Glomerulus: Filtration occurs here within the Bowman's capsule.
- Bowman's Capsule: Collects filtrate.
- PCT: Substantial reabsorption of water, ions, and organic nutrients occurs here.
- Loop of Henle: Concentrates urine.
- DCT: Balances ion and water levels.
- Collecting Duct: Delivers urine to the renal pelvis from multiple nephrons.
Nephron Processes
- Ultrafiltration: Blood pressure drives water and solutes out of the blood into the nephron at the Bowman's capsule.
- Reabsorption: Substances and water are reabsorbed into the bloodstream, primarily in the PCT.
- Tubular Secretion: Additional unwanted substances are added to the filtrate from the blood in the DCT.
- Urine Formation: Final adjustments occur in the collecting duct; urine is stored in the bladder.
Regulation and Homeostasis
- Osmoregulation manages water balance.
- The urinary system regulates pH by reabsorbing or secreting hydrogen and bicarbonate ions.
- Excretion of urea and salts removes metabolic waste and excess substances.
- The lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor.
- The liver metabolizes waste for excretion.
- The skin eliminates salts and urea through sweat.
Osmoregulation and Hormones
- Homeostasis is the body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes.
- The kidneys regulate water and salt levels with the help of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone.
- Osmoregulation balances water and salt levels in blood and tissue fluids, managed by ADH and aldosterone.
Role of ADH
- ADH is produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland.
- It increases water reabsorption in the kidneys by making the collecting ducts and distal convoluted tubules more permeable to water.
- Dehydration increases ADH secretion, leading to water conservation and concentrated urine.
- Overhydration decreases ADH secretion, producing dilute urine.
Role of Aldosterone
- Aldosterone is produced in the adrenal cortex.
- It increases sodium ion reabsorption and potassium ion secretion in the nephron.
- Aldosterone secretion is stimulated by increased blood potassium or decreased sodium levels and is influenced by the renin-angiotensin system when blood pressure is low.
- It influences water retention through sodium reabsorption, impacting blood volume and blood pressure.
Kidney Disease Introduction
- Kidney diseases impair the kidneys’ ability to filter blood, remove waste, balance electrolytes, and regulate blood pressure.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Overview: a long-term condition that causes gradual kidney function loss.
- Diabetes, hypertension, and other health issues can cause it.
- Symptoms: Fatigue, swelling (edema), and changes in urine output.
- If untreated, it progresses to kidney failure, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- Overview: a sudden reduction in kidney function attributed to severe dehydration, injury, or reaction to certain medications.
- Symptoms: Sudden decrease in urine output, swelling, and confusion.
- Treatment: Requires immediate medical intervention.
- Severe cases may lead to lasting damage.
Kidney Stones
- Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys.
- Symptoms: Intense pain in the back or side, blood in urine, and nausea.
- Prevention/Treatment: Staying hydrated and, in some cases, surgical removal or shock wave therapy to break up stones.
Glomerulonephritis
- Overview: Is the inflammation of the glomeruli.
- Can be acute or chronic, often resulting from infections, autoimmune diseases, or other systemic conditions.
- Symptoms: Blood in urine, high blood pressure, and swelling.
- Treatment: May include medications to reduce inflammation and control blood pressure, depending on the underlying cause.
Impact on the Body
- Kidney diseases may cause waste accumulation, fluid imbalances, and electrolyte disturbances.
- Cardiovascular diseases, anemia, and bone disorders risks may increase over time.
Prevention and Management
- Lifestyle Changes: Following a healthy diet, managing blood pressure and blood sugar levels, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking and excessive medication use can prevent kidney damage.
- Regular Monitoring: Detecting kidney diseases early through regular blood and urine tests may prevent progression to more severe stages.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.