Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the process of removing waste products from the body called?
What is the process of removing waste products from the body called?
- Respiration
- Circulation
- Excretion (correct)
- Digestion
Which gas is excreted by the lungs?
Which gas is excreted by the lungs?
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- Carbon dioxide (correct)
- Nitrogen
Which of the following does the skin excrete?
Which of the following does the skin excrete?
- Bile and vitamins
- Undigested food
- Carbon dioxide and oxygen
- Urea, salt and excess water (correct)
Which organ excretes feces?
Which organ excretes feces?
Which of the following is a nitrogenous waste excreted by the kidneys?
Which of the following is a nitrogenous waste excreted by the kidneys?
Which organ removes drugs and bile pigments from the blood?
Which organ removes drugs and bile pigments from the blood?
What is the main structural and functional unit of the kidney?
What is the main structural and functional unit of the kidney?
What percentage of urine is water?
What percentage of urine is water?
Which structure carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder?
Which structure carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder?
Where is urine stored before it is expelled from the body?
Where is urine stored before it is expelled from the body?
Through which structure is urine expelled from the body?
Through which structure is urine expelled from the body?
What is the filtering unit within the nephron called?
What is the filtering unit within the nephron called?
What useful substances are reabsorbed by the tubules of the nephrons?
What useful substances are reabsorbed by the tubules of the nephrons?
What is the process of expelling urine called?
What is the process of expelling urine called?
Which of the following is a common symptom of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Which of the following is a common symptom of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Kidney stones are crystal-forming substances such as:
Kidney stones are crystal-forming substances such as:
What is the process of regulating salt and water concentration in the blood called?
What is the process of regulating salt and water concentration in the blood called?
In diabetes, what is excreted through urine in excess?
In diabetes, what is excreted through urine in excess?
What is the function of dialysis or an artificial kidney?
What is the function of dialysis or an artificial kidney?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the excretory system?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the excretory system?
Which of the following processes is directly responsible for removing carbon dioxide from the body?
Which of the following processes is directly responsible for removing carbon dioxide from the body?
The skin contributes to excretion by eliminating which combination of substances?
The skin contributes to excretion by eliminating which combination of substances?
Which of these organs primarily functions to remove drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments from the bloodstream?
Which of these organs primarily functions to remove drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments from the bloodstream?
Why is the excretion of metabolic waste products essential for living organisms?
Why is the excretion of metabolic waste products essential for living organisms?
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of organs involved in urine formation and elimination?
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of organs involved in urine formation and elimination?
What is the role of the glomerulus within the nephron?
What is the role of the glomerulus within the nephron?
Why is the reabsorption of glucose in the kidney tubules important?
Why is the reabsorption of glucose in the kidney tubules important?
If a patient's urine analysis reveals a high concentration of glucose, which condition might this indicate?
If a patient's urine analysis reveals a high concentration of glucose, which condition might this indicate?
The primary function of osmoregulation in the kidneys is to:
The primary function of osmoregulation in the kidneys is to:
What is dialysis used for in patients with kidney failure?
What is dialysis used for in patients with kidney failure?
How do kidney stones typically cause pain?
How do kidney stones typically cause pain?
What characteristic is commonly associated with urine affected by a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
What characteristic is commonly associated with urine affected by a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
Which component of urine is present in the lowest percentage?
Which component of urine is present in the lowest percentage?
In addition to the kidneys, which other organ plays a role in maintaining fluid balance and eliminating excess salts from the body?
In addition to the kidneys, which other organ plays a role in maintaining fluid balance and eliminating excess salts from the body?
What distinguishes the role of the ureters from that of the urethra in the urinary system?
What distinguishes the role of the ureters from that of the urethra in the urinary system?
What would be the likely effect on urine production if the kidneys failed to reabsorb sodium ions?
What would be the likely effect on urine production if the kidneys failed to reabsorb sodium ions?
Why are water-soluble vitamins like B and C excreted in urine when consumed in excess?
Why are water-soluble vitamins like B and C excreted in urine when consumed in excess?
What is the functional significance of the high pressure within the glomerulus?
What is the functional significance of the high pressure within the glomerulus?
How does the length of the urethra differ between males and females, and why is this difference significant?
How does the length of the urethra differ between males and females, and why is this difference significant?
How do the Kidney's 'help' maintain homeostasis, and why is this important?
How do the Kidney's 'help' maintain homeostasis, and why is this important?
If the kidneys fail to reabsorb sufficient water, but continue to filter waste, what direct effect would this have on the composition of urine?
If the kidneys fail to reabsorb sufficient water, but continue to filter waste, what direct effect would this have on the composition of urine?
Two patients present with kidney stones. Patient A's stones are composed of calcium oxalate, while Patient B's stones are composed of uric acid. Assuming no other underlying conditions, which patient is more likely to also have a history of gout?
Two patients present with kidney stones. Patient A's stones are composed of calcium oxalate, while Patient B's stones are composed of uric acid. Assuming no other underlying conditions, which patient is more likely to also have a history of gout?
A patient is diagnosed with diabetes. Beyond increased glucose in the urine, what other change involving kidney function is most likely to occur over time if the diabetes is poorly managed?
A patient is diagnosed with diabetes. Beyond increased glucose in the urine, what other change involving kidney function is most likely to occur over time if the diabetes is poorly managed?
If a drug inhibits the reabsorption of sodium ions in the kidney tubules, which of the following indirect effects is most likely to occur?
If a drug inhibits the reabsorption of sodium ions in the kidney tubules, which of the following indirect effects is most likely to occur?
A researcher is studying the impact of a novel diuretic drug on kidney function. Which specific measurement would provide the most direct indication of the drug's effect on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
A researcher is studying the impact of a novel diuretic drug on kidney function. Which specific measurement would provide the most direct indication of the drug's effect on the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
A patient with advanced kidney disease has been advised to restrict their protein intake to manage their symptoms. What is the primary reason for this dietary recommendation?
A patient with advanced kidney disease has been advised to restrict their protein intake to manage their symptoms. What is the primary reason for this dietary recommendation?
In a scenario where the efferent arteriole of a glomerulus becomes constricted, how would this impact the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and Bowman's capsule hydrostatic pressure?
In a scenario where the efferent arteriole of a glomerulus becomes constricted, how would this impact the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and Bowman's capsule hydrostatic pressure?
A person is experiencing metabolic alkalosis. How would the kidneys likely respond to help restore acid-base balance in the body?
A person is experiencing metabolic alkalosis. How would the kidneys likely respond to help restore acid-base balance in the body?
Someone who has liver failure may accumulate excess ammonia in their blood. How does this directly affect the kidneys' function in nitrogenous waste excretion?
Someone who has liver failure may accumulate excess ammonia in their blood. How does this directly affect the kidneys' function in nitrogenous waste excretion?
A marathon runner collapses after a race and is diagnosed with rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown). How might this condition acutely impact kidney function?
A marathon runner collapses after a race and is diagnosed with rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown). How might this condition acutely impact kidney function?
What feedback mechanism is activated when the body experiences a significant increase in osmolarity (concentration of solutes) due to dehydration?
What feedback mechanism is activated when the body experiences a significant increase in osmolarity (concentration of solutes) due to dehydration?
How does the use of ACE inhibitors (drugs that block the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme) affect kidney function, particularly in individuals with hypertension or heart failure?
How does the use of ACE inhibitors (drugs that block the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme) affect kidney function, particularly in individuals with hypertension or heart failure?
During a prolonged period of starvation, the body breaks down muscle tissue for energy. How does this catabolic state affect urea production and excretion by the kidneys?
During a prolonged period of starvation, the body breaks down muscle tissue for energy. How does this catabolic state affect urea production and excretion by the kidneys?
If the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of a nephron is damaged, what critical function of the kidney would be most directly impaired?
If the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of a nephron is damaged, what critical function of the kidney would be most directly impaired?
A patient presents with hyperaldosteronism (excessive aldosterone secretion). How will this condition primarily affect the composition and volume of urine?
A patient presents with hyperaldosteronism (excessive aldosterone secretion). How will this condition primarily affect the composition and volume of urine?
A person living in a desert environment is likely to have hormonal adjustments that minimize water loss. Which hormonal changes would be most adaptive in this situation?
A person living in a desert environment is likely to have hormonal adjustments that minimize water loss. Which hormonal changes would be most adaptive in this situation?
If the loop of Henle were completely non-functional, how would this directly impact the kidney's ability to produce concentrated urine?
If the loop of Henle were completely non-functional, how would this directly impact the kidney's ability to produce concentrated urine?
In the context of kidney physiology, what is the primary functional significance of the countercurrent multiplier system in the loop of Henle?
In the context of kidney physiology, what is the primary functional significance of the countercurrent multiplier system in the loop of Henle?
How would a significant increase in the levels of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) affect sodium and water balance in the body?
How would a significant increase in the levels of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) affect sodium and water balance in the body?
A new drug is developed that selectively blocks the Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. What effect would this drug likely have on urine concentration and electrolyte balance?
A new drug is developed that selectively blocks the Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. What effect would this drug likely have on urine concentration and electrolyte balance?
Excretion is the process of removing waste products from the body.
Excretion is the process of removing waste products from the body.
Lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor produced during digestion.
Lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor produced during digestion.
The liver excretes urea, salt, and excess water through sweat glands.
The liver excretes urea, salt, and excess water through sweat glands.
The large intestine excretes feces through the anus.
The large intestine excretes feces through the anus.
Kidneys excrete urea and nitrogen in urine.
Kidneys excrete urea and nitrogen in urine.
The liver removes drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments from the blood.
The liver removes drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments from the blood.
Urea and uric acid are nitrogenous wastes produced by the breakdown of carbohydrates.
Urea and uric acid are nitrogenous wastes produced by the breakdown of carbohydrates.
Water-soluble vitamins like B, C, and K are stored in the body.
Water-soluble vitamins like B, C, and K are stored in the body.
The excretory system includes kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
The excretory system includes kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Nephrons are the structural and functional units of the liver.
Nephrons are the structural and functional units of the liver.
Urine is composed of 95% water, 2.5% urea, and 2.5% other waste products.
Urine is composed of 95% water, 2.5% urea, and 2.5% other waste products.
Ureters carry urine from the urinary bladder to the kidneys.
Ureters carry urine from the urinary bladder to the kidneys.
The glomerulus is a filter located within the nephron.
The glomerulus is a filter located within the nephron.
UTI is caused by viruses entering the urinary tract.
UTI is caused by viruses entering the urinary tract.
Dialysis is used when the kidneys fail to filter blood efficiently.
Dialysis is used when the kidneys fail to filter blood efficiently.
The primary function of the excretory system is to remove waste products and maintain homeostasis, including water and salt balance.
The primary function of the excretory system is to remove waste products and maintain homeostasis, including water and salt balance.
The large intestine is the primary organ responsible for filtering urea and nitrogenous wastes from the bloodstream in humans.
The large intestine is the primary organ responsible for filtering urea and nitrogenous wastes from the bloodstream in humans.
Uric acid is produced during the breakdown of amino acids in the liver, making it a nitrogenous waste excreted by the kidneys.
Uric acid is produced during the breakdown of amino acids in the liver, making it a nitrogenous waste excreted by the kidneys.
The main components of urine are 50% water, 40% urea, and 10% waste products.
The main components of urine are 50% water, 40% urea, and 10% waste products.
Nephrons reabsorb useful substances like carbon dioxide, potassium ions, and proteins back into the bloodstream after filtration.
Nephrons reabsorb useful substances like carbon dioxide, potassium ions, and proteins back into the bloodstream after filtration.
The glomerulus, located within Bowman's capsule, uses high pressure to filter waste substances and useful molecules from the blood into the tubules.
The glomerulus, located within Bowman's capsule, uses high pressure to filter waste substances and useful molecules from the blood into the tubules.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are typically caused by viral infections, leading to symptoms like fever and muscle aches.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are typically caused by viral infections, leading to symptoms like fever and muscle aches.
The accumulation of crystal-forming substances, like calcium oxalate, exclusively leads to bladder stones, not kidney stones.
The accumulation of crystal-forming substances, like calcium oxalate, exclusively leads to bladder stones, not kidney stones.
Dialysis is a procedure that helps maintain constant salt and water concentrations in the body when kidneys fail, but it doesn't filter the blood.
Dialysis is a procedure that helps maintain constant salt and water concentrations in the body when kidneys fail, but it doesn't filter the blood.
Unlike water-soluble vitamins, excess amounts of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, and E are readily excreted in urine, preventing their buildup in the body.
Unlike water-soluble vitamins, excess amounts of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, and E are readily excreted in urine, preventing their buildup in the body.
The urethra is longer in females than in males, which contributes to a lower incidence of urinary tract infections in women.
The urethra is longer in females than in males, which contributes to a lower incidence of urinary tract infections in women.
Osmoregulation, performed by the kidneys, involves regulating sugar levels in the blood to prevent diabetes.
Osmoregulation, performed by the kidneys, involves regulating sugar levels in the blood to prevent diabetes.
Bile pigments, produced in the kidneys, are degraded and then excreted through the feces.
Bile pigments, produced in the kidneys, are degraded and then excreted through the feces.
The urinary bladder propels urine to the outside of the body through a tube called the ureter.
The urinary bladder propels urine to the outside of the body through a tube called the ureter.
Individuals with diabetes will excrete excess sugar through their sweat glands to maintain a stable blood sugar level.
Individuals with diabetes will excrete excess sugar through their sweat glands to maintain a stable blood sugar level.
The primary function of the excretory system is to facilitate nutrient absorption, rather than waste removal, from the body.
The primary function of the excretory system is to facilitate nutrient absorption, rather than waste removal, from the body.
The large intestine primarily excretes carbon dioxide and water vapor while the lungs excrete feces.
The large intestine primarily excretes carbon dioxide and water vapor while the lungs excrete feces.
The purpose of the excretory system is to maintain equilibrium within the body despite external changes; this regulatory process is known as homeostasis.
The purpose of the excretory system is to maintain equilibrium within the body despite external changes; this regulatory process is known as homeostasis.
Bile pigments are synthesized within the kidneys and subsequently transported to the liver for degradation and excretion through urine.
Bile pigments are synthesized within the kidneys and subsequently transported to the liver for degradation and excretion through urine.
Nephrons facilitate the reabsorption of waste products, ensuring their efficient elimination from the bloodstream.
Nephrons facilitate the reabsorption of waste products, ensuring their efficient elimination from the bloodstream.
The glomerulus uses active transport to selectively filter waste substances from the blood based on molecular size and charge.
The glomerulus uses active transport to selectively filter waste substances from the blood based on molecular size and charge.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are primarily caused by viral pathogens.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are primarily caused by viral pathogens.
Kidney stones exclusively consist of calcium phosphate.
Kidney stones exclusively consist of calcium phosphate.
In individuals with diabetes, the kidneys compensate for elevated blood sugar levels by synthesizing insulin.
In individuals with diabetes, the kidneys compensate for elevated blood sugar levels by synthesizing insulin.
Dialysis fully restores normal kidney function, eliminating the need for lifestyle adjustments in patients with renal failure.
Dialysis fully restores normal kidney function, eliminating the need for lifestyle adjustments in patients with renal failure.
The process of removing waste products from the body is called ______.
The process of removing waste products from the body is called ______.
The lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor produced during ______.
The lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor produced during ______.
The skin excretes urea, salt, and excess water through ______ glands.
The skin excretes urea, salt, and excess water through ______ glands.
The large intestine excretes faeces through the ______.
The large intestine excretes faeces through the ______.
The kidneys excrete urea and nitrogen in ______.
The kidneys excrete urea and nitrogen in ______.
The liver removes wastes like drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments from the ______.
The liver removes wastes like drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments from the ______.
Urea and uric acid are examples of nitrogenous ______.
Urea and uric acid are examples of nitrogenous ______.
Bile pigments are produced by the ______ and excreted through urine (after degradation).
Bile pigments are produced by the ______ and excreted through urine (after degradation).
Excess water-soluble vitamins like B, C, and K are excreted in ______.
Excess water-soluble vitamins like B, C, and K are excreted in ______.
The excess of salts are expelled from our body through sweat and kidneys in ______.
The excess of salts are expelled from our body through sweat and kidneys in ______.
Kidneys are the bean-shaped reddish-brown structures that filter ______.
Kidneys are the bean-shaped reddish-brown structures that filter ______.
[Blank] are the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
[Blank] are the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
Ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary ______.
Ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary ______.
The urinary bladder opens into the ______, through which urine is expelled.
The urinary bladder opens into the ______, through which urine is expelled.
Regulating the concentration of salts and water in the blood is called ______.
Regulating the concentration of salts and water in the blood is called ______.
The process of maintaining the concentration of salts and water in the blood by the kidneys is called ______.
The process of maintaining the concentration of salts and water in the blood by the kidneys is called ______.
Within the nephron, the ______ is responsible for the initial filtration of waste substances from the blood due to high pressure.
Within the nephron, the ______ is responsible for the initial filtration of waste substances from the blood due to high pressure.
During respiration, the lungs excrete ______ and water vapor as waste products.
During respiration, the lungs excrete ______ and water vapor as waste products.
The ______ are the structural and functional units of the kidney, responsible for removing waste products from the blood.
The ______ are the structural and functional units of the kidney, responsible for removing waste products from the blood.
Excess water-soluble vitamins, like vitamins B, C, and K, are expelled from the body via ______.
Excess water-soluble vitamins, like vitamins B, C, and K, are expelled from the body via ______.
In the event of kidney failure, ______ is used as an artificial means to filter and clean the blood.
In the event of kidney failure, ______ is used as an artificial means to filter and clean the blood.
______ are narrow, long tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
______ are narrow, long tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
The skin excretes urea, salt, and excess water through ______ present in it.
The skin excretes urea, salt, and excess water through ______ present in it.
A common symptom of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a strong and frequent urge to ______.
A common symptom of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a strong and frequent urge to ______.
______ are formed when the urine contains more crystal-forming substances such as calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, and uric acid.
______ are formed when the urine contains more crystal-forming substances such as calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, and uric acid.
The breakdown of amino acids in the liver leads to the production of nitrogenous wastes such as urea and ______.
The breakdown of amino acids in the liver leads to the production of nitrogenous wastes such as urea and ______.
The ______ transports urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
The ______ transports urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
The liver produces ______, whose pigments get degraded and expelled outside through urine, contributing to its color.
The liver produces ______, whose pigments get degraded and expelled outside through urine, contributing to its color.
In individuals with diabetes, the excess sugar in the blood is excreted through ______.
In individuals with diabetes, the excess sugar in the blood is excreted through ______.
The ______ intestine is responsible for the excretion of feces through the anus.
The ______ intestine is responsible for the excretion of feces through the anus.
The process of regulating salt and water concentration in the blood by the kidneys is called ______.
The process of regulating salt and water concentration in the blood by the kidneys is called ______.
The ______ are the structural and functional units of the kidney, responsible for removing waste products from the blood and regulating water balance.
The ______ are the structural and functional units of the kidney, responsible for removing waste products from the blood and regulating water balance.
In the context of kidney function, the ______ is a filter within the nephron contained in Bowman's capsule where waste substances are removed from the blood under high pressure.
In the context of kidney function, the ______ is a filter within the nephron contained in Bowman's capsule where waste substances are removed from the blood under high pressure.
[Blank] is a procedure used when kidneys fail to filter blood efficiently, involving a machine to artificially clean the blood.
[Blank] is a procedure used when kidneys fail to filter blood efficiently, involving a machine to artificially clean the blood.
The excess of water-soluble vitamins, such as B, C, and K, are primarily excreted from the body through ______.
The excess of water-soluble vitamins, such as B, C, and K, are primarily excreted from the body through ______.
The condition known as ______ is characterized by a significant increase in blood sugar levels, leading to excess sugar being excreted through urine.
The condition known as ______ is characterized by a significant increase in blood sugar levels, leading to excess sugar being excreted through urine.
[Blank] or renal calculi are formed when urine contains more crystal-forming substances such as calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, and uric acid.
[Blank] or renal calculi are formed when urine contains more crystal-forming substances such as calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, and uric acid.
The ______ is a muscular sac in which urine is stored before it is excreted from the body.
The ______ is a muscular sac in which urine is stored before it is excreted from the body.
The ______ is the tube through which urine is expelled from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
The ______ is the tube through which urine is expelled from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body.
[Blank] is a term for infections caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, potentially affecting the kidneys, ureter, or urethra.
[Blank] is a term for infections caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, potentially affecting the kidneys, ureter, or urethra.
Name one waste product excreted by the lungs.
Name one waste product excreted by the lungs.
Which organ excretes urea, salt, and excess water through sweat?
Which organ excretes urea, salt, and excess water through sweat?
What is the main waste product excreted by the kidneys?
What is the main waste product excreted by the kidneys?
Name the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
Name the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
What is the tube through which urine is expelled from the body called?
What is the tube through which urine is expelled from the body called?
What is the name given to the process of expelling urine?
What is the name given to the process of expelling urine?
Name a crystal-forming substance that can lead to kidney stones.
Name a crystal-forming substance that can lead to kidney stones.
What type of infection is UTI?
What type of infection is UTI?
What is used to filter and clean the blood when kidneys fail?
What is used to filter and clean the blood when kidneys fail?
Which organ removes waste like drugs and bile pigments from the blood?
Which organ removes waste like drugs and bile pigments from the blood?
How does the liver contribute to the excretory system?
How does the liver contribute to the excretory system?
What is the role of nephrons in the kidney?
What is the role of nephrons in the kidney?
Describe the composition of urine.
Describe the composition of urine.
What are the main functions of the kidneys in the human body?
What are the main functions of the kidneys in the human body?
What is the function of the ureters?
What is the function of the ureters?
How does the urinary bladder function in the excretory system?
How does the urinary bladder function in the excretory system?
Describe the role of skin in excretion.
Describe the role of skin in excretion.
What are nitrogenous wastes and how are they formed?
What are nitrogenous wastes and how are they formed?
What is a UTI, and what are its common symptoms?
What is a UTI, and what are its common symptoms?
How are kidney stones formed?
How are kidney stones formed?
Explain the term 'osmoregulation' and why is it important?
Explain the term 'osmoregulation' and why is it important?
In the context of kidney function, what occurs during dialysis?
In the context of kidney function, what occurs during dialysis?
What is the role of reabsorption in nephrons, and which substances are typically reabsorbed?
What is the role of reabsorption in nephrons, and which substances are typically reabsorbed?
How is diabetes related to the excretory system?
How is diabetes related to the excretory system?
Explain how the nephron's structure is specifically adapted to perform its dual roles in waste removal and nutrient reabsorption within the kidney.
Explain how the nephron's structure is specifically adapted to perform its dual roles in waste removal and nutrient reabsorption within the kidney.
Describe the homeostatic role of the kidneys beyond waste removal, focusing on how they respond to fluctuations in blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
Describe the homeostatic role of the kidneys beyond waste removal, focusing on how they respond to fluctuations in blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
If a patient's urine sample shows a high concentration of protein, what specific part of the nephron might be damaged, and how would this damage lead to proteinuria?
If a patient's urine sample shows a high concentration of protein, what specific part of the nephron might be damaged, and how would this damage lead to proteinuria?
Compare and contrast the mechanisms by which the kidney and the lungs contribute to the excretion of waste products from the body.
Compare and contrast the mechanisms by which the kidney and the lungs contribute to the excretion of waste products from the body.
In what ways does kidney function change in response to dehydration, and how do these changes help the body conserve water?
In what ways does kidney function change in response to dehydration, and how do these changes help the body conserve water?
Explain the process of dialysis. What aspects of kidney function does it replicate, and what limitations does it have compared to a healthy, functioning kidney?
Explain the process of dialysis. What aspects of kidney function does it replicate, and what limitations does it have compared to a healthy, functioning kidney?
How does the body maintain the balance of salt and water concentration, and what is this process called?
How does the body maintain the balance of salt and water concentration, and what is this process called?
Describe how diabetes can lead to kidney damage, and what specific structural changes occur in the kidneys of individuals with long-term, uncontrolled diabetes.
Describe how diabetes can lead to kidney damage, and what specific structural changes occur in the kidneys of individuals with long-term, uncontrolled diabetes.
Explain how a urinary tract infection (UTI) can ascend from the urethra to the kidneys, and what potential complications can arise if the infection is not treated promptly.
Explain how a urinary tract infection (UTI) can ascend from the urethra to the kidneys, and what potential complications can arise if the infection is not treated promptly.
Discuss the factors that contribute to the formation of kidney stones and explain why some individuals are more prone to developing them than others.
Discuss the factors that contribute to the formation of kidney stones and explain why some individuals are more prone to developing them than others.
Flashcards
Excretion
Excretion
The process of removing harmful and unwanted metabolic wastes from the body.
Lungs (Excretion)
Lungs (Excretion)
Organs responsible for excreting carbon dioxide and water vapor during respiration.
Skin (Excretion)
Skin (Excretion)
Organ responsible for excreting urea, salt, and excess water through sweat glands.
Large Intestine (Excretion)
Large Intestine (Excretion)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys (Excretion)
Kidneys (Excretion)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver (Excretion)
Liver (Excretion)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urea and Uric Acid
Urea and Uric Acid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Tract Components
Urinary Tract Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephrons
Nephrons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureters
Ureters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder
Urinary Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urination
Urination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Stone
Kidney Stone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes
Diabetes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dialysis
Dialysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Composition
Urine Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Failure
Kidney Failure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Excretion
Vitamin Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extra Salts Excretion
Extra Salts Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys
Kidneys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine
Urine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron Function
Nephron Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Re-absorption
Re-absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
UTI Symptoms
UTI Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Role
Kidney Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes and Urine
Diabetes and Urine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Artificial kidney or Dialysis
Artificial kidney or Dialysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Calculi
Renal Calculi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Artificial Kidney
Artificial Kidney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Stone Formation
Kidney Stone Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Pigments Excretion
Bile Pigments Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney and Osmoregulation
Kidney and Osmoregulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Salts Excretion
Salts Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Stone Size
Kidney Stone Size
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Entering Nephron
Blood Entering Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Location
Kidney Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Type 2
Diabetes Type 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Content
Urine Content
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration process of blood
Filtration process of blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Outflow
Vitamin Outflow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where are kidneys located?
Where are kidneys located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra's role
Urethra's role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urea Formation
Urea Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Salt Balance
Salt Balance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron Input
Nephron Input
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron Structure
Nephron Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Osmoregulation?
What is Osmoregulation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is an Artificial Kidney?
What is an Artificial Kidney?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do Kidney Stones do?
What do Kidney Stones do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is UTI?
What is UTI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Ureters?
What are Ureters?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the Kidneys?
What are the Kidneys?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are nephrons?
What are nephrons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter Function
Ureter Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder Function
Urinary Bladder Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
What is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Dialysis?
What is Dialysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What function does the glomerulus do?
What function does the glomerulus do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Kidney Stone (renal calculi)?
What is a Kidney Stone (renal calculi)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Osmoregulation mediated by the Kidneys?
What is Osmoregulation mediated by the Kidneys?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Excretion is the removal of harmful and unwanted metabolic wastes from the body.
- Bodily activities produce waste products such as undigested food, water, carbon dioxide, heat, and urea.
- Undigested food is a waste product.
- Waste products like urea can be harmful and toxic if they accumulate in the body.
- Organisms have unique mechanisms to remove waste products.
Excretion in Humans
- Lungs excrete carbon dioxide and water vapor produced during respiration.
- Skin excretes urea, salt, and excess water through sweat glands.
- The large intestine excretes feces through the anus.
- Kidneys excrete urea and nitrogen in urine.
- The liver removes wastes from the blood, including drugs, vitamins, and bile pigments.
- The excretory system in humans is also called the urinary system.
Excreted Substances
- Urea and uric acid are nitrogenous wastes from amino acid breakdown in the liver, and they are excreted through the kidneys.
- Bile pigments are produced by the liver, are degraded, and expelled through urine.
- Excess water-soluble vitamins (B, C, K) are excreted in urine.
- Excess salts are expelled through sweat and in urine by the kidneys.
Excretory System Organs
- A pair of kidneys are part of the excretory system.
- Ureters are part of the excretory system.
- The urinary bladder is a component of the excretory system.
- The urethra is part of the excretory system.
- The urinary tract includes kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra.
- The urethra is longer in males than in females.
Kidneys
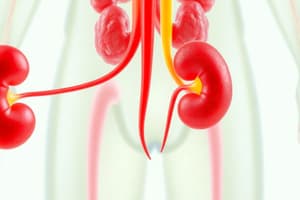
- Kidneys are bean-shaped, reddish-brown structures located above the waist on either side of the backbone.
- Kidneys consist of nephrons, which are structural and functional units that remove waste and regulate water balance.
- Liquid urine, containing 95% water, 2.5% urea, and 2.5% waste products, is formed in the kidneys.
Ureters
- Ureters are narrow tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder
- The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine and is located at the bottom of the abdomen.
- Urine passes from the kidneys through the ureters into the bladder.
- Urine collects and is stored in the urinary bladder.
Urethra
- The urethra is a tube through which urine is expelled from the body.
Kidney Function
- Each kidney contains about a million nephrons that filter blood.
- Each nephron consists of a glomerulus filter inside a Bowman’s capsule, and a coiled tubule ending in a collecting duct.
- High pressure in the glomerulus removes waste substances from the blood, which becomes urine in the tubules.
- Nephron tubules reabsorb useful substances like sugar and sodium ions, returning them to the blood.
- The blood leaving the kidney is purified of wastes but contains necessary substances in the right amounts.
- The urine formed is sent to the ureters and collects in the urinary bladder before being expelled through the urethra via urination.
- The process of expelling urine is called urination.
- Urine contains water, urea, uric acid, and mineral salts.
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- UTI is caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract.
- Most bacteria are expelled through urination, but infections can occur in kidneys, ureter, or urethra if bacteria persist.
- Symptoms include a frequent urge to urinate.
- Symptoms include cloudy, bloody or strong-smelling urine.
- Symptoms include pain or a burning sensation during urination.
Kidney Stones
- Kidney stones are formed when urine contains excess crystal-forming substances like calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, and uric acid.
- Kidney stones can be small or up to 2.5 cm in diameter.
- Small stones may pass without surgery, while large stones may require surgical removal.
- Kidney stones can cause blood in the urine.
- Kidney stones can cause severe abdominal pain if they block the ureter.
Osmoregulation
- Kidneys maintain salt and water concentration in the blood.
- This process of regulating salt and water concentration is called osmoregulation.
Diabetes
- Diabetes is a condition marked by high blood sugar levels, with excess sugar being excreted in urine.
Artificial Kidneys
- Dialysis or artificial kidneys filter and clean the blood when kidneys fail due to injury or infection preventing waste accumulation.
- Dialysis serves the function of kidneys artificially.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.