Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which region of Europe is known for having the warmest climate?
Which region of Europe is known for having the warmest climate?
- Central Europe
- Northern Europe
- Southern Europe (correct)
- Eastern Europe
The aratrum is a type of heavy plow used in Southern Europe for farming.
The aratrum is a type of heavy plow used in Southern Europe for farming.
False (B)
What percentage of the medieval European population worked in agriculture?
What percentage of the medieval European population worked in agriculture?
90 percent
Southern Europe is separated from the rest of Europe by the ______ mountain ranges.
Southern Europe is separated from the rest of Europe by the ______ mountain ranges.
Match the regions of Europe with their descriptions:
Match the regions of Europe with their descriptions:
What technological advancement allowed for faster draft animals to be used in farming?
What technological advancement allowed for faster draft animals to be used in farming?
Farmers in ancient Rome widely adopted the moldboard plow due to its efficiency in heavy soil.
Farmers in ancient Rome widely adopted the moldboard plow due to its efficiency in heavy soil.
What period is known as the Medieval Climatic Optimum?
What period is known as the Medieval Climatic Optimum?
The Great Bovine Pestilence of 1319-1320 caused a significant reduction in ___ products.
The Great Bovine Pestilence of 1319-1320 caused a significant reduction in ___ products.
Match the following agricultural advancements to their effects:
Match the following agricultural advancements to their effects:
What was one consequence of the increased population during the Middle Ages?
What was one consequence of the increased population during the Middle Ages?
Heavy rains and flooding were less dangerous to people than long-term climate changes.
Heavy rains and flooding were less dangerous to people than long-term climate changes.
What impact did the introduction of rye and barley have on agriculture in northern climates?
What impact did the introduction of rye and barley have on agriculture in northern climates?
Waterwheels and windmills increased the amount of work that could be done, providing ______ to power various activities.
Waterwheels and windmills increased the amount of work that could be done, providing ______ to power various activities.
Which of the following events is associated with the spread of the Black Death?
Which of the following events is associated with the spread of the Black Death?
Flashcards
Medieval Europe's Agriculture
Medieval Europe's Agriculture
Ninety percent of medieval Europeans were farmers, making agriculture crucial to understanding their environment interactions.
Southern Europe's Farming
Southern Europe's Farming
Southern European agriculture differed from other regions due to its climate, using the aratrum, a light plow.
Europe's Five Regions
Europe's Five Regions
Europe is divided into five regions: Northern, Southern, Eastern, Western, and Central, each with its own physical geography and climate.
Europe's Physical Geography
Europe's Physical Geography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human-Environment Interaction (Medieval Europe)
Human-Environment Interaction (Medieval Europe)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moldboard plow
Moldboard plow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Manorial system
Manorial system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horseshoes and horse collar
Horseshoes and horse collar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crop rotation
Crop rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medieval Warm Period
Medieval Warm Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Climate effects on agriculture
Climate effects on agriculture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water and windmills
Water and windmills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specialization and trade
Specialization and trade
Signup and view all the flashcards
Black Death
Black Death
Signup and view all the flashcards
Increased transportation
Increased transportation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Human-Environment Interaction in Medieval Europe
- Medieval Europe saw complex interactions between humans and the environment, not just environmental impact on humans.
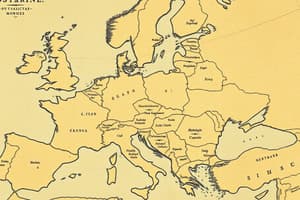
Basic Physical Geography of Europe
- Europe is divided into five regions: Northern, Southern, Eastern, Western, and Central.
- Each region has distinct characteristics: physical geography, climate, native plants/animals.
- Northern Europe (Scandinavia, Denmark, Iceland) experiences long periods of limited daylight.
- Southern Europe (Iberian, Apennine, Balkan Peninsulas) has a warm climate, geographically separated by mountains (Pyrenees, Alps, Carpathians).
- Eastern Europe forms a boundary between Northern, Southern, and Central Europe, extending in both latitude and longitude.
- Western Europe (France, Belgium, Netherlands, Great Britain, Ireland) includes the Iberian Peninsula, despite its westerly location.
- Central Europe is landlocked, bordering all the other European regions.
Medieval European Agriculture
- 90% of medieval Europe's population was involved in agriculture.
- Southern Europe's dry, hot climate supported the aratrum (light plow).
- Northern European soil (north of Alps/Pyrenees) required the moldboard plow (deep plowing).
- The moldboard plow, needing more draft animals, remained less common due to the manorial system's emergence. Long, rectangular plots were better suited to it.
- Technological advancements—horseshoes, horse collars, three-field crop rotation, manure use, rye and barley adoption—led to increased food production and population growth. The Medieval Warm Period (1150-1350) also contributed.
- Frequent crop failures (1243, 1258, 1315-1317 Great Famine, Bovine Pestilence 1319-1320) strained resources and likely contributed to the high mortality associated with the Black Death (1347-1352).
- The use of the aratrum over the moldboard plow in certain regions showcases human adaptation and the influence of local geographic conditions.
Increased Population and Its Consequences
- Population growth led to specialization, new forms of human-environment interaction, and increased trade.
- Water and wind power (waterwheels and windmills) became widely used for various tasks in agriculture, industry, and daily life (e.g., milling, brewing, wool preparation, metalworking).
- Trade networks expanded, connecting Europe and other parts of the world.
- Transport challenges included natural hazards and human-caused obstacles.
- Shipping advancements (cogs) led to increased wood use, deforestation, and urban pollution.
Pollution
- Population growth and expansion led to deforestation and increased fuel use (e.g. Coal), impacting air quality.
- Urbanization further contributed to pollution.
- Growing trade spurred concerns about environmental "nuisances" (e.g., waste, polluted streams) in cities like London.
- The Black Death spread via trade routes.
- Canals and locks were built to overcome geographic and waterway challenges and facilitate trade.
Trade & Transport
- Trade networks expanded, connecting Europe and other parts of the world.
- Merchants faced natural hazards and human-caused obstacles.
- Expanded trade routes facilitated the spread of products and, during the black death, disease across Afroeurasia.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.