Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the internal framework of the human body called?
What is the internal framework of the human body called?
Skeletal system
At what age does the human skeleton reach maximum density?
At what age does the human skeleton reach maximum density?
- 30 years
- 10 years
- 20 years (correct)
- 40 years
Which of the following is not a type of bone classification?
Which of the following is not a type of bone classification?
- Round Bones (correct)
- Irregular Bones
- Long Bones
- Flat Bones
What are the three types of muscles in the muscular system?
What are the three types of muscles in the muscular system?
What does the circulatory system consist of?
What does the circulatory system consist of?
Veins carry blood away from the heart.
Veins carry blood away from the heart.
The main organs of the digestive system include the mouth, stomach, and ________.
The main organs of the digestive system include the mouth, stomach, and ________.
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
Which of the following food hygiene practices helps to ensure food safety?
Which of the following food hygiene practices helps to ensure food safety?
What is the average requirement of sleep for an individual?
What is the average requirement of sleep for an individual?
Match the following types of refuse with their descriptions:
Match the following types of refuse with their descriptions:
What is the process by which waste products are removed from the body called?
What is the process by which waste products are removed from the body called?
What was the previous name of the Department of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy before it was renamed in November 2003?
What was the previous name of the Department of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy before it was renamed in November 2003?
The National Cadet Corps (NCC) was awarded the Limca Book of Records for the smallest yoga performance by a single youth organization.
The National Cadet Corps (NCC) was awarded the Limca Book of Records for the smallest yoga performance by a single youth organization.
On which date is International Day of Yoga celebrated?
On which date is International Day of Yoga celebrated?
What are the six major functions performed by the human skeleton?
What are the six major functions performed by the human skeleton?
Which of the following is a method to prevent insect-borne diseases? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following is a method to prevent insect-borne diseases? (Select all that apply)
Match the types of bones with their classifications:
Match the types of bones with their classifications:
The human skeleton is composed of around ______ bones at birth.
The human skeleton is composed of around ______ bones at birth.
Early diagnosis can help prevent the spread of disease in patients.
Early diagnosis can help prevent the spread of disease in patients.
What is the recommended action in case of contact with sick or dead animals?
What is the recommended action in case of contact with sick or dead animals?
What is one method of disinfecting articles in contact with patients?
What is one method of disinfecting articles in contact with patients?
What should be done in the case of protruding organs due to an abdominal injury?
What should be done in the case of protruding organs due to an abdominal injury?
It is safe to apply ice to a snake bite area.
It is safe to apply ice to a snake bite area.
Burns may be caused by __________ or __________.
Burns may be caused by __________ or __________.
Which vaccine is used to prevent rabies?
Which vaccine is used to prevent rabies?
What is a common treatment for a snake bite?
What is a common treatment for a snake bite?
What is a key sign of internal bleeding?
What is a key sign of internal bleeding?
Which of the following is used for making bricks?
Which of the following is used for making bricks?
What is the primary use of Soft Core?
What is the primary use of Soft Core?
The Hard Core is used for metaling of roads.
The Hard Core is used for metaling of roads.
What type of latrines are used in areas with a proper sewage system?
What type of latrines are used in areas with a proper sewage system?
What is a Bore Hole Latrine?
What is a Bore Hole Latrine?
What are the two important functions of a Water Seal Latrine?
What are the two important functions of a Water Seal Latrine?
What is the purpose of a Soakage Pit?
What is the purpose of a Soakage Pit?
Good health includes both physical and mental well-being.
Good health includes both physical and mental well-being.
Which of the following is NOT a component of health?
Which of the following is NOT a component of health?
What is one indicator of mental disorders?
What is one indicator of mental disorders?
What is a common disease spread through water?
What is a common disease spread through water?
Mental health does not affect physical health.
Mental health does not affect physical health.
What should be done if someone is choking?
What should be done if someone is choking?
The main causes of Asphyxia include drowning, hanging, suffocation, _____, electric shock, and certain diseases.
The main causes of Asphyxia include drowning, hanging, suffocation, _____, electric shock, and certain diseases.
Breathing occurs in three phases: inspiration, expiration, and pause.
Breathing occurs in three phases: inspiration, expiration, and pause.
What should be done for a patient who is unconscious?
What should be done for a patient who is unconscious?
What is the best position for a person suffering from breathing difficulties?
What is the best position for a person suffering from breathing difficulties?
What type of gas is commonly inhaled that can lead to Asphyxia?
What type of gas is commonly inhaled that can lead to Asphyxia?
In case of electric shock, the first step is to ____ the current.
In case of electric shock, the first step is to ____ the current.
A traction splint is used for fractures of the pelvis.
A traction splint is used for fractures of the pelvis.
Match the following types of wounds with their descriptions:
Match the following types of wounds with their descriptions:
What day is declared by the UNO as the International Day of Yoga?
What day is declared by the UNO as the International Day of Yoga?
Yoga has its origins in ancient China.
Yoga has its origins in ancient China.
What is the aim of dressing a wound?
What is the aim of dressing a wound?
What has yoga entered into in modern times?
What has yoga entered into in modern times?
Who is known as the father of yoga?
Who is known as the father of yoga?
Which of the following is NOT one of the eight folds of yoga?
Which of the following is NOT one of the eight folds of yoga?
Yoga is a team activity.
Yoga is a team activity.
What are some benefits reported by yoga practitioners?
What are some benefits reported by yoga practitioners?
What does regular yoga practice increase in the brain?
What does regular yoga practice increase in the brain?
How might yoga affect people with heart disease?
How might yoga affect people with heart disease?
Yoga helps in reducing symptoms of __________.
Yoga helps in reducing symptoms of __________.
What is one psychological benefit of yoga?
What is one psychological benefit of yoga?
Which asana is said to help with insomnia, asthma, and hysteria?
Which asana is said to help with insomnia, asthma, and hysteria?
Yoga can be detrimental to individuals with certain __________.
Yoga can be detrimental to individuals with certain __________.
Which type of yoga is recommended for children under 16?
Which type of yoga is recommended for children under 16?
What is the main function of Siddhasana?
What is the main function of Siddhasana?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Health and Hygiene Overview
- Study material includes topics on Health & Hygiene, Judging Distances, Map Reading, and Obstacles.
- Emphasizes the importance of first aid knowledge for saving lives.
Structure and Functioning of the Human Body
- The human body consists of complex systems requiring basic understanding for effective first aid.
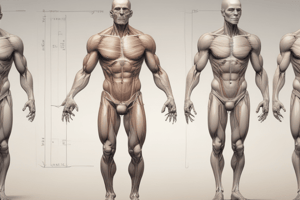
- Skeletal System: Composed of approximately 300 bones at birth, reduced to 206 in adulthood due to fusion.
- Divided into Axial Skeleton (skull, rib cage, vertebral column) and Appendicular Skeleton (limbs, shoulder, and pelvic girdles).
- Major functions of the skeleton: support, movement, protection, blood cell production, mineral storage, and endocrine regulation.
- Muscular System: Includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles; responsible for body movement and blood circulation.
- Muscles constitute about 50% of body weight; they form the flesh of the body.
- Muscle types:
- Voluntary (Skeletal): Attached to bones, responsible for joint movements; 47% of body weight.
- Involuntary: Controlled by autonomic nervous system.
- Cardiac: Found in the heart, striated but functionally involuntary.
Organ Systems Overview
-
Circulatory System: Composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood; responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients while removing waste.
- The heart is a four-chambered organ located in the thorax, weighing about 300g for males and 250g for females.
- Blood vessels consist of arteries (carry blood away from the heart), capillaries (exchange of substances), and veins (bring blood back to the heart).
-
Respiratory System: Facilitates gas exchange, consisting of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
-
Digestive System: Involves organs that process food, converting complex substances into simpler forms for absorption.
-
Excretory System: Manages waste removal; organs involved include the skin, lungs, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
-
Nervous System: Comprises the Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord), Peripheral Nervous System (connects CNS to body), and Autonomic Nervous System (controls involuntary functions).
Hygiene and Sanitation
- Maintaining hygiene aids in preventing infections and promotes health in individuals and communities.
- Personal Hygiene: Essential practices include sufficient sleep (7-8 hours), regular bathing, brushing teeth, and nail care.
- Food Hygiene: Involves safety measures from food production to consumption; critical to prevent foodborne illnesses.
- Five keys to safer food: Keep clean, separate raw and cooked, cook thoroughly, maintain safe temperatures, use safe water and materials.
Specifics on Food Hygiene
- Safe milk production involves healthy animals, clean handling, and proper pasteurization.
- Meat and fish hygiene focus on freshness and sanitation to prevent food poisoning.
- Eggs need washing to ensure hygiene, with fruits and vegetables requiring thorough washing before consumption.
Sanitation
- Definition focuses on maintaining clean living environments by managing waste and refuse.
- Major waste types include human excreta, stable litter, dry refuse, and liquid wastes.
- Various refuse disposal methods: filling, controlled tipping, incineration, composting, burial, and sorting.
Disposal of Human Waste
- Essential for preventing diseases and contamination of the environment.
- Two systems exist:
- Sewered Areas: Utilize flush latrines; require consistent water supply.
- Unsewered Areas: Use domestic latrines, such as borehole and dug well latrines for natural waste management.
Conclusion
- Knowledge of body systems and hygiene practices is foundational for health, hygiene, and first aid skills development.
- Ensures individual and community health standards are upheld through awareness and education.### Sanitation and Latrines
- Sandy soil allows pit depths for latrines to be reduced to 1.5 to 2 meters.
- Water seal latrines prevent flies and foul odors, with the RCA type being popular.
- Deep trench latrines should be three feet wide, at least eight feet deep, and filled with soil upon camp departure to aid in decomposition.
- Shallow trench latrines, for camps under a week, involve 3-foot long, 1-foot wide, and 2-foot deep trenches, filled after 24 hours.
- Funnel urinals are typically used in camps and placed over soakage pits.
- Soakage pits for liquid waste should measure 4 feet by 4 feet and 5 to 6 feet deep, filled with stones and bricks.
- Solid waste disposal involves either burial or burning; municipal arrangements are recommended for garbage disposal.
Sewage Treatment and Disposal
- Effective sewage treatment includes screening, chambering, primary sedimentation, trickling filters, and activated sludge processes.
- Disposal methods for untreated sewage include:
- Sea outfall for coastal regions.
- River outfall for towns near rivers.
- Land treatment primarily for villages.
- Oxidation ponds for sewage degradation.
Physical and Mental Health
- Health encompasses physical, mental, social well-being, adapting to changes, and managing stress.
- Elements of good health include the absence of disease, efficient workability, stress endurance, cheerfulness, and well-being.
- Components of health are physical activity, nutrition, limitations on alcohol and drugs, self-care, and adequate rest.
- Regular physical activity enhances both physical and mental health, with a recommendation of 7-9 hours of quality sleep.
Mental Health
- Mental health influences emotions, relationships, stress management, and life choices; it's vital at every life stage.
- Key indicators of mental disorders include social embarrassment, pessimism, undue anxiety, and irritability.
- Improving mental health can be achieved through a stress-free environment, regular examinations, educational guidance, and extracurricular activities.
Infectious and Contagious Diseases
- Diseases result from abnormal conditions affecting structures or functions in the body, with classifications as:
- Excremental diseases (e.g., typhus, dysentery) transmitted through human excreta.
- Droplet infections (e.g., cold, influenza) spread through respiratory droplets.
- Contact diseases (e.g., syphilis) require direct body contact.
- Insect-borne diseases (e.g., malaria, dengue) transmitted by blood-sucking insects.
- Water-borne diseases (e.g., cholera), arise from contaminated water sources.
- Animal-borne diseases (e.g., rabies, anthrax) transmitted through animal interaction.
Preventive Health Measures
- Preventing excremental and water-borne diseases includes:
- Disinfecting water and ensuring food hygiene.
- Proper disposal of human waste.
- Preventing droplet infections involves masks, adequate ventilation, and avoiding overcrowding.
- Contact disease prevention includes patient segregation and early diagnosis.
- Insect-borne disease prevention requires eliminating breeding sites and using insect repellents.
- Ensuring a hygienic and clean environment is crucial in controlling disease spread.### Ionizing Radiation for Disinfection
- Ionizing radiations include X-rays, gamma rays, beta rays, and ultraviolet radiation.
- These methods are costly and unsuitable for small-scale applications.
Alternative Disinfection Methods
- Infrared rays and filtration can also be used for disinfection and sterilization.
Chemical Agents for Sterilization
- Common chemical agents include phenol, Savlon, potassium permanganate, and hydrogen peroxide.
- Effectiveness is contingent upon the concentration used.
Patient Feeding Guidelines
- Serve clean, preferably boiled water, in covered containers.
- Provide balanced, well-cooked meals that are hygienically prepared, using minimal oil and condiments.
- Avoid serving stale or cold food, or food exposed to flies and insects.
- Do not serve food sourced from restaurants or roadside vendors.
Inoculations and Vaccinations
- Vaccinations are offered for free under various government programs at Primary Health Centers or hospitals.
- Important vaccines include:
- Rabipur for Rabies
- TAB for Typhoid
- Hepatitis B vaccine
- Tetanus Toxoid (TT)
- Oral Polio vaccine
Challenges in Diagnosing Infectious Causes
- Chronic diseases often have multifactorial causes.
- Environmental and genetic variations among populations complicate diagnosis.
- New molecular and immunological techniques offer potential solutions.
First Aid Fundamentals
- First aid involves immediate assistance to preserve life and prevent worsening conditions.
- Techniques are straightforward and typically use basic equipment, administered by laypeople until professional help arrives.
Recognizing Internal Injuries
- Symptoms of internal injuries include cold clammy skin, weak or rapid pulse, shallow breathing, pale face, and restlessness.
- Internal trauma can often remain unnoticed until severe.
Closed Chest Injuries
- Serious nature due to critical organs in the chest cavity; always seek professional help.
- Rib injuries can vary in severity and may lead to complications.
Signs of Rib Injuries
- Trouble breathing, tenderness at injury site, deformity, and possible blood in cough.
Treatment for Closed Chest Injuries
- Call for an ambulance, assist the victim into a comfortable position, and conduct a secondary survey.
Open Chest Wounds
- Identified by air escaping from the chest wall and possible sucking sounds.
Treatment for Open Chest Wounds
- Assess airway, call for assistance, and do not remove embedded objects.
Abdominal Injuries
- If organs are visible, cover them with a moist, sterile dressing without pushing them back in.
Burns and Scalds
- Burns can result from heat or chemical exposure; treatment includes rinsing and protecting the area.
Snake Bites
- Require rapid reassurance, application of a light constricting tourniquet, and quick evacuation for medical treatment.
Treatment for Scorpion and Dog Bites
- Similar to snake bite protocols, emphasizing wound cleaning and observing for rabies in dog bites.
Foreign Bodies
- In eyes, ears, or nose should not be removed forcefully, prompting immediate medical evaluation.
Asphyxia Overview
- Defined as impaired breathing leading to oxygen deprivation, with various causes including drowning and choking.
- Treatment involves ensuring an open airway and administering artificial respiration if necessary.
First Aid for Drowning
- Clear air passages, provide artificial respiration, and keep the patient warm.
First Aid for Electric Shock
- Disconnect power source safely, check for breathing, and administer artificial respiration as needed.
Insensibility and Unconsciousness
- Caused by interruptions in brain function; treatments focus on maintaining an open airway and monitoring vital signs.
Mouth to Mouth Respiration
- A key method for artificial respiration, requiring a clean airway and a structured technique to deliver breaths effectively.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.