Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the heart?
What is the primary function of the heart?
- To provide oxygen to the lungs
- To remove carbon dioxide from the body
- To pump blood only to the brain
- To provide a constant and equal flow of blood throughout the body (correct)
What is the purpose of the coronary vessels?
What is the purpose of the coronary vessels?
- To supply oxygen to the lungs
- To remove waste products from the body
- To supply blood to the heart muscle itself (correct)
- To pump blood to the rest of the body
What is the term for the flow of blood throughout the entire body?
What is the term for the flow of blood throughout the entire body?
- Coronary circulation
- Pulmonary circulation
- Cardiac circulation
- Systemic circulation (correct)
What is the function of the superior and inferior vena cavae?
What is the function of the superior and inferior vena cavae?
What is the importance of blood flow to cells?
What is the importance of blood flow to cells?
What is the term for the flow of blood between the heart and lungs?
What is the term for the flow of blood between the heart and lungs?
What is the location of the heart?
What is the location of the heart?
What is the result of a lack of blood flow to cells?
What is the result of a lack of blood flow to cells?
What is the primary role of the ribcage in relation to the heart?
What is the primary role of the ribcage in relation to the heart?
What is the term that describes the flow of blood that supplies oxygen and nutrients to all cells in the body?
What is the term that describes the flow of blood that supplies oxygen and nutrients to all cells in the body?
Which blood vessels supply blood to the heart muscle itself?
Which blood vessels supply blood to the heart muscle itself?
What is the result of the heart's pumping action?
What is the result of the heart's pumping action?
What is the purpose of the diaphragm in relation to the heart?
What is the purpose of the diaphragm in relation to the heart?
What would occur if the heart failed to maintain a constant flow of blood throughout the body?
What would occur if the heart failed to maintain a constant flow of blood throughout the body?
What is the relationship between the coronary vessels and systemic circulation?
What is the relationship between the coronary vessels and systemic circulation?
Where does blood from the feet and legs flow back to?
Where does blood from the feet and legs flow back to?
From where does blood flow into the heart?
From where does blood flow into the heart?
What is the location of the jugular veins?
What is the location of the jugular veins?
When does the heart start pumping?
When does the heart start pumping?
What is the heart surrounded by?
What is the heart surrounded by?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Heart and Its Functions
- The heart is located between the two lungs, surrounded by the ribcage, which provides protection to the heart and lungs.
- The heart is protected by the ribcage, which forms the walls and floor of the thorax, and the diaphragm forms the ceiling.
The Heart's Functions
- The heart's primary function is to provide a constant and equal flow of blood throughout the body, ensuring all cells receive oxygen and nutrients.
- The heart is a strong pump that drains blood from the body and pumps it back out, providing systemic circulation.
Systemic Circulation
- Systemic circulation refers to the flow of blood throughout the entire body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to all cells.
- The heart pumps blood into the aorta, which then distributes it to the rest of the body.
- The superior and inferior vena cavae return blood from the body to the heart.
Pulmonary Circulation
- Pulmonary circulation refers to the flow of blood between the heart and lungs, providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide.
- The heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, and then returns to the heart.
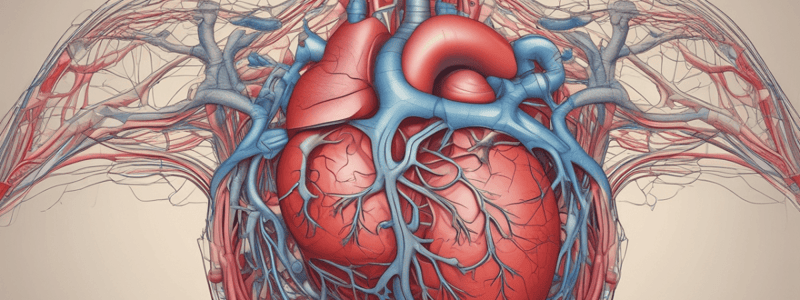
Coronary Vessels
- The coronary vessels supply blood to the heart muscle itself, providing oxygen and nutrients to the heart's cells.
- The coronary vessels are part of the systemic circulation, as their primary function is to supply the heart muscle.
Importance of Blood Flow
- Blood flow is essential for the survival of cells, as it provides oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products.
- Without blood flow, cells would accumulate waste and eventually die.
- The heart's function is crucial in maintaining a constant flow of blood throughout the body, ensuring the survival of all cells.
Location and Protection of the Heart
- Situated between the two lungs, surrounded by the ribcage for protection
- The ribcage forms the walls and floor of the thorax, while the diaphragm forms the ceiling
Functions of the Heart
- Primary function: provide constant and equal flow of blood throughout the body
- Ensure all cells receive oxygen and nutrients
- Acts as a strong pump to drain blood from the body and pump it back out for systemic circulation
Systemic Circulation
- Refers to the flow of blood throughout the entire body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to all cells
- Heart pumps blood into the aorta, which distributes it to the rest of the body
- Superior and inferior vena cavae return blood from the body to the heart
Pulmonary Circulation
- Refers to the flow of blood between the heart and lungs, providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
- Heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, and then returns to the heart
Coronary Vessels
- Supply blood to the heart muscle itself, providing oxygen and nutrients to the heart's cells
- Part of the systemic circulation, with the primary function of supplying the heart muscle
Importance of Blood Flow
- Essential for cell survival, as it provides oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products
- Cells would accumulate waste and eventually die without blood flow
- The heart's function is crucial in maintaining a constant flow of blood throughout the body, ensuring the survival of all cells
Location and Protection of the Heart
- Situated between the two lungs, surrounded by the ribcage for protection
- The ribcage forms the walls and floor of the thorax, while the diaphragm forms the ceiling
Functions of the Heart
- Primary function: provide constant and equal flow of blood throughout the body
- Ensure all cells receive oxygen and nutrients
- Acts as a strong pump to drain blood from the body and pump it back out for systemic circulation
Systemic Circulation
- Refers to the flow of blood throughout the entire body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to all cells
- Heart pumps blood into the aorta, which distributes it to the rest of the body
- Superior and inferior vena cavae return blood from the body to the heart
Pulmonary Circulation
- Refers to the flow of blood between the heart and lungs, providing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
- Heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, and then returns to the heart
Coronary Vessels
- Supply blood to the heart muscle itself, providing oxygen and nutrients to the heart's cells
- Part of the systemic circulation, with the primary function of supplying the heart muscle
Importance of Blood Flow
- Essential for cell survival, as it provides oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products
- Cells would accumulate waste and eventually die without blood flow
- The heart's function is crucial in maintaining a constant flow of blood throughout the body, ensuring the survival of all cells
Heart Structure and Function
- The heart is a vital organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, starting from the 8th week of fetal development and continuing until death.
- It is located in the center of the chest, surrounded by other organs.
Blood Circulation
- Blood from all parts of the body flows back into the heart, which then pumps it back out to the periphery.
- Blood from the feet and legs flows back to the heart through veins.
- Blood from the head and arms flows back to the heart through jugular veins, which merge into a large vein at the top of the heart.
Heart Chambers
- The heart has multiple chambers where blood flows in and out.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.