Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is one significant characteristic of Homo habilis?
What is one significant characteristic of Homo habilis?
- Larger brow ridges than its predecessors
- Increased cranial capacity over earlier hominids (correct)
- First to develop complex language
- Used advanced wooden tools
Which hominid species is recognized as the first to likely migrate out of Africa?
Which hominid species is recognized as the first to likely migrate out of Africa?
- Homo erectus (correct)
- Australopithecines
- Paranathropus
- Homo habilis
What type of tools is associated with Homo erectus?
What type of tools is associated with Homo erectus?
- Acheulean tools
- Copper tools
- Mousterian tools
- Oldowan-style tools (correct)
Which of the following best describes 'premodern humans'?
Which of the following best describes 'premodern humans'?
What subsistence strategy is likely associated with Homo habilis?
What subsistence strategy is likely associated with Homo habilis?
What is the primary characteristic of polygenic adaptation?
What is the primary characteristic of polygenic adaptation?
Why is lighter skin advantageous in colder environments?
Why is lighter skin advantageous in colder environments?
How do genetic ancestry tests typically determine a person's ancestry?
How do genetic ancestry tests typically determine a person's ancestry?
Which condition is NOT a result of adaptive selection in human populations?
Which condition is NOT a result of adaptive selection in human populations?
What term describes a group of similar halotypes sharing a common ancestor?
What term describes a group of similar halotypes sharing a common ancestor?
Which factor does NOT influence the definition of reference populations in genetic ancestry tests?
Which factor does NOT influence the definition of reference populations in genetic ancestry tests?
Why is genetic drift important in the study of population genetics?
Why is genetic drift important in the study of population genetics?
What effect does changing reference group data have on genetic ancestry tests?
What effect does changing reference group data have on genetic ancestry tests?
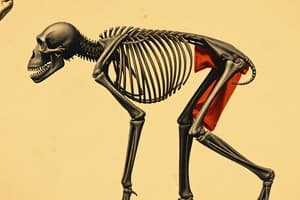
What primarily characterizes the muscle fibers of chimpanzees?
What primarily characterizes the muscle fibers of chimpanzees?
Which feature supports the hypothesis that Homo erectus practiced persistence hunting?
Which feature supports the hypothesis that Homo erectus practiced persistence hunting?
What adaptation aids humans in thermoregulation during physical activity?
What adaptation aids humans in thermoregulation during physical activity?
What is one reason humans may have a higher percentage of body fat compared to other primates?
What is one reason humans may have a higher percentage of body fat compared to other primates?
Which of the following is NOT a health benefit of exercise?
Which of the following is NOT a health benefit of exercise?
How do fast-twitch muscle fibers compare to slow-twitch fibers?
How do fast-twitch muscle fibers compare to slow-twitch fibers?
What key evolutionary trait assists humans in avoiding unnecessary energy expenditure?
What key evolutionary trait assists humans in avoiding unnecessary energy expenditure?
Which characteristic is associated with slow-twitch muscle fibers?
Which characteristic is associated with slow-twitch muscle fibers?
What time period does the term 'Paleolithic' refer to, according to the content?
What time period does the term 'Paleolithic' refer to, according to the content?
According to the 'Paleo Diet', which macronutrient should make up the largest percentage of calories?
According to the 'Paleo Diet', which macronutrient should make up the largest percentage of calories?
Which of the following is NOT recommended by the 'Paleo Diet'?
Which of the following is NOT recommended by the 'Paleo Diet'?
What is a characteristic of the diets of hunter-gatherers as mentioned in the content?
What is a characteristic of the diets of hunter-gatherers as mentioned in the content?
What do critiques of the 'Paleo Diet' emphasize?
What do critiques of the 'Paleo Diet' emphasize?
Which condition reflects the concept of evolutionary mismatch?
Which condition reflects the concept of evolutionary mismatch?
What has been a result of the nutrition transition mentioned in the content?
What has been a result of the nutrition transition mentioned in the content?
What is a common feature of hunter-gatherer diets compared to the typical American diet?
What is a common feature of hunter-gatherer diets compared to the typical American diet?
Which of the following factors is associated with a longer expected lifespan at age 15 among hunter-gatherers?
Which of the following factors is associated with a longer expected lifespan at age 15 among hunter-gatherers?
What does the 'Paleo Diet' suggest regarding the consumption of added sugars?
What does the 'Paleo Diet' suggest regarding the consumption of added sugars?
What is the primary aim of the One Health initiative?
What is the primary aim of the One Health initiative?
Which of the following is a method of non-shivering thermogenesis?
Which of the following is a method of non-shivering thermogenesis?
What role does Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) play in thermoregulation?
What role does Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) play in thermoregulation?
During acclimatization to cold stress, which of the following changes occurs?
During acclimatization to cold stress, which of the following changes occurs?
What is a common genetic adaptation to cold stress observed in circumpolar populations?
What is a common genetic adaptation to cold stress observed in circumpolar populations?
What is triiodothyronine (T3) and its role during winter?
What is triiodothyronine (T3) and its role during winter?
Which physiological response is part of the allostatic response to heat stress?
Which physiological response is part of the allostatic response to heat stress?
What physiological change is NOT typically observed during acclimatization to heat stress?
What physiological change is NOT typically observed during acclimatization to heat stress?
Flashcards
Homo habilis
Homo habilis
Early hominin (2.4 million years ago) with reduced facial size, moderate brow ridges, and increased brain size (630 cc).
Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Hominin first found outside Africa (2 million years ago), with a larger body size and brain size (750-1250 cc) than Homo habilis.
Archaic H. Sapiens
Archaic H. Sapiens
Premodern human group (Neanderthals, Denisovans, H. Heidelbergensis) with suspected evolution influenced by genetic drift and mutation.
Hard Selective Sweep
Hard Selective Sweep
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polygenic Adaptation
Polygenic Adaptation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin pigmentation
Skin pigmentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lactose tolerance
Lactose tolerance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paleo Diet
Paleo Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Haplogroup
Haplogroup
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hunter-gatherer lifespan
Hunter-gatherer lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fast-twitch muscle fibers
Fast-twitch muscle fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slow-twitch muscle fibers
Slow-twitch muscle fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bipedalism
Bipedalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metabolic adaptation to cold climates
Metabolic adaptation to cold climates
Signup and view all the flashcards
One Health
One Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evolutionary Mismatch
Evolutionary Mismatch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT)
Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allostatic Response to cold stress
Allostatic Response to cold stress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allostatic Response to heat stress
Allostatic Response to heat stress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acclimatization to cold
Acclimatization to cold
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acclimatization to heat
Acclimatization to heat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic adaptation to cold
Genetic adaptation to cold
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nutrition transition
Nutrition transition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Hominid Evolution
-
Homo habilis (2.4 million years ago)
- Reduced facial size
- Moderate-small brow ridges
- Encephalization (increased brain size relative to body size)
- Homo habilis - 630 cc
- Paranthropus - 520 cc
- Australopithecines - 442 cc
- Possibly the first hominins to use stone tools for grinding food
- Hunter-gatherer subsistence strategy
-
Homo erectus (2 million years ago, East Africa)
- First hominid group found outside of Africa
- Oldowan-style tools
- Body size:
- Weight > 100 lbs; average height ~ 5’6”
- “Nariokotome Boy” (Kenya)
- Brain size:
- Cranial capacity between 750 - 1250 cc
- Overlaps modern human cranial capacity
- Possibly existed for over 1 million years
Premodern Humans
- "Archaic H. Sapiens" (no clear consensus, but includes Neanderthals, Denisovans, and H. Heidelbergensis)
- Genetic drift and mutation are thought to have played a role in their evolution
Human Adaptation
- Hard Selective Sweep Model:
- Humans migrating into new environments experience strong selection for new beneficial mutations
- Polygenic Adaptation:
- Natural selection for multiple alleles that already exist in the population
- Each allele has a small effect on the adaptive phenotype
- A faster mode of adaptation
- Examples of Selective Sweeps:
- Skin pigmentation:
- UV radiation and vitamin D production
- Darker skin in higher UV environments
- Lighter skin in lower UV environments
- Metabolic adaptation to cold climates:
- Alaskan-native populations have higher frequencies of alleles related to cold adaptation
- Lactose tolerance:
- Infectious disease susceptibility:
- Malaria and the sickle cell allele
- Adaptation to high altitude hypoxia
- Skin pigmentation:
Direct-to-Consumer Ancestry Testing
- DNA ancestry tests compare the test-taker's haplogroups to the frequency of haplogroups in reference populations.
- Haplogroup: A group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor.
- The genetic clustering in a reference population depends on which individuals are included in the database.
- Changes in the reference group data can change the results of the test.
"Paleo Diet"
- Argues that a healthy diet should mimic the diet of Paleolithic hunter-gatherers.
- Reasons:
- Human digestion and nutritional needs may not be adapted to post-agricultural revolution diets.
- Archaeological evidence suggests that agriculture doesn't inherently lead to healthier populations.
- Diets rich in added sugar, low fiber, and refined carbohydrates are associated with metabolic diseases.
- Insufficient time for substantial genomic adaptations to contemporary diets (exceptions: lactase persistence, enhanced salivary amylase production).
- Macronutrient composition:
- 35% of calories from protein
- 45% of calories from carbohydrates (mostly non-starchy fruits and vegetables with high fiber)
- 28-47% of calories from fat (low saturated fat)
- Avoids added sugar, dairy, grains, starchy tubers, and legumes.
Health of Hunter-Gatherers
- Low rates of chronic diseases (heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, cancer).
- Expected lifespan at birth: 30-40 years old (due to high infant mortality).
- Expected lifespan at age 15: 72 years old.
Critiques of the “Paleo Diet”
- There is no single Paleolithic diet.
- Wide variation in macronutrient composition and plant- vs. animal-derived foods across populations.
- Wide variation across seasons and years.
- Archaeological evidence for consumption of cereals, starchy tubers, and legumes during the Paleolithic.
- Not all aspects of modern diets are inherently unhealthy.
Common Characteristics of Hunter-Gatherer Diets
- Mix of meat, fish, and plants.
- More fiber than typical American diets.
- Most carbohydrates come from vegetables and starchy plants.
- Low glycemic index.
Nutrition Transition
- Shift from subsistence to wage/market economy.
- Increased availability of market foods and energy.
- Reduced activity and energy expenditure.
Physical Activity and the Constrained Total Energy Expenditure Hypothesis
- Evolutionary mismatch conditions refer to diseases more prevalent or severe today than in the past due to inadequate adaptation to modern environments.
- Sedentary Lifestyle as an Evolutionary Mismatch:
- Last common ancestor (LCA) between humans and chimps had many chimpanzee-like characteristics.
- Chimpanzee physical activity:
- Twice as strong as humans.
- Walk less than 1.5 miles per day.
- Rarely sprint.
- Leg muscles are mostly fast-twitch fibers.
- Can’t cool effectively through sweating.
Fast-Twitch vs. Slow-Twitch Muscle Fibers
-
Fast Twitch:
- Can split ATP very quickly.
- Rely on anaerobic metabolism.
- Contract 2-3 times faster than slow-twitch.
- Good for short bursts of strength or speed.
-
Slow Twitch:
- More metabolically efficient.
- Rely on aerobic metabolism.
- Slower speed of contraction.
- Greater endurance than fast-twitch.
Evolution of Bipedalism
- Australopithecus: Pronounced adaptations to bipedalism.
- Homo erectus:
- Persistence hunting.
- Expanded gluteus maximus.
- Short toes.
- Head stabilization for running.
- Humans evolved to be adapted for regular, moderate amounts of endurance physical activity.
- More slow-twitch muscle fibers.
- Evolved efficient sweating for thermoregulation.
- Large glutes.
- Humans evolved to avoid unnecessary energy expenditure.
- Humans have a higher percentage of body fat than other primates.
- Adaptation to intermittent caloric scarcity.
- Muscles consume 40% of RMR.
Health Benefits of Exercise
- Reduces inflammation.
- Improves heart muscle and circulatory system.
- Prevents dysregulation of the metabolic system.
- Prevents bone loss.
- Improves the nervous system.
One Health
- "There is just one health" - William Karesh
- Aim: Improve health and well-being through prevention/mitigation of crises at the interface of humans, animals, and their environments.
- Emphasis on collaboration.
Alaska One Health Group
- Formed in early 2013.
- Meets quarterly to discuss emerging One Health issues.
- Created the Local Environmental Observers Network:
- Network of local observers and topic experts who share knowledge about unusual animal, environment, and weather events.
Thermal Comfort and the Energetics of Thermoregulation
- Allostatic Response to Cold Stress:
- Shivering.
- Non-shivering thermogenesis (heat production through biological mechanisms separate from muscle twitching).
- Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT):
- High in mitochondria, activated to produce heat in response to cold.
- Increases when exposed to cold.
- Acclimatization to Cold Stress:
- Increase in BAT.
- Elevated RMR (resting metabolic rate).
- Increased T3 production and tissue uptake.
- Efficient cycling between vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
- Lower shivering threshold.
- Reduced NST (non-shivering thermogenesis) in skeletal muscle.
- Seasonal changes in BMR among indigenous Siberians.
- Increased T3 production, but higher rate of T3 entering the tissue leads to a net decline in blood T3 levels in winter.
Developmental Adaptations to Cold Stress
- Early childhood may be a period of sensitivity for plasticity in BAT.
Genetic Adaptation to Cold Stress
- Multiple genes found in circumpolar populations show evidence of natural selection related to BAT regulation.
- Most alleles potentially adaptive to cold climates are found in low frequencies globally.
- Exceptions: CPT1a and PLA2G2A
Allostatic Response to Heat Stress
- Increase in sweat production.
- Vasodilation.
- Increase in heart rate.
- Increase in blood viscosity.
Acclimatization to Heat Stress
- Increased sweat.
- Increase in sodium concentration in sweat.
- Elevated core/rectal temperature.
- Reduced cutaneous vasodilation.
Developmental and Genetic Adaptations to Heat Stress
- This aspect was not discussed.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.